![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List 3 naturally occurring estrogens by their potency
|
estradiol (E2) > estrone (E1) > estriol (E3)
|
|
|
Contrast synthetic steroidal and nonsteroidal estrogens
|
steroidals have a cholesterol backbone
|
|
|
List 3 synthetic steroidal and 3 synthetic nonsteroidal estrogens
|

|
|
|
Enzyme responsible for conversion of testosterone to estrogen
|
aromitase
|
|
|
1. primary location of estrogen receptors in cell
2. long term effect (in general) 3. short term effect (in general) |
1. nucleus
2. receptors homodimerize, bind ERE on multiple genes, affect protein synthesis 3. activate kinase systems and Ca mobility |
|
|
5 reproductive effects of estrogen
|
1. primary & secondary female sex characteristics
2. puberty changes 3. neuroendo regulation of menstruation 4. endometrial growth 5. secretion of thin cervical mucous |
|
|
Source of estrogen and progesterone during the NL menstrual cycle & their effect on endometrium
|
estrogen: maturing follicles in ovary, promotes endometrial prolif
progesterone: corpus luteum, maintains thickened endometrium |
|
|
Metabolic effects of estrogen:
1. cholesterol 2. blood pressure 3. thrombotic activity 4. bone 5. liver |
1. increase HDL, decrease LDL, increase bile excretion
2. increase BP via renin 3. promote thrombosis 4. decrease resorption 5. increase protein synthesis |
|
|
5 major clinical uses of estrogens
|

|
|
|
5 drug preparations of estrogen
|
1. conjugated
2. estradiol (PO) 3. estradiol (TD) 4. ethinyl estradiol 5. DES |
|
|
7 contraindications of using estrogen preparations
|

|
|
|
Tamoxifen:
--indication --MOA in breast, endometrium, bone --6 SEs |

|
|
|
Tamoxifen:
1. 2 contraindications 2. 2 tx considerations |
1. hx of DVT/PE, pregnancy
2. 4-6 increase in endometrial cancer incidence, use < 5 yrs to minimize endometrial risk |
|
|
Clomiphene:
1. 1 indication 2. MOA in hypothalamus/pituitary, ovaries 3. 4 SEs |
1. female infertility from ovulatory ds
2. estrogen antag in hypoth/pituitary (increase GnRH/FSH/LH), partial agonist in ovaries 3. thromboembolism, ovarian cysts/hypertrophy, flushing/vasomotor sxs, abd discomfort |
|
|
Clomiphene:
--6 contraindications --1 tx consideration |

|
|
|
Raloxifene:
1. indication 2. MOA in breast, uterus, bone 3. 4 SEs |
1. osteoporosis prevention/tx
2. estrogen agon in bone, antag in uterus & breast 3. retinal vascular occlusion, venous thromboembo, hot flashes, leg cramps |
|
|
Raloxifene:
1. 2 contraindications 2. 1 tx consideration |
1. preg, hx of venous thromboembo
2. decrease risk of invasive breast cancer in postmenopausal women w/ osteoporosis |
|
|
Fulvestrant:
--indication --MOA --5 SEs |

|
|
|
Fulvestrant:
1. 1 contraindication 2. 1 tx consideration |
1. preg
2. pure estrogen antag w/ no agon activty |
|
|
4 aromatase inhibitors and their MOAs (2)
|
anastrozole (compet inhib)
letrozole (compet inhib) exemestane (irrev inhib) formestane (irrev inhib) |
|
|
Drug indication of aromatase inhibitors
|
Tx/prevention of estrogen receptor positive early-stage, locally advanced, and metastatic breast cancer
|
|
|
Describe 4 physiological actions of progesterone
|
1. neuroendo reg of menstrual cycle
2. induce secretory uterine endometrium (implantation) 3. thick cervical mucus 4. increase body temp |
|
|
3 clinical uses of progestins
|
1. in OCPs (w/ or w/out ethinyl estradiol)
2. component of HRT in menopause 3. Rx for dys/oligomenorrhea, endometriosis, PCOS |
|
|
MOA of progestin-only contraceptives (primary & secondary)
|
primary: decrease GnRH pulse frequency & GnRH responsiveness of AP
secondary: alter tubal peristalsis, endometrium, cervical mucous (thick) |
|
|
Key concept of using combined OCPs (E2 + P)
|
mimic neg feedback on gonadotropin secretion in luteal phase
|
|
|
Mefepristone (RU-486):
1. drug indication 2. MOA |
1. abortion (through day 49 of pregnancy)
2. blocks progesterone receptor binding |
|
|
Consequences of estrogen deficiency:
--4 early --4 intermediate --3 long term |
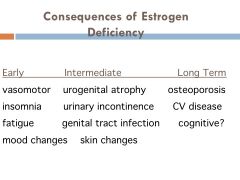
|
|
|
4 major indications for female HRT
|
1. vasomotor instability
2. mood changes 3. urogenital atrophy 4. osteoporosis |

