![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the UK definitions of perinatal and infant death? |
Miscarriage – pregnancy loss < 24 weeks |
|
|
What are the rates associated with perinatal and infant death? |
Stillbirth rates – number of stillbirths for each 1000 total births (live and stillbirths) |
|
|
What are the modifiable factors that contribute to death? |
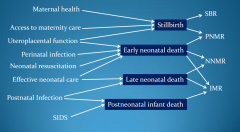
|
|
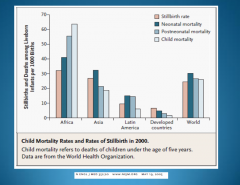
What factors explain these international differences in perinatal mortality? |
Maternal health |
|
|
What major diseases contribute to perinatal mortality in the UK? |
Prematurity (Surfactant deficiency, periventricular haemorrhage, necrotising enterocolitis, infection) |
|
|
What are the relative proportions of the above causes of death in newborns? |
Immaturity related conditions 58.5% |
|
|
What are the causes of stillbirths and their relative proportions? |
Remaining antepartum deaths (unexplained) 51.4% |
|
|
What are the proportions of causes of neonatal mortality? |
Immaturity related conditions 55% |
|
|
What are the causes of postneonatal infant mortality? |
Congenital anomalies 28.9% |
|
|
Which birthweights are associated with the highest mortality rates? |
<1500g in all stillbirths, perinatal, neonatal, postneonatal |
|
|
Which ethnicity has the highest risk of perinatal mortality? |
Bangladesh, Pakistani, African |
|
|
What measures contribute to perinatal mortality? |
Specific diseases & conditions
|

