![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
These G-proteins are activated by which receptors?
Gi Gs Gq |
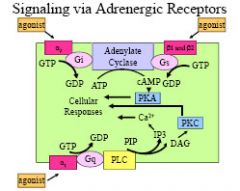
Gi - alpha2
Gs - beta1 beta 2 Gq - alpha1 |
|
|
Mechanism:
Guanethidine |
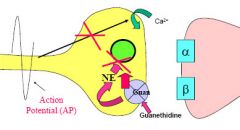
Guanethidine enters the NET, uncouples AP from calcium entry, and stabilizes the vesicular membrane.
|
|
|
Mechanism:
Reserpine |
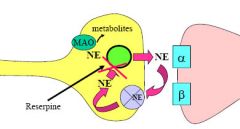
Reserpie enters the terminal, stabilizes the vesicular membrane, causing depletion of NE over time.
It keeps NE from being stored. |
|
|
You are NE.
What receptor do you like? |

Alpha1 +4
Beta1 +4 |
|
|
You are Isoproterenol.
What receptor do you like? |

Beta1
Beta2 |
|
|
You are Epi (low)
What receptor do you like? |

Beta1 +3
Beta2 +3 |
|
|
You are Epi (high)
What receptor do you like! |

Alpha1 +4
Beta1 +4 Beta2 +4 |
|
|
You are Dopamine (low)
What receptor do you like? |

DA +2
Beta1 +2 Beta2 +1 |
|
|
You are Dopamine (high)
What receptor do you like? |

Alpha1, Beta1, Beta2, DA +4
(equally) |
|
|
You are Dobutamine (low)
What receptor do you like? |

Beta1
|
|
|
You are Dobutamine (high)
What receptor do you like? |

Beta1 +4
Alpha1, Beta2 +2 *Loses selectivity at higher doses *Low dose is Beta1 >> Beta2 |
|
|
Beta1's favorite agonist
|
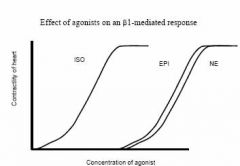
Isoproterenol > epi = norepi
|
|
|
Alpha1's favorite agonist?
|
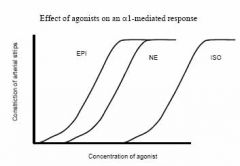
Epi > NE >> iso
|
|
|
Beta2's favorite agonist?
|
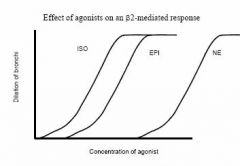
iso > epi >> NE
|
|
|
Describe the synthesis of NE:
|
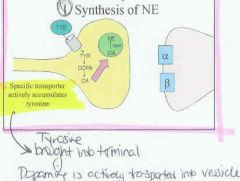
Tyrosine > into the neuron actively > Dopa > Dopamine > into vesicle actively > Dopamine-Beta-Hydroxylase makes NE
|
|
|
What's the interaction of tyramine when using an MAOI?
|
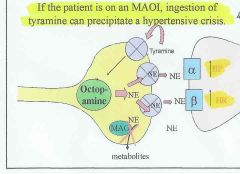
Can cause hypertensive crisis (MAO is the gut normally metabolizes tyramine, but with a MAO-i this is reduced, tyramine becomes Octopamine in the neuron which then enters the vesicle, displacing the NE. With no MAO to metabolize it, the excess NE reverses the NET and dumps the NE into the synapse, causing hypertensive crisis)
|
|
|
What is unique about Dobutamine?
|
It increases contractility WITHOUT increasing heart rate, via beta-1 stimulation.
|
|
|
What are the 4 rules of catecholamines?
|
1: Increasing size of amino group substitution increases beta receptor affinity.
2: -OH groups at 3 & 4 positions confer maximum alpha and beta activity. 3: Removal of -OH from ring increases CNS penetration. 4: Non catecholamines are not metabolized by COMT; substitution of the alpha-Carbon blocks MAO metabolism. (amphetamine has a longer half-life) |
|
|
Structurally, beta agonists have what feature?
|
Beta agonists have greater amino group substitution.
Dobutamine |
|
|
Structurally, what increases the likelihood for CNS penetration?
|
Lack of -OH group on the ring helps it to get into the CNS, but it will have less affinity/activity at Alpha and Beta receptors.
|
|
|
What determines how catecholamines and non-catecholamines are metabolized?
|
Non-catecholamines are not metabolized by COMT.
Substitution of the Alpha-Carbon blocks MAO metabolism. |
|
|
How is blood pressure affected by Dopamine?
|
BP decreased by DA receptors in renal and mesenteric beds where perfusion is increased.
BP decreased by Beta2 activation. BP increased (very high dose) by Alpha1 activation. |
|
|
Phenylephrine is an example of what?
|
Non-catecholamine (not metabolized by COMT)
Alpha1 stimulant |
|
|
Ephedrine is an example of what?
|
Weak Alpha-1 and Beta agonist.
It also enhances the release of NE. A CNS stimulant. Nasal decongestant and pressor agent. |
|
|
How do Xanthines work?
|
Inhibit phosphodiesterase, to stop the breakdown of cAMP. Gives the same effect as beta stimulation, because cAMP increases.
Aslo, they antagonize adenosine receptors causing CNS stimulating effects. It knocks adenosine off the "sleepy receptors". |
|
|
Is reflex tach worse with selective or non-selective alpha blockers?
|
Reflex tach is WORSE with non-selective alpha blockers than with a selective alpha-1 blocker, because if alpha-2 is blocked there is no feedback inhibition. More NE is released, causing more Beta-1 stimulation and faster HR.
Phentolamine is non-selective. Decrease BP Increase HR (reflex) |
|
|
Draw what Epi reversal looks like in Dog-Lab. Which alpha blocker are they likely to use?
|
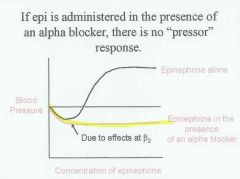
Phentolamine (non-selective alpha blocker)
|
|
|
What are the vascular and blood pressure effects of non-selective Beta-blockers?
|
1: Reduction in Cardiac Output (more pronounced during exercise)
2: Reduction in plasma renin 3: Decrease in sympathetic tone via effects in CNS B2 block may increase TPR slightly. Decrease in renin due to B1 block. NET EFFECT: reduction in BP. Decreased conduction velocity, O2 demand and rate of depolarization. |
|
|
Which agonists are used in pregnancy for essential hypertension?
|
alpha-methyl-dopa
|

