![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the differential diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease?
|
-Pelvic Inflamatory Disease
-Acute Salpingitis -Tubo-ovarian abscess -Pelvic Abscess |
|
|
What are the etiologies of acute salpingitiis?
|
Gonococcal & nongonococcal
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of acute salpingitis?
|
-Gonococcal (GC) & Chlamydia
|
|
|
What is the next most common cause of acute salpingitis?
|
Mixed organisms - 30-40% cases result of normal flora in vagina & rectum.
|
|
|
What Happens in tubo-ovarian abscess & What is the result of tubo-ovarian abscess
|
-Large collection of pus
-inevitable infertility |
|
|
What are the process of PID?
|
Acute, subacute, or chronic infection of tubes, ovaries, & adjacent tissues.
|
|
|
What is the source of infection in PID?
|
Most are bacterial
|
|
|
What are the three pathways of infection?
|
-Intra-abdominal spread
-Lymphatic spread -Hematogenous spread |
|
|
What organism is associated with intra-abdominal spread
|
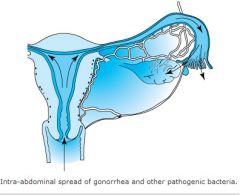
Gononrrhea
|
|
|
What organism is associate with hematogenous spread?
|
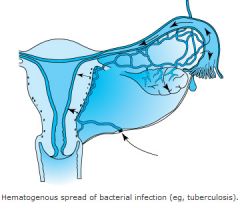
tuberculosis
|
|
|
What is another route for bacteria to spread?
|
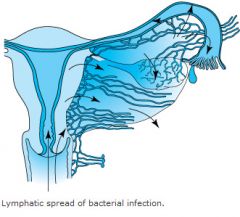
Lymphatic spread
|
|
|
What is the CDC minimum criteria for the diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)?
|
-Lower abdominal tenderness
-Adnexal tenderness -Tenderness with cervical motion |
|
|
What are the CDC additional criteria for the diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)?
note: Patients with PID should have 1 or more of these. |
-Oral temperature of more than 101〫F.
-Abnormal cervical and vaginal discharge. -Elevated Erythrocyte sedimentation Rate (ESR) -Elevated C-reactive protein Level -Laboratory documentation of cervical infection with N gonorrhoreae or C trachomatis. |
|
|
What are the CDC elaborate criteria (additional findings) in pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) ?
|
-Histopathic evidence of endometritis at endometrial biopsy
-thickened fluid-filled tubes with or without free pelvic fluid or a tubo-ovarian complex on transvaginal sonograms or other images -Laparoscopic abnormalites with PID. |
|
|
-Sudden onset that usually follows menses;
-Heavy vaginal discharge; -Generalized abdominal & pelvic tenderness; -Plus one or more of the following; --Temp > 101 F --leukocytosis > 10,000 --Inflammatory mass on exam or sonogram. |
Acute Salpingitis
|
|
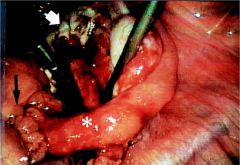
Cervi is dilated; endometrial cavit is raw & open. This is ____ bacteria culture conditions
|
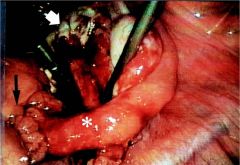
Good
|
|
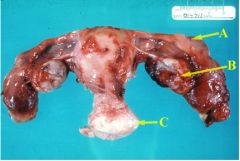
This is a hysterectomy of both tubes. They are clubbed & closed. It is ______ to do a hyserectomy for only tubes.
|
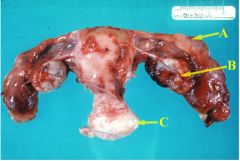
unusual
|
|
|
What you do with purulent material from culdocentesis or laparoscopy?
|
Take it & culture it
|
|
|
If gram negative diplococci are found, what bug has the patient been infected with?
|
Neisseira gonnorhea.
|
|
|
-purulent material on culdocentesis or laparoscopy
-elevated sed rate -gram negative diplococci What is the disease? |
Acute salpingitis.
|
|
|
If you find blood on culdocentesis, what are the implications for diagnosis?
|
-Ruptured ectopic pregnancy
-Hemorrhage from corpus luteum -Retrograde menstruation -Rupture of spleen or liver. -Gastrointestinal bleeding -Acute salpingitis |
|
|
If you find pus on culdocentesis, what are the implications for diagnosis?
|
-Ruptured tubo-ovarian abscess.
-Ruptured appendix or viscus. -Rupture of diverticular abscess -Uterine abscess with myoma. |
|
|
If you find cloudy fluid on culdocentesis, what are the implications for diagnosis?
|
-Pelvic peritonitis (such as is seen with acutegonococcal salpingitis.)
