![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
BRAND NAME
adenosine |
Adenocard
|
|
CLASS
adenosine |
antiarrhythmic, endogenous nucleoside
|
|
MECHANISM OF ACTION
adenosine |
Slows conduction time through the AV node; can interrupt re-entrant pathways through the AV node.
Slows sinus rate. Larger doses decrease BP by decreasing peripheral resistance. |
|
INDICATIONS
adenosine |
Conversion of SVTs with no known AFib or AFlutter
Wide complex tachycardia of uncertain origin unresponsive to lidocaine. |
|
CONTRAINDICATIONS
adenosine |
Known AFib or AFlutter.
Sick sinus syndrome, 2nd or 3rd degree AV blocks; except in pts with a functioning ventricular pacemaker. Use cautiously in patients with known asthma (has precipitated acute bronchospasm). Patients on theophylline and related methylxanthines. Patients on dipyridamole (Persantine) or carbamazepine (Tegretol). Cardiac transplant patients are more sensitive to adenosine and require only a small dose (relative). Pregnancy (no controlled studies). |
|
ADVERSE REACTIONS
adenosine |
CV: TRANSIENT dysrhythmias (systole, bradycardia, PVC's) occur in 55% of pts (none reported as irreversible).
Palpitations, chest pressure, CP, hypotension, transient HTN; facial flushing, sweating. RESP: Dyspnea, hyperventilation, tightness in throat, bronchospasm. CNS: lightheadedness, HA, dizziness, paresthesia, apprehension, blurred vision, neck-back pain. GI: nausea, metallic taste. |
|
ADULT DOSAGE
adenosine |
INITIAL: 6 mg rapid IV/IO push over 1-3 seconds
ADMINISTRATION PROCEDURE: 18 ga IV/IO AC↑, press print on monitor, use hub closest to IV catheter to push drug, immediate 20 mL flush in other hub. REPEAT: 12 mg rapid IV/IO push over 1-3 seconds (twice) if needed. Repeat only after 1-2 minutes if no response. ADMINISTRATION PROCEDURE: 2 repeat doses if needed: press print, hub closest to IV catheter to push drug, immediate 20 mL flush in other hub. |
|
PEDIATRIC DOSAGE
adenosine |
(Drug of choice for treating SVT in symptomatic infants and children).
INITIAL: 0.1 mg/kg as a rapid IV/IO push. ADMINISTRATION PROCEDURE: Largest IV/IO, press print on monitor, use hub closest to IV catheter to push drug, immediate 2-3 mL flush in other hub. REPEAT: If no response, dose may be doubled 1 time (0.2 mg/kg) using same administration procedure. MAX SINGLE DOSE 12 mg. INFANTS WITH SVT ASSOCIATED WITH SHOCK: Adenosine may precede cardioversion if vascular access is available, but cardioversion should not be delayed while obtaining IV access. |
|
BONUS
adenosine |
Adenosine is not blocked by atropine.
Dysrhythmias may recur (short half life). Second dose must be prepared and available. Check for crystallization in cold climates. |
|
BRAND NAME
diltiazem |
Cardizem
|
|
CLASS
diltiazem |
calcium channel blocker, calcium antagonist
|
|
MECHANISM OF ACTION
diltiazem |
PHARMACOLOGICAL: Inhibits calcium ion influx across cell membranes during cardiac depolarization, decreases SA & AV conduction and dilates coronary and peripheral arteries and arterioles.
CLINICAL: Slows the rapid ventricular rate associated with AFib and AFlutter, and reduces coronary and peripheral vascular resistance. |
|
INDICATIONS
diltiazem |
Rapid ventricular rates associated with AFib and AFlutter, and for PSVT refractory to adenosine.
|
|
CONTRAINDICATIONS
diltiazem |
Hypotension (less than 90 mmHg systolic)
Acute MI Cardiogenic shock VT or wide-complex VT of unknown origin Second or third-degree AV block Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome Sick sinus syndrome Beta blocker use |
|
ADVERSE REACTIONS
diltiazem |
CV: hypotension, bradycardia, heart block, CP, asystole.
GI: N/V CNS: HA, fatigue, drowsiness |
|
ADULT DOSAGE
diltiazem |
INITIAL: 0.25 mg/kg IV/IO (usually 20 mg) administered over 2 minutes
REPEAT IN 15 MIN IF RESPONSE IS INADEQUATE: 0.35 mg/kg IV/IO administered over 2 min MAINTENANCE INFUSION: 5.0-15.0 mg/hr |
