![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
explain the MECHANISM responsible for the SHORT duration of ANESTHETIC action of THIOPENTAL(PENTOTHAL) following IV injection.
|
Termination of Drug Action occurs through REDISTRIBUTION
REDISTRIBUTION happens when a highly LIPID SOLUBLE DRUG(e.g. thiopental (Pentothal) that acts on the BRAIN or CARDIOVASCULAR system is administered rapidly by IV injection. Due to HIGH BLOOD FLOW to the brain, the drug reaches its maximum concentration in brain within a minute after IV injection. Then, the plasma concentrations falls as thiopental diffuses out of the brain and into other tissues, such as muscle. • Thus, onset of anesthesia is rapid, but so is its termination. |
|
|
identify the four important patterns of biotransformation.
|
1) active drug TO inactive metabolite
(2) active drug TO active metabolite (3) inactive drug TO active metabolite (prodrug) (4) active drug TO toxic metabolite (e.g., acetamenophen) |
|
|
identify the two possible changes in drug characteristics that biotransformation of a drug accomplishes.
|
1) increases water solubility by making MORE POLAR metabolites, less lipid-soluble.
(2)INACTIVATES drug-but NOT always. |
|
|
prodrug
|
Prodrugs are pharmacologically inactive compounds that are converted to active metabolites in the body.
|
|
|
Define “Phase I” reactions.
|
Usually convert the parent drug to a MORE POLAR metabolite by introducing or unmasking a polar functional group (-OH, -SH, -NH2).
|
|
|
Define “ Phase II” reactions.
|
involves CONJUGATIONS which is Chemical combination of drug or metabolite with an endogenous substance (e.g. GLUCORONIC ACID, SULFATE, GLYCENE, ACETATE) to yield drug conjugates.
• In general, conjugates are POLAR molecules, EASILY EXCRETED ; usually pharmacologically INACTIVE. |
|
|
biotransformation involving microsomal oxidation reactions are catalyzed by ________ which includes _______ and requires and _________.
|
mixed function oxidase systems (MFOs)/cytochrome P450/NADPH/ molecular O2
|
|
|
identify those biotransformation reactions that are carried out by the hepatic mixed function oxidase system (Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenase System).
|
aromatic and aliphatic hydroxylation, N -, O-, and S-dealkylation, N-oxidation, S-oxidation, deamination and desulfuration
|
|
|
Identify types of drugs that are capable of conjugation with glucuronic acid.
|
phenols, alcohols, carboxylic acids and amines
|
|
|
identify the major drug conjugation reactions that occur in humans.
|
GLUCURONIDE CONJUCATION
acetylation sulfate conjugation glycine conjugation glutathione conjugation methylation |
|
|
define microsomal enzyme induction
|
numerous drugs and environmental chemicals(“xenobiotics”) have been shown to cause INCREASED microsomal enzyme activity CYTOCROME P450 with continued administration
|
|
|
What are the possible consequences of microsomal enzyme induction?
|
Can lead to an INCREASED rate of biotransformation and decreased level of the parent drug, resulting in TOLERANCE DEVELOPEMENT, INCREASED REACTIVE INTERMEDIATES, & DRUG INTERACTIONS
|
|
|
predict the renal handling of a drug when the physicochemical properties are known e.g. lipid solubility
|
In general, more lipid soluble compounds undergo biotransformation first beforeexcretion.
|
|
|
predict the renal handling of a drug when the physicochemical properties are known
e.g., pKa |
Acids: alkalinizing the urine with sodium bicarbonate speeds excretion of weak acids e.g. salicylate
Bases: acidifying urine with ammonium chloride speeds excretion of weak bases e.g. amphetamine |
|
|
predict the renal handling of a drug when the physicochemical properties are known
e.g.,degree of ionization. |
?
|
|
|
predict how acidification or alkalinization of the urine will affect the renal excretion of a specific drug.
|
Acids: alkalinizing the urine with sodium bicarbonate speeds excretion of weak acids e.g. salicylate
Bases: acidifying urine with ammonium chloride speeds excretion of weak bases e.g. amphetamine |
|
|
define “enterohepatic circulation”.
|
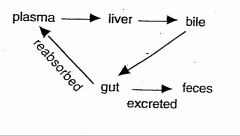
enterheptatic cycling
|

