![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What neurotransmitter is released in the somatic nervous system? |
actyelcholine |
|
|
What is the differennce in neurotransmitters in sympathetic and parasympathtic systems? |
Sympathetic- actylcholine acts on ganglion or adrenal medulla to release norepiphrine or epiniphrine. Parasympathetic- postganglionic axon relases acetalcholine. |
|
|
In pregnaglionic neurons what receptors does acetylcholine bind with? |
nicotinic or mucarinic |
|
|
what receptors does norepiniphrin act on? |
alpha/ beta receptors |
|
|
In postganglioinc neurons what receptors does acteylcholine bind with |
muscarinic |
|
|
what are 4 effector organs of the PNS |
cardiac muscle smooth muscle glands adipose tissue |
|
|
PNS have ______ receptors SNS have__________ receptors |
cholinergic noradrengeric |
|
|
in an action potential in the brain Calcium and sodium go _______ and potassium goes _____ |
in, out |
|
|
where do most drugs act in the brain? |
synaptic cleft |
|
|
what do sympathomimetics do? |
stimulate sympathetic nervous system |
|
|
what family does ephedrine fall under? |
sympathomimetics |
|
|
what do alpha 1 receptors do? |
vasoconstriction of periphery increased closure of urinary sphinters increase secreations pupil dialtion |
|
|
what do alpha 2 recepotors? |
vasoconstiction of arteries decreased GI motility decresed smooth muscle contraction |
|
|
what do beta 1 do? |
increased cardiac muscle contractions |
|
|
what do beta 2 receptors? |
stiumulation leads to vasodiolation, bronchodilation |
|
|
what are two gi complications of taking spmpathtics |
increased GI motility- diarehha
Increased GI secreations- peptic ulcers. |
|
|
any drug that influences the PNS has a ______ onset of action |
slower |
|
|
what do cholinomimetics do? |
PNS stimulation |
|
|
what does the drug actylcholine cause |
bradycardia |
|
|
what does nicotine cause |
bradycardia |
|
|
what does mucomyst do? |
increase secreations |
|
|
what does pilocarpine do? |
decrease intraocular pressure |
|
|
do your pupils constrict or dialate with cholinomimetics? |
constrict! |
|
|
what does atropine do? |
anticholinergic- induces tachycarida |
|
|
what does scopolamine do? |
anticholinergics- treats motion sickness by blocky actetychloline |
|
|
What does ditropan do? |
anticholnerigc- treats bladder spasms |
|
|
what does atrovent do? |
anticholnergic- rescue drug for asthma- bronchodialtion |
|
|
if it inhibits PNS then it will stiumulate ___ |
SNS |
|
|
how do neuromuscular blocking agents work? |
they block acetylcholine- nicotinic antagonists |
|
|
what do neuromuscular blocking agents do? |
used as paralytics, general anestheisia, stops breathing- your brain is usally still kicking but you cant move. |
|
|
what does the suffic 'uronium' mean? |
neuromuscular blockersp nicotinic antagonists. |
|
|
what is succinylcholine? |
paralytic- neuromuscular blockers- super short half life |
|
|
what does rocuronium do? |
nictinic antagonist used with general anesthisa, rapid onset, IV |
|
|
what are the 3 anesthsia treatment goals |
unconsciouness loss of responce to pain lost of reflexes- no muscle movemnts |
|
|
what does propofol do? |
induces unconsciousness- rapid onset IV resp depression hypotension decresed CNS perfusion NO ANALGESIA |
|
|
what do Isoflurane, Halothane do? |
cause uncounicouness- inhalation |
|
|
what drug is used for analgesia in GA |
fentanyal |
|
|
How does local anesthesia work? |
reduces influx Na in cells- no action potential generated no Ach secreation |
|
|
what do drugs with the suffix caine do? |
local anesthitic |
|
|
what routes can local anestheitic be delivered? |
SC, epidural, spinal |
|
|
why is epinephrine often included in SC injections |
because it causes vasoconstriction- reduces blood flow to area |
|
|
what areas of the body do we not give epiniphrine to? |
ears nose penis toes and fingers |
|
