![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Divisions del Nervous system (SN). En qué parte de la ciudad vives? |
1. Central (Brain + Spinal Cord) 2. Peripheral (Autonomic + Somatic) |
|
|
|
Sympathetic and parasympathetic are divisions of... |
Autonomic nervous system |
|
|
|
Which body functions are stimulated by the parasympathetic nervous system? Which neurotransmitter does it primarly use? |
Sexual arousal Salivation Lacrimation Urination, digestion, and defecation.
Acetylcholine as its neurotransmitter |
|
|
|
Name two drugs that are inhibitors of NET (Norepinephrine transporter). Thus prolong its actions at the receptor |
TCA (eg. imipramine) Cocaine |
|
|
|
Name two enzymes that metabolize NA in the nerve terminal |
MAO COMP (catechol-O-methyltransferases) |
|
|
|
Which common part of adrenergic agonist is essential for its adrenergic activity? What is the general pharmacophore? |
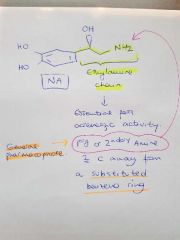
Essential: Ethylamine chain Pharmacophore: Primary or secondary amine 2 C away from a substituted benzeno ring |
|
|
|
What is Adrenaline I.V. used for? |
1. Treat cardiac arrest and hypotensive crisis (eg. during anaphylactic reactions) due it to its: Vasoconstrictor Chronotropic (+) Inotropic (+)
2. Mixed with local anesthetics (such lidocaine) to produce localized vasoconstriction to prolong duration of action and minimize the local anesthetic systemic effects |
|
|
|
What does "inotropic" refer to? |
Strength of contraction of heart muscle (myocardial |
|
|
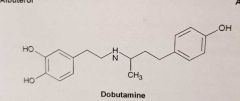
What is the selectivity of dobutamine for adrenergic receptors? |
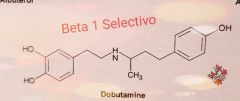
Beta 1 selective |
|
|
|
Dobutamine Main use and SE |
Acute HF B1 receptor stimulation = Increase AMPc en myocardium = However, in this case: Increase opening of L-type calcium channels: Enhance CONTRACTILITY
SE: Tachyarrhytmias Ischemia
|
|
|
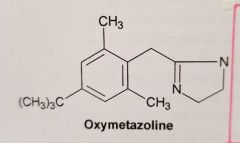
What is the selectivity of oxymetazoline for adrenergic receptors? |
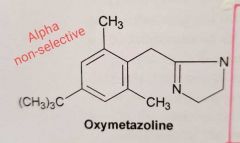
Alpha-non selective: Alpha 1 Alpha 2 Wiki: Oxymetazoline is a selective α₁ adrenergic receptor agonist and α₂ adrenergic receptor partial agonist. ????? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
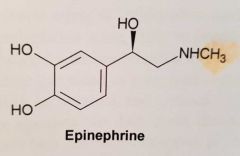
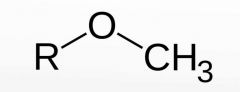
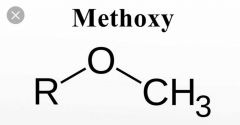
Have a look at the Adrenaline molecule. How can you improve the α1 receptor affinity?
Name the two drugs obtained and their use in I.V. administration |
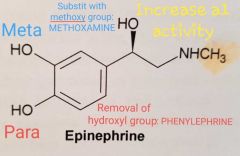
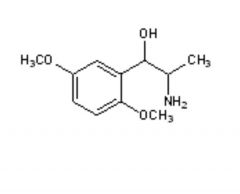
I.V. to maintain systemic blood pressure in hypotensive conditions Methoxamine Phenylephrine |
|
|
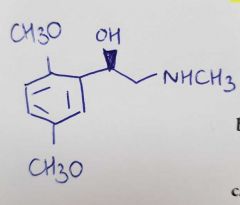
Name this molecule and its affinity to alpha adrenergic receptors |
Methoxamine Alpha 1 - selective |
|
|
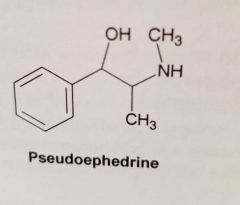
What is the selectivity of pseudoephedrine for adrenergic receptors? |

Mixed: * Alpha-agonist * Indirect (NA releasing) agent |
|
|
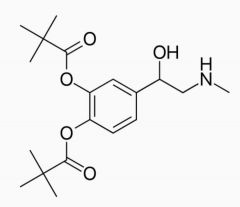
What is dipivefrin? What does it treat? How does it achieves it action? Razona... |
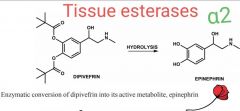
Cathecol diester PRODRUG of adrenalin * To treat open-angle glaucoma * Tissue esterases cleave the ester bonds to regenerate adrenaline * Adrenaline activates alpha2 receptors on the ciliary body = To decrease aqueous humor production |
|
|
|
Draw a IMIDAZOLINE ring |
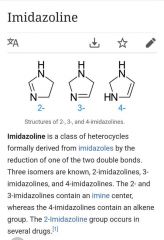
2 N + 3 C + 1= |
|
|
|
Name 2 imidazoline derivatives Which alpha- activity do they have? How can Alpha 1- activity be increased? |
* Clonidine * Oxymetazoline Alpha 1 and Alpha 2 agonists activity
Pero ojo... oxymetazoline tiene más afinidad por alpha-1... Ahora veremos como la ha conseguido |
|
|
|
Oxymetazoline: It is a Selective alpha-agonist (alpha 1 and alpha 2) How has the alpha-1 agonist activity has been increased |
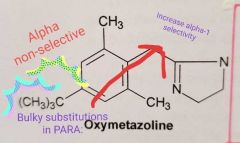
With BULKY substitution in para |
|
|
|
