![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the methods to produce magnetic supports? |
Encapsulation Infiltration Coating Combination |
|
|
Explain the method of encapsulation |
Encapsulation of solid magnetic elements within gels etc |
|
|
Explain the method of infiltration |
Infiltration of porous supports with fine magnetic sub-particles |
|
|
Explain the method of coating |
Coating magnetic core particles with natural or synthetic polymers |
|
|
What are the various combinations for the production of magnetic supports? |
Encapsulation and coating or infiltration and coating |
|
|
What is Ferromagnetism? |
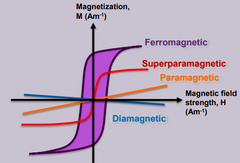
Materials attracted towards the magnetic field lines when placed in a magnetic field. The induced force experienced has a strong non linear dependence on the strength of the magnetic field. |
|
|
What is Paramagnetism? |
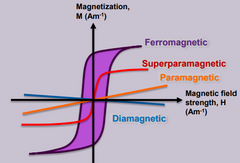
Materials that have induced magnetic forces that respond linearly to the applied magnetic field |
|
|
What is Diamagnetism? |
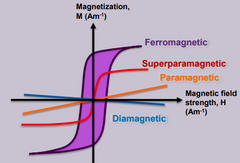
Materials that do not have a form of paramagnetism or ferromagnetism properties |
|
|
What is Superparamagnetism? |
Materials that respond to a magnetic field stronger than paramagnetic materials but have no magnetic memory. |
|
|
What are advantages of Superparamagnetic particles? |
Easy re suspension Large Surface Area Slow Sedimentation Uniform distribution in the suspension media |
|
|
What are the advantages of ferromagnetic particles? |
Very Strong Magnetic Properties Fast separation with an external magnetic field |
|
|
What is the formula for Lepidocrocite? |
gamma-FeOOH |
|
|
What is the formula for Feroxyhyte? |
delta-FeOOH |
|
|
What are the strongly magnetic iron oxides? |
Maghemite & Magnetite |
|
|
What is the lattice of Hematite? |
HCP |
|
|
What is the lattice of Maghemite |
CCP |
|
|
What are the magnetic properties of Maghemite? |
Ferrimagnetic |
|
|
What is the lattice of Goethite? |
HCP |
|
|
What is the lattice of Akaganeite? |
HCP |
|
|
What is the lattice of Lepidocrocite? |
CCP |
|
|
What is the lattice of Feroxyhyte? |
HCP |
|
|
What is the lattice of Ferrihydrite? |
HCP |
|
|
How do you use Agarose in Encapsulation? |
Dissolve, incorporate magnetic particles and use controlled cooling and stirring conditions to determine particle size distribution |
|
|
What are the magnetic characteristics for a HGMF and why? |
Superparamagnetic - No magnetic memory so can be repeatedly used High Magnetisation - Ensures fast separation through high magnetic velocity (Vm) |
|
|
What size should the particles be in a HGMF and why? |
0.5-2 microns - gives sufficient surface area - Too small means low Vm and poor magnetic separation |
|
|
What shape and uniformity should particles be in a HGMF and why? |
Spherical - To achieve high packing densities Monosized - All particles move with same Vm |
|
|
What density should particles in a HGMF be and why? |
2.5-4 gcm-3 - Allows slow settling at a zero field |
|
|
What is the stability of particles in a HGMF and why? |
Physico-chemically robust construction - To tolerate harsh cleaning chemicals and prevent corrosion |
|
|
What is the surface architecture of a particle in a HGMF and why? |
Highly Folded Surfaces - Enhances product sorption capacity |
|
|
What is the porosity of a particle in a HGMF and why? |
Non-porous - Better fouling resistance |
|
|
What is the surface chemistry of a particle in a HGMF and why? |
Neutral, hydrophillic and easy to derivitise binding surface - Enables ligands to be coupled at high densities |
|
|
What are the advantages of a type VIII magnetic support? |
SA>110m2g-1 Easily derivatised surface High Qmax |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of a type VIII magnetic support? |
tedious manufacture low filter capacity release from magnetic filterssometimes difficult |
|
|
What are the advantages of a type IV magnetic support? |
facile manufacture monodisperse protein friendly binding surface high filter capacity superior release from magneticfilters |
|
|
What are the disadvantages of a type IV magnetic support? |
SA <40 m2/g rel. difficult to derivatise low Qmax |
|
|
What are the four labels for the blueprint of a magnetic adsorbent? |
1. Magnetic Core Material 2. Particle Coatings 3. Small Stable Ligands 4. Finished Product |
|
|
What are the properties of the magnetic core material in a magnetic adsorbent? |
Monodisperse - <1micron and composed of 10nm crystals Superparamgnetic Highly Textured Surface |
|
|
What are the properties of the particle coatings in a magnetic adsorbent? |
must be very thin should not coalesce particles neutral hydrophilic exterior surfaces easy to derivatise protection against corrosion |
|
|
What are the properties of the finished product in a magnetic adsorbent? |
cheap scaleable consistent quality fine-tuned for separation |
|
|
Give three examples of small stable ligands in a magnetic adsorbent |
Ion exchangers Mixed mode Pseudoaffinity mimics |
|
|
What are the main steps in HGMF? |
1. Batch adsorption 2. Adsorbent Collection 3. Washing 4. Elution 5. Adsorbent Release |
|
|
Does ferrihydrite have a high or low surface area? |
High |
|
|
Does magnetite have a high or low surface area? |
Low |

