![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Bones of the pelvis |
Two hips bones - Ilium - Ischium - Pubis Sacrum Coccyx |
|
|
|
What divide the pelvis into the false and true pelvis? |
Pelvic brim |
|
|
|
What structures for the pelvic brim/inlet? |
Sacral promontory Ileopectineal lines Symphysis pubis |
|
|
|
What structures form the pelvic outlet? |
Coccyx Ischial tuberosities Pubic arch |
|
|
|
What structures divide the sciatic notches into the greater and lesser sciatic foramen? |
Sacrotuberous ligament Sacrspinous ligament |
|
|
|
Joints of the pelvis |
Sacroiliac Sacrococcygeal Symphysis pubis |
|
|
|
Type of joint of the sacroiliac joint? |
Synovial |
|
|
|
Type of joint of Symphysis Pubis |
Cartilaginous |
|
|
|
Type of joint of Sacrococcygeal joint |
Cartilaginous |
|
|
|
Order of allowable movement among pelvic joints. |
Sacrococcygeal > Sacroiliac > Symphysis pubis |
|
|
|
Sex differences of the pelvis |
False pelvis shallower in femalesPelvic inlet oval in females, heart shaped in malesPelvic cavity roomier and shorter in femalesPelvic outlet larger in femalesIschial tuberosities everted in femalesSacrum shorter, wider, flatter in femalesSubpubic angle rounder and wider in females |
False pelvis Pelvic inlet Pelvic cavity Pelvic outlet Ischial tuberosities Sacrum Subpubic angle |
|
|
Normal measure of diagonal conjugate |
5 inches or 13 cm |
|
|
|
Distance between Ischial tuberosities |
4 inches or 10 cm |
|
|
|
What forms the anterior pelvic wall? |
Pubic bones Pubic rami Symphysis Pubis |
|
|
|
What forms the posterior pelvic wall |
Sacrum Coccyx Piriformis |
|
|
|
What forms the lateral pelvic walls |
Ilium Ischiac Obturator membrane Sacrotuberous ligament Sacrspinous ligament Obturator internus muscle |
|
|
|
1. Name of the fibrous sheet that almost completely closes the Obturator foramen. 2. Small gap in #1. 3. Structures that pass through #2. |
1. Obturator membrane 2. Obturator canal 3. Obturator nerve and vessels |
|
|
|
Extent of sacrotuberous ligament |
Sacrum/coccyx Ischial tuberosity Posteroinferior iliac spine |
|
|
|
Extent of sacrospinous ligament |
Sacrum/coccyx Ischial spine |
|
|
|
Composition of the levator ani |
Puborectalis Pubococcygeus Iliococcygeus |
|
|
|
Muscles of the Pelvic walls and floor |
Piriformis Obturator internus Levator ani Coccygeus |
|
|
|
Origin, Insertion, Action, Nerve of piriformis |
O: front of sacrum I: Greater trochanter of femur A: lateral rotator of the femur N: sacral plexus |
|
|
|
Origin, Insertion, Action, Nerve of Obturator internus |
O: Obturator membrane I: Greater trochanter of the femur A: lateral rotator of the femur N: sacral plexus |
|
|
|
Origin, Insertion, Action, Nerve of levator ani |
O: body of Pubis, fascia of Obturator internus, spine of the Ischium I: perineal body, anococcygeal body, prostate, vagina, rectum, anus A: anal sphincter, supports pelvic viscera N: pudendal nerve, 4th sacral nerve |
|
|
|
Origin, Insertion, Action, Nerve of coccygeus |
O: Ischial spine I: lower end of the sacrum/coccyx A: assists levator ani, flexes coccyx N: 4th and 5th sacral nerve |
|
|
|
Types of Pelvis |
Gynecoid Android Anthropoid Platypeloid |
|
|
|
Structures that pass through the greater sciatic foramen |
Pudendal nerve Nerve to Obturator internus Internal Pudendal vessels Piriformis Superior & Inferior gluteal nerves and vessels Sciatic nerve Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve Nerve to quadratus femoris |
|
|
|
Structures passing through the lesser sciatic foramen |
Pudendal nerve Nerve to Obturator internus Tendon to Obturator internus Internal Pudendal vessels |
|
|
|
Define Uterine prolapse |
Protrusion of uterus into the vagina |
|
|
|
Define cystocele |
Herniation of bladder into the upper part of the anterior wall of the vagina |
|
|
|
Define rectocele |
Herniation of the rectum into the lower posterior Vaginal wall |
|
|
|
The perineum is divided into two triangles, namely: |
Urogenital triangle Anal triangle |
|
|
|
Composition of urogenital triangle |
Male: root of scrotum and penis, urogenital passages Female: external genitalia, orifices of urethra and vagina |
|
|
|
Composition of anal triangle |
Anal canal Extrlernal anal sphincter Ischioanal fossae |
|
|
|
What divides the perineum into the urogenital and anal triangles? |