-Twisted adnexal cyst. -Other causes of peritonitis: (appendicitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, perforated ulcer carcinomatosis, echinococcosis.) |
|
|
What are the signs and symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)?
|
-Pelvic pain
-purulent discharge -fever, consider other pathology if fever is not present. |
|
|
What labs are consistent with a diagnosis of PID?
|
-Leukocytosis with left shift (inc. # of immature WBC)
-luid from culdocentesis positive. |
|
|
What imaging studies are used in work up of PID?
|
-Abdominal x-ray
-vaginal ultrasound |
|
|
What is the differential dx of PID?
|
-Acute appendix
-ectopic pregnancy -ruptured corpus luteum cyst -Diverticulitis -Adnexal torsion -endometriosis -acute UTI -colitis |
|
|
What can a patient who has a history of diverticulitis have?
|
A ruptured diverticuli.
|
|
|
What are the complications of PID?
|
-Peritonitis
-Pelvic thrombophlebitis -abscess formation -adnexal destruction with resultant infertility(due to destruction of fimbriae externi) -intestinal adhesions and obstruction |
|
|
How do you prevent acute salingitis?
|
-Early recognition and treatment of minimal disease
-Empiric therapy is started as soon as presumptive diagnosis is made. |
|
|
What therapy does most acute salingitis respond to?
|
Most acute salpingitis responds to outpatient antibiotics.
|
|
|
What scenarios are patients treat in the hospital?
|
-Severe cases or if diagnosis is uncertain,or
|
|
|
What does in-patient therapy include?
|
IV Antibiotics, Analgesics, bed rest & removal of IUD if present.
|
|
|
What does IV antibiotic therapy consist of?
|
A single injection of ceftriaxone or spectromycin for GC
|
|
|
Who requires in patient therapy?
|
-patient with an abscess(patient can hardly move)
Patient with temperature > 102.2° F -PT with marked abdominal guarding or rebound tenderness (peritoneal signs) -pt who does not respond to outpatient therapy (Outpatient Antibiotics unable to penetrate abscess) |
|
|
What are components of inpatient treatment?
|
Bed rest, IV antibiotics & possible surgical exploration.
|
|
|
What is prognosis based on?
|
Out come is related to prompt treatment with adequate meds.
|
|
|
How many episodes of salingitis are required to cause infertility?
|
A single episode can cause infertility.
|
|
|
How often does a single episode of acute salingitis cause infertility?
|
l2 - l8% of cases
|
|
|
what are patients with acute sapingitis at greater risk for?
|
ectopic pregnancy
|
|
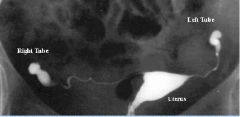
By restoring patentcy of the uterine tubes in a laparoscopic procedure, does this make the tube functional?
|
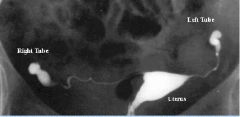
No and there is an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
|
|
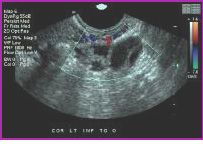
What findings are seen in this sonograph?
|
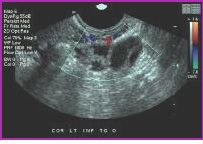
septated; scar tissue encompasses abscess
|
|
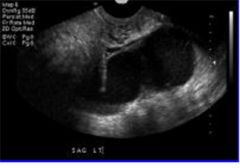
What is this?
|
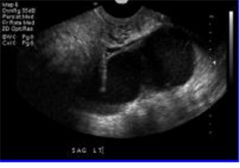
Large tubovarian abscess.
|
|
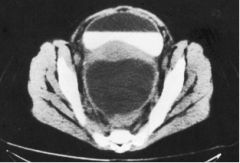
What structure has the fluid-air line?
|
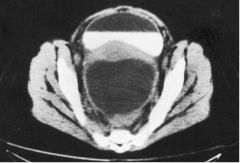
Bladder
|
|
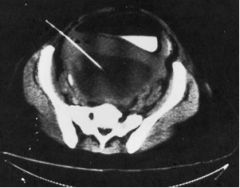
What procedure is being performed?
|
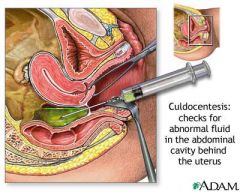
culdocentesis
|
|
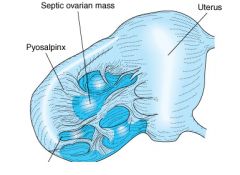
What do we see on this cartoon?
|
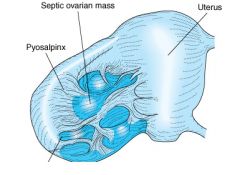
This is what an ovarian cyst looks like and we see scar tissue filling and is thick.
|
|
|
What is Tubo-ovarian abscess the result of?
|
It is usually the result of acute or recurrent salpingitis
|
|
|
What can rupture of an tubo-ovarian result in?
|
Rupture may result in cul-de-sac abscess.
|
|
|
Fever, cash. desquamation of palms & soles of feet (looks sunburn, shock
|
Toxic Shock Syndrome
|
|
|
What is the key to TSS?
|
PT is menstruating and using tampons
|
|
|
what does the rash look like?
|
Sun burn on face, trunk, and proximal extremities
|
|
|
What tampons are a greater risk and why?
|
super-absorbant; They dry out the vaginal wall. Making it susceptible to bacterial attack
|
|
|
what kind of therapy is required by patients with toxic shock syndrome?
|
Aggressive therapy includes fluids, antibiotics, steroids, blood products
|
|
|
what is the morbidity & mortality of toxic shock syndrome. ?
|
3-6% mortality
|
|
|
What is cervical motion tenderness?
|
Pain when the cervix is moved by the doctor's examining finger.
|

