![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
By CDC and AAP definition, anemia (ages 9 mo – 24 mo) is a hemoglobin less than _______
|
11 g/dL
|
|
|
Normal hearing threshold is at what minimal decibels?
|
20 dB
|
|
|
Type II Diabetes screening should be initiated for:
BMI greater than or equal to _____ % Beginning at age _____ years or at the start of puberty At a frequency of every _____ years If TWO or more of the following risk factors are present ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ |
BMI > 85%
Age 10 yrs every 2 yrs Risk factor 1: ethnicity (American Indian, black, Hispanic, Pacific Islander) Risk factor 2: Family History (1st/2nd degree relative with Type II DM) Risk factor 3: Signs of insulin resistance (acanthosis, HTN, dyslipidemia, PCOS) |
|
|
What is a normal Ear Canal Volume for interpreting a tympanogram?
|
0.2 – 2.0
|
|
|
Vitamin A deficiency puts you at risk for severe infections. In developing countries, the top two most common infections in Vitamin A deficient persons are ____ and ____.
|
Measles and diarrhea
|
|
|
By CDC definition, overweight is from _______ to ______ % BMI?
|
85 – 95%
|
|
|
By CDC definition, obese is a BMI greater than ______ %
|
95%
|
|
|
What medical conditions would lead to
Vitamin A deficiency through malabsorption? |
Celiac disease, hepatic disease, low protein or low fat diets
|
|
|
Name 4 clinical features of Vitamin A deficiency.
|
Night blindness (nyctalopia)
Xerophthalmia (dry eyes from keratinization of conjunctiva) Follicular hyperkeratosis (dry skin on extensor surfaces) Bitot spots (silvery patches on conjunctiva) |
|
|
True or False: Breastfeeding is protective for Vitamin A deficiency.
|
TRUE
|
|
|
Name 3 clinical features of Vitamin A excess.
|
Increased ICP
Carotenemia Painful joints Hair loss Drowsiness |
|
|
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is hydroxylated in two places in the body to form the physiologically active form. Name the two organs.
|
Liver converts D3 into 25-hydroxyl-D3
Kidney: next into 1,25-dihydroxy-D3 |
|
|
List 4 reasons for Vitamin D deficiency.
|
Unsupplemented exclusive breastfeeding with inadequate light exposure
Darkly pigmented children. Rapidly growing children and teens. Malabsorption states (celiac, CF, anticonvulsants) |
|
|
Name 3 clinical signs of Vitamin D deficiency
|
Bowlegs, kyphosis, delayed dentition, widened wrists, visible rachitic rosary, FTT, frontal bossing, widened sutures, seizures/tetany
|
|
|
What daily volume of formula is adequate to prevent Vitamin D deficiency?
|
500 cc per day
|
|
|
What is the daily recommended dose of Vitamin D for newborns?
|
400 IU Vitamin D
|
|
|
Name clinical features of Vitamin D excess.
|
Kidney stones, polyuria, polydipsia, hypotonia, anorexia, HTN, corneal clouding
|
|
|
What medical conditions predispose to Vitamin D deficiency?
|
short bowel syndrome
Cholestatic liver disease VLBW preemies Any malabsorption state Abetalipoproteinemia |
|
|
What autosomal-recessive inborn error of metabolism has Vitamin E deficiency and presents with steatorrhea from birth, pigmented retinopathy, and progressive ataxia?
|
Abetalipoproteinemia
|
|
|
What are the clinical features of Vitamin E deficiency?
|
hyporeflexia
Ophthalmoplegia Muscle weakness Ataxia Hemolytic anemia |
|
|
Where is Vitamin K made in the human body?
|
Made by bacteria in intestines and absorbed in jejunum
|
|
|
What are the 3 nutritional chemical components of all formulas?
|
Protein, Carboyhydrate, Lipid
|
|
|
What are the two main proteins in human milk, formula, and cow milk?
|
Casein and whey
|
|
|
What is the percentage casein and whey:
Breast milk ___% casein ____% whey Cow’s milk ___% casein ____% whey |
Breast milk
30% casein 70% whey Cow milk 80% casein 20% whey |
|
|
Which milk protein is more digestible
Casein or whey? |
Whey
|
|
|
Of the milk whey proteins, what are the two predominant protein species?
|
Alpha-lactoglobulin
Beta – lactoglobulin |
|
|
Which of the whey proteins (alpha-lactoglogulin or beta-lactoglobulin) is more prevalent in:
Human milk vs. Cow milk |
Human milk: alpha lactoglobulin predominates
Cow milk: beta lactoglobulin predominates |
|
|
TRUE or FALSE: Formula contains 50% more protein than breast milk
|
TRUE
|
|
|
The predominant protein in preterm formula is casein or whey?
|
Whey
|
|
|
Lipids provide ____ % of the caloric content of breast milk
|
50%
|
|
|
What substance do premature infants lack in their intestines to absorb/digest lipids?
|
They do not have adequate bile acids
|
|
|
Name the type of lipid that can be absorbed directly into the portal system rather than being emulsified by bile acids.
|
Medium chain triglycerides
|
|
|
What is the major carbohydrate in human milk
|
Lactose (glucose + galactose)
|
|
|
What is the major carbohydrate of standard cow-milk formulas?
|
Lactose (glucose + galactose)
|
|
|
What is the major carbohydrate in soy formulas?
|
Corn syrup solids (glucose polymers) or sucrose (glucose + fructose)
|
|
|
Preterm formulas predominantly contain what type of carbohydrate?
|
Glucose polymers 60%
Lactose 40% |
|
|
Name 3 biologically active products found in breast milk NOT found in formula.
|
Oligosaccharides (reduce bacterial attachment)
Nucleotides (enhances immune response) Growth factors (Epidermal GF, Nerve GF) Cellular components than enhance immune system (lactoferrin, lysozyme) Secretory IgA Cytokines |
|
|
Preterm formula contains a higher or lower osmolality for the immature kidneys?
|
Higher osmolality
|
|
|
In galactosemia, which formula is preferred?
|
Soy formula
|
|
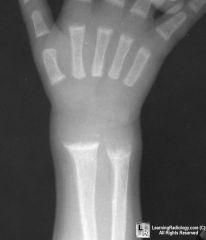
Describe the metaphyses in this xray
|
metaphyseal cupping and fraying from Vitamin D deficiency
|