Perineal body |
|
|
|
Contents of the Ischioanal fossa |
Inferior rectal vessels and nerve Perineal branch of the femoral cutaneous nerve |
|
|
|
Contents of the superficial perineal space |

|
|
|
|
Contents of deep perineal space |
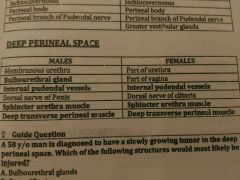
|
|
|
|
An episiotomy is an incision of the posterior wall of the vagina. Give two types. |
Median Mediolateral |
|
|
|
How is a median episiotomy oriented? |
Goes posteriorly and midline, through the perineal body |
|
|
|
How is a mediolateral episiotomy oriented? |
Extends obliquely posterolaterally. Extends through the bulbospongiosus and transversus perineus muscles. |
|
|
|
Which type of episiotomy has less risk of inciting the fibers of the external anal sphincter? |
Mediolateral episiotomy |
|
|
|
Anterior Division Branches of Internal Iliac Artery |
Inferior vesical (male) / Vaginal (female) Inferior gluteal Internal pudendal Middle rectal Obturator Uterine Umbilical / Superior Vesical |
IIIMOVUU |
|
|
Posterior Division Branches of Internal Iliac Artery |
Iliolumbar Lateral Sacral Superior gluteal |
|
|
|
Structures supplied by inferior gluteal artery |
Pelvic diaphragm Gluteus maximus |
|
|
|
Structures supplied by umbilical artery |
Obliterates, becomes superior vesical artery. Upper portion of bladder. |
|
|
|
Structures supplied by Obturator artery |
Pelvic muscles Medial thigh |
|
|
|
Structures supplied by Vaginal / inferior vesical |
Vaginal - vagina Inferior vesical - body of bladder - prostate - seminal vesicle - ductus deferens - lower ureters |
|
|
|
Structures supplied by uterine artery |
Uterus, cervix, ovaries, vagina |
|
|
|
Structures supplied by middle rectal |
Rectum Anal canal |
|
|
|
Branches of the internal pudendal artery |
Inferior rectal Perineal Superficial perineal Deep artery of penis/clitoris Dorsal artery of penis/clitoris Skin and muscles of anal and urogenital triangles (perineum) |
|
|
|
Which branch of the internal iliac artery has no accompanying vein? |
Umbilical artery |
|
|
|
Roots of the Sciatic Nerve |
L4-S3 |
|
|
|
Roots of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve |
S1-S3 |
|
|
|
Branches of the Sciatic Nerve |
Common peroneal nerve Tibial nerve |
|
|
|
Posterior branches of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve |
Superior gluteal L4-S1 Inferior gluteal L5-S2 Piriformis S1-S2 Perforating cutaneous S2-S3 |
|
|
|
Anterior Branches of Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve |

|
|