|
what does glutamate do? |
excites the brain |
|
|
what are 3 inhibitory neurotransmitters? what is the function of these |
dopamine, serotonin, GABA- BALENCE MOOD |
|
|
what are 3 excitatory neurotransmitters and what is the function? |
dopamine, norepinephrin, epinephrine Stimulates brain |
|
|
what happens when we have a chloride influc |
inhibition |
|
|
How does GABA work? |
make chloride ion gates open therefore there is an influx which causes inhibition. |
|
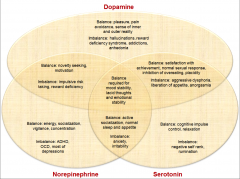
|
study it |
|
|
an imbalence of what neurotrasnmitter is the cause for depression? |
norepinphrine and serotoin |
|
|
what are 3 core charcterics of depression? |
persitant low mood loss of pleaure functional impairment |
|
|
what does serotonin do? |
enhances sense of well-being |
|
|
what is the first line therpy for depresison |
SSRI- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor |
|
|
what is second line therpy for depression |
SNRI serotonine and norepiniphrine reuptake inhiitors |
|
|
what do fluoxetine, sertraline, paroxetine do? |
SSRI |
|
|
what are the side effect for SSRI's? |
headache,nausea, insomnia, nervousness; CYP 2D6, 3A4 inhibition |
|
|
how many patients will not respond to antidepressents? |
1/3 |
|
|
what neurotranmitter imbalence cause anxiety |
GABA serotonin |
|
|
what is a good class of drugs for panic attacks and why? |
benzodiazepines |
|
|
what is good long term treatment for anxiety |
SSRI SNRI |
|
|
how do benzodiazepines work? |
increases actions of GABA- global CNS sedation |
|
|
what do midazolam, lorazapam, diazepam, clonazepam do? |
benzodiazepines |
|
|
what imbalence of neuro transmiters cause seziures? |
GABA and Sodium effluc |
|
|
how do we treat sezures? |
decrease excitabiltiy of cells- benzodiazepines- valium |
|
|
What drugs is the best for treating status epilepticus |
valium barbituates antieplitic drugs |
|
|
do febrile seziures in ped patientns cause long term damage? |
nope!` |
|
|
how do barbituates work? |
enchance GABA receptor binding |
|
|
what class of drugs do phenobarbital and pentobarbital fall in?
|
barbituates- |
|
|
what class does phenytoin fall under? |
antieplitic- enhances NA efflux |
|
|
how does phenobarbital impact metabolism |
Phenobarbitalis metabolized extensively by CYP 3A4, and acts as an inducer of this enzymegroup |
|
|
which barbituate can cause really bad allergies? |
phenobarbital |
|
|
what is the ADME for phenytoin? |
half life= 22 hrs highly protien bound highy CYP2C9 metabolized |
|
|
what is the first line drug for chronic pain? how does it work? |
Gabapentin- increaseschloride influx=cellular de-excitation & modulates GABA to decreaseneuronal excitability |
|
|
what is the ADME for gabapentin |
high lipophilic- excreted unchanged |
|
|
which street drugs are stimulants |
crystal meth, cocaine, LSD, ecstasy, PCP |
|
|
what street drugs are seditiaves |
heroin, cannabinoids, opiods |
|
|
how does cocaine work? |
Increaseddopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine- good feelings |
|
|
how does crystal work? |
–Increaseddopamine, epinephrine, norepi shorter half life |
|
|
hows does tobacco work? |
Increasednicotine receptor binding=post-ganglionic neuron stimulation=increased dopamineproductio
|
|
|
how does alcohol work? |
–Bindsto Ach & serotonin receptors, stimulating CNS–Alsobinds to GABA, decreasing excitability–Phaseof stimulation followed by sedation
|
|
|
what happens in parkonson? |
theaccumulation of Lewybodies & destruction of Dopamine neurons |
|
|
how do we treat parkinsons? |
increase dopamine levels L-DOPA |
|
|
what happens during alzheimers? |
associated with lossof Ach-containing cellsrelated to memory processing but spreads to other brain areas. Accumulation of β-amyloiddeposits = creates plaques |
|
|
what are 7 high 1st pass metabolism drugs |
•Morphine•Demerol•Diazepam
•Midazolam•Lidocaine •Propranolol•Imipramine |