Oxymetazoline: it is used as topical decongestant due to its DIRECT ________ ACTION in the nasal mucosa |
Vasoconstriction |
|
|
|
What is systemic administration? |
Systemic administration is a route of administration of medication, nutrition or other substance into the circulatory system so that the entire body is affecte |
|
|
|
Clonidine: reduces tonic __________ output from the sistema nervioso _______ by activating __________ alpha-2 adrenoreceptors |
Clonidine: reduces tonic SYMPATHETIC output from the sistema nervioso CENTRAL by activating CENTRAL alpha-2 adrenoreceptors
Ha quedado claro el concept de CENTRAL ACTING???? |
|
|
|
Terbutaline: Beta2 Agonist * _______ AMPc in bronquial smooth muscle =
* _______ Ca intracellular =
Broncodilation
Which other effect does it have and which other drug also has the same use? |
Terbutaline: Beta2 Agonist * Increase AMPc in bronquial smooth muscle =
* Decrease Ca intracellular = Broncodilation
Systemically: Slow down premature labour (tocolytics) Also, ritodrine (beta-2 agonist also) |
|
|
|
Clonidine sudden withdraw: |
Enhace SN sympathetic outflow: HTA Sweating Tachycardia Tremors
|
|
|
|
Apraclonidine Brimonidine (Alphagan-P)
Are derivatives of _________ They are used topically to selective activate which receptors? Where? To treat what? |
Derivatives of CLONIDINE Alpha 2 in the EYE To treat open-angle glaucoma |
|
|
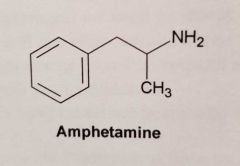
Amphetamine. MA? |
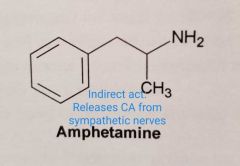
Only releases CA from sympathetic nerves (indirect action) |
|
|
|
Main adverse effect of imidizoline nasal decongestants? Which product is less likely to produce it? |
Rebound congestion (Phenylephrine: less likely to produce it) |
|
|
|
Beta-2 agonist SE?
Ayuda: Piensa en un b2 agonist
|
Tachycardia Muscle tremors Insomnia
* Due to their actions at cardiac and other beta-receptors (their selectivity is not absolute)
Respiras, pero corazón a tope, tiemblas y no te duermes 🤪🤪🤪 |
|
|
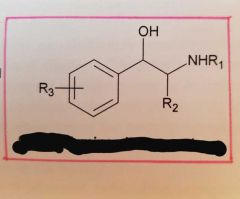
What is this? |
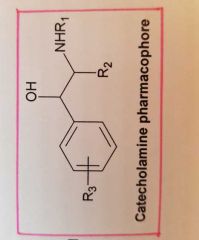
Primary or secundary amino 2 C away from Substitured benzene ring |
|
|
|
Clonidine IV : Actives central alpha-2 receptors. Use to treat HTA. Which SE are associated to this? |
Bradycardia Hypotension Sedation Dry mouth 🤐 |
|
|
|
Terbutaline: B2 agonist. How the B2 selectivity was achieved?
Easy peasy! 🤗 |
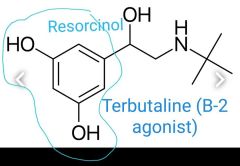
Changing catechol ring to Resorcinol
|
|
|
|
Which alpha adrenergic receptors have been identified? |
1A 1B 1D 2A 2B 2C |
|
|
|
Which types of alpha-adrenoreceptors |
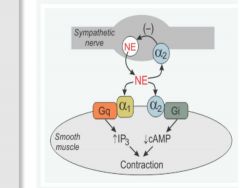
Vascular smooth muscle has two types of alpha-adrenoceptors: alpha1 (α1) and alpha2 (α2). The α1-adrenoceptors are the predominant α-receptor located on vascular smooth muscle. These receptors are linked to Gq-proteins that activate smooth muscle contraction through the IP3 signal transduction pathway. Depending on the tissue and type of vessel, there are also α2-adrenoceptors found on the smooth muscle. These receptors are linked to Gi-proteins, and binding of an alpha-agonist to these receptors decreases intracellular cAMP, which causes smooth muscle contraction. There are also α2-adrenoceptors located on the sympathetic nerve terminals that inhibit the release of norepinephrine and therefore act as a feedback mechanism for modulating the release of norepinephrine.Alpha-agonists constrict both arteries and veins; however, the vasoconstrictor effect is more pronounced in the arterial resistance vessels. Constriction of the resistance vessels (small arteries and arterioles) increases systemic vascular resistance, whereas constriction of the venous capacitance vessels increases venous pressure.
|
|
|
|
Beta-blocker overdose can be life-threatening. What is the treatment? |
Glucagon and dobutamine/milrinone. |
|
|
|
TCA and cocaine: They prolong the action of ________ at the receptor by inhibition of _________. |
Name two drugs that are inhibitors of NET (Norepinephrine transporter). Thus prolong its actions at the receptor |
|