|
PEDIATRIC DOSAGE
diltiazem |
The safety and efficacy of this drug for use in children has not been established.
|
|
BONUS
diltiazem |
Avoid use in pts with poison or drug induced tachycardia.
CaCl can be used to prevent hypotensive effects of this drug and treat patients with a calcium channel blocker OD. Beta blocker use. |
|
|
BRAND NAME
amiodarone |
Amiodarone
|
|
|
CLASS
amiodarone |
anti-arrhythmic agent
|
|
|
MECHANISM OF ACTION
amiodarone |
Multiple effects on potassium, sodium and calcium channels.
Prolongs action potential, refractory period. Ventricular automaticity (potassium channel blockade). Slows membrane depolarization and impulse conduction (sodium channel blockade). Negative chronotropic activity in nodal tissue, rate reduction, and antisympathetic activity (calcium channel and B-blockade). Dilates coronary arteries due to calcium channel and alpha-adrenergic blocking action. |
|
|
INDICATIONS
amiodarone |
Treatment of: DEFIB! - refractory VF/pulseless VT, polymorphic VT, and wide complex tachycardia of uncertain origin.
Control hemodynamically stable VT when cardioversion is unsuccessful. Adjunct to cardioversion of SVT and PSVT. Rate control in AFib or AFlutter. |
|
|
CONTRAINDICATIONS
amiodarone |
Bradycardia
Second or third degree heart block unless a functioning pacemaker is present. Cardiogenic shock Hypotension Pulmonary congestion |
|
|
ADVERSE REACTIONS
amiodarone |
CV: bradycardia, hypotension, asystole/cardiac arrest, AV block
TORSADES DE POINTES: (prolongs QT interval), CHF GI & HEPATIC: N/V, abnormal LFTs SKIN: slate-blue pigmentation OTHER: fever, HA, dizziness, flushing, abnormal salivation, photophobia |
|
|
ADULT DOSAGE
amiodarone |
VF/PULSELESS VT: 300 mg IV/IO push over 30-60 seconds, may repeat in 3-5 min with 150 mg IV/IO push
WIDE COMPLEX TACHYCARDIAS, AFLUTTER, AFIB, SVT WITH CARDIOVERSION: 150 mg IV/IO over 10 min (mix in 50 mL bag of D5W) may repeat q 10 min. MAINTENANCE INFUSION POST RESUSCITATION/CONVERSION: After successful defib, follow with 1 mg/min IV/IO infusion for 6 hours, then up to 0.5 mg/min IV/IO infusion for up to 18 hours, max daily dose is 2.2 grams. |
|
|
PEDIATRIC DOSAGE
amiodarone |
VF/PULSELESS VT: 5 mg/kg IV/IO push (max 300 mg single dose), may repeat x 2 q 5 min to a total max of 15 mg/kg/day.
PROBABLY VT WITH PULSE: 5 mg/kg IV/IO administered over 20 min, may repeat two more times to a total of 15 mg/kg/day. |
|
|
BONUS
amiodarone |
Half-life may exceed 40 days.
Patient must be on a cardiac monitor - monitor the HR and rhythm. |
|
BRAND NAME
calcium chloride |
Calcium Chloride
|
|
CLASS
calcium chloride |
electrolyte
|
|
MECHANISM OF ACTION
calcium chloride |
Increases extracellular and intracellular calcium levels.
Stimulates release of catecholamines. Increases cardiac contractile state (+ inotropic effect). May enhance ventricular automaticity. Inhibits the effects of adenosine on mast cells. |
|
INDICATIONS
calcium chloride |
Acute hypocalcemia
Calcium channel blocker OD Acute hyperkalemia (known or suspected) Hypermagnesemia (Magnesium OD) Pre-treatment for IV verapamil administration |
|
CONTRAINDICATIONS
calcium chloride |
Hypercalcemia
Concurrent digoxin therapy (relative) |
|
ADVERSE REACTIONS
calcium chloride |
Brady-asystolic arrest
Severe tissue necrosis if solution extravasates. Use cautiously in patients on digitalis; may cause serious arrhythmias. |
|
ADULT DOSAGE
calcium chloride |
HYPOCALCEMIA, CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKER OD, HYPERKALEMIA, HYPERMAGNESEMIA: 5-10 mL (0.5-1 gm) of CaCl 10% IV/IO. May repeat in 10 min.
PRE-TREATMENT FOR IV VERAPAMIL ADMINISTRATION: 3 mL of 10% CaCl. May be repeated once. |
|
PEDIATRIC DOSAGE
calcium chloride |
HYPOCALCEMIA, CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKER OD, HYPERKALEMIA AND HYPERMAGNESEMIA: 0.2-0.25 mL/kg of a 10% solution IV/IO infused slowly.
|
|

BRAND NAME
atropine sulfate |
Atropine Sulfate
|
|

CLASS
atropine sulfate |
anticholinergic agent, antidote, antispasmodic, antiarrhythmic, antimuscarinic
|
|

MECHANISM OF ACTION
atropine sulfate |
PHARMACOLOGICAL: Blocks the action of acetylcholine as a competitive antagonist at muscarinic receptor sites in smooth muscle, secretory glands, and the drying of secretions. Atropine reverses the muscarinic effects of cholinergic poisoning by primarily reversing bronchorrhea and bronchoconstriction. At high enough doses, atropine may have an effect on nicotinic receptors responsible for restlessness, hallucinations, disorientation, and/or delirium.
CV: ↑ HR (+ chronotropic effect); ↑ conduction velocity (+ dromotropic effect); ↑ force of contraction (slight)(+ inotropic effect), ↑ CO. RESP: Decreased mucus production; increased bronchial smooth muscle relaxation (bronchodilation). GI: Decreased GI secretion and motility. GU: Decreased urinary bladder tone. MISC: Mydriasis (pupillary dilation); decreased sweat production. |
|

INDICATIONS
atropine sulfate |
Symptomatic bradycardia (sinus, junctional, AV blocks causing hypotension, ventricular ectopy, CP, ALOC, etc.), monitored pt only.
Asystole (after epi) monitored pt only. PEA with actual or relative bradycardia (after epi) monitored pt only. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor poisoning (organophosphate, carbamate cholinergic poisoning). |
|

CONTRAINDICATIONS
atropine sulfate |
Hypersensitivity to atropine or any component of the formulation - Belladonna alkaloid allergy.
Glaucoma, acute narrow angle (relative contraindication for pt with symptomatic bradycardia) adhesions between the iris and lens. Myasthenia gravis (unless used to treat side effects of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor). Tachycardia, asthma, thryotoxicosis, Mobitz type II block, 3rd degree heart block, hepatic disease, renal disease, obstructive uropathy. Obstructive GI disease, paralytic ileus, intestinal atony of the elderly or debilitated pt, severe ulcerative colitis, or ulcerative colitis. PREGNANCY RISK FACTORS/CONSIDERATIONS: Atropine has been found to cross the human placenta. Trace amounts of atropine can enter breast milk. |
|

ADVERSE REACTIONS
atropine sulfate |
MAJOR: Tachydysrhythmias, flushing, ventricular irritability, exacerbation/initiation of angina, acute narrow glaucoma, blurred vision, mydriasis, agitation to delirium, bloating, constipation, decreased gastric emptying.
MINOR: Dry mouth/mucous membranes, loss of taste, N/V, urinary retention, neuromuscular weakness, decreased sweating, ↑ body temp. |
|

ADULT DOSAGE
atropine sulfate |
SYMPTOMATIC BRADYCARDIA: IV/IO - 0.5 mg IV push q 5 min. Do NOT exceed a total dose of 3 mg or 0.04 mg/kg if symptoms profound.
ASYSTOLE: IV/IO - 1 mg. Repeat q 3-5 min (generally up to 3 doses) if asystole persists. Total dose should not exceed 0.04 mg/kg. ORGANOPHOSPAHTE OR CARBAMATE POISONING: IV/IO - Initially: 1-5 mg. Doses should be doubled q 5 min until signs of muscarinic excess abate (clearing of bronchial secretions, bronchospasm, and adequate oxygenation). |
|

PEDIATRIC DOSAGE
atropine sulfate |
SYMPTOMATIC BRADYCARDIA: IV/IO - 0.02 mg/kg (min of 0.1 mg), repeat q 5 min to a max total dose of 1 mg in children and 2 mg in adolescents.
MAX SINGLE DOSE: Child: 0.5 mg, Adolescent: 1 mg. ORGANOPHOSPHATE/CARBAMATE CHOLINERGIC POISONING: IV/IO - 0.03-0.05 mg/kg q 10-20 min until cholinergic symptoms minimize, then every 1-4 hours for at least 24 hours. |
|

BONUS
atropine sulfate |
Administering too small of a dose or administering too slowly may result in PARADOXICAL BRADYCARDIA.
|
|

BRAND NAME
lidocaine HCl |
Xylocaine
|
|

CLASS
lidocaine HCl |
antiarrhythmic, local anesthetic
|
|

MECHANISM OF ACTION
lidocaine HCl |
Decreases automaticity by slowing the rate of spontaneous phase 4 depolarization.
Terminates re-entry by decreasing conduction in re-entrant pathways (by slowing conduction in ischemic tissue, equalizes conduction speed among fibers). ↑ ventricular fibrillation threshold. |
|

INDICATIONS
lidocaine HCl |
Suppression of ventricular arrhythmias (VT, VF, PVC's).
Prophylaxis against recurrence after conversion from VT or VF. Frequent PVC's (>6 min, 2 or more in a row, multiform PVC's, or R-on-T phenomenon). Pre-intubation for head trauma or suspected intracranial hemorrhage. |
|

CONTRAINDICATIONS
lidocaine HCl |
Known hypersensitivity/allergy.
Use extreme caution in pts with conduction disturbance (2nd or 3rd degree heart block). DO NOT TREAT ECTOPIC BEATS IF HR IS < 60. THEY ARE PROBABLY COMPENSATING FOR THE BRADYCARDIA; INSTEAD, TREAT THE BRADYCARDIA! |
|

ADVERSE REACTIONS
lidocaine HCl |
CV: May also cause SA nodal depression or conduction problems and hypotension in large doses, or if given too rapidly.
Excessive doses in pediatric pts may produce myocardial and circulatory depression. CNS: In large doses drowsiness, disorientation, paresthesia, decreased hearing acuity, muscle twitching, agitation, focal or generalized seizures. |
|

ADULT DOSAGE
lidocaine HCl |
PULSELESS VF/VT: Initial bolus of 1-1.5 mg/kg IV/IO push q 3-5 min to a total dose of 3 mg/kg.
An initial bolus of 1.5 mg/kg should be given for cardiac arrest situations. Following the return of a spontaneous rhythm, initiate a drip at 2-4 mg/min for maintenance infusion. ANTIDYSRHYTHMIC OR RHYTHMS WITH A PULSE: Initial boluses can be given as 1-1.5 mg/kg IV/IO push and additional boluses can be given as 0.5-0.75 mg/kg q 5-10 min to a total dose of 3 mg/kg. Following the return of a spontaneous rhythm, initiate a drip at 2-4 mg/min. MAINTENANCE INFUSION: Started after return of spontaneous rhythm for either indication above. Add 1-2 gm to a 250 mL NS or 5% dextrose solution or use premixed solution (2 gm in 500 mL) and initiate a drip at 2-4 mg/min according to concentration. Patients > 70 years or with hepatic, renal disease or poor perfusion state - reduce maintenance infusion by half. Pre-intubation for head trauma or suspected intracranial hemorrhage (consider administration of 1 mg/kg IV bolus 1-2 min prior to intubation.) |
|

PEDIATRIC DOSAGE
lidocaine HCl |
INITIAL BOLUS DOSES: 1 mg/kg, may repeat 1 time in 3-5 min for VF/Pulseless VT or in 15 min if used for refractory dysrhythmias with a pulse (VT with pulse, significant ventricular ectopy).
INFUSION WITH RETURN OF SPONTANEOUS RHYTHM, OPTIONAL: 20-50 mcg/kg/min; prepared by adding 120 mg (3cc) of 1 gm/25 mL (40 mg/mL) solution to 97 mL NS, yielding 1200 mcg/mL. 1 mL/kg/hr delivers 20 mcg/kg/min. 2.5 mL/kg/hr delivers 50 mcg/kg/min. |
|

BONUS
lidocaine HCl |
Decrease maintenance infusion by 50% in cases of CHF, shock, or liver disease.
|
|
BRAND NAME
verapamil HCl |
Isoptin, Calan, Verelan
|
|
CLASS
verapamil HCl |
calcium channel blocker
|
|
MECHANISM OF ACTION
verapamil HCl |
Blocks calcium ion influx into cardiac and smooth muscle cells causing a depressant effect on the contractile mechanism resulting in negative inotropy.
Reduces contractile tone in vascular smooth muscle resulting in coronary and peripheral vasodilation. Slows conduction and prolongs refractory period in the AV node due to calcium channel blocking. Slows SA node discharge. In summary, decreases myocardial contractile force and slows AV conduction. |
|
INDICATIONS
verapamil HCl |
SVT
AFib & AFlutter with RVR |
|
CONTRAINDICATIONS
verapamil HCl |
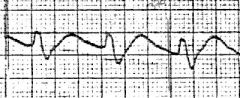
AV block, sick sinus syndrome, any wide QRS complex tachycardia.
Shock Severe CHF |
|
ADVERSE REACTIONS
verapamil HCl |
Extreme bradycardia
Asystole AV Block Hypotension CHF |
|
ADULT DOSAGE
verapamil HCl |
2.5-5 mg SLOW IV/IO push over 2-3 min. May rebolus in 15-30 min with 5-10 mg IV/IO push until a max dosage of 20 mg.
|
|
PEDIATRIC DOSAGE
verapamil HCl |
Not used.
|
|
BONUS
verapamil HCl |
Not compatible with IV beta-blockers.
Vagal maneuvers may be tried first. Avoid verapamil in pts with wide-QRS tachycardia unless it is KNOWN WITH CERTAINTY to be supraventricular in origin. |

