![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
If you see labs with:
- plasma amino acids and urin organic acids - metabolic acidosis with urine ketones - increased anion gap You should think about ______ In born error in metabolims? |
Amino acid diseases
(Maple syrup urine) |
|
|
|
If you seelabs with:
- Plasma ammonium - NO metabolic acidosis - respiratory alkalosis You should think about ______ In born error in metabolims? |
Hyperammonemia
(Ornithine transcarbamylase or OTC deficiency) |
- increased glutamine
- mild or no liver dysfxn |
|
|
If you seelabs with:
- plasma amino acids and urin organic acids - metabolic acidossi with urine ketones - plasma ammonium - increased glycine - abnomral urine organic acids - increased anion gap You should think about ______ In born error in metabolims? |
Organic acid disease
(propionic acidemia) |
|
|
|
If you seelabs with:
- NBS enzymatic testing - urine organic acids - liver enzyme analysis You should think about ______ In born error in metabolims? |
Sugar intolerances: galactosemia, fructosuria
|
|
|
|
How are most inborn erros of metabolism inherited?
|
AR >>> X linked
few AD "newer" mitochondrial |
|
|
|
When should you suspect an inborn error of metabolism in an infant with acute encephalopathy?
|
** when the encephalopathy occurs without warning and progresses rapidly
** NOT associated with focal neuro deficits ** normal birth, normal pregnancy - sxs: unexplained seizures, lethargy, coma, hypo/hypertonia |
|
|
|
How does chronic encephalopathy present?
|
** Slowly progressively symptoms from the build up of toxic metabolites
|
|
|
|
What events will exacerbate energy defect metabolic disorders?
|
** Fasting or illness with increased energy needs can exacerabate the disorder and bring on decompensation
|
|
|
|
If you see a kid with:
- hypoketotic hypoglycemia - hypotonia - cardiomyopathy - SIDS death You should think about ______ |
Fatty Acid oxidation defects
|
|
|
|
If you see a kid with:
- hepatogmgaly - hypoglycemia - lactic acidosis - FTT You should think about ______ |
Glycogen storage disease
|
|
|
|
If you see a kid with:
- lactic acidosis - seizures - cardiomyoathy - hypotonia/ muopathy - +/- hypoglycemia You should think about ______ |
mitochondrial disorders
|
|
|
|
Name 3-6 Lysosomal storage disease:
|
- Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) types I-IX
- Gaucher disease - Niemann-Picc disease, types A, B, C - Tay-Sachs disease - Fabry Disease - Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis |
|
|
|
Name 3-5 Peroxisomal storage diseases:
(All are AR except one!) |
- Zellweger syndrome spectrum
- X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) - Refsum disease - Mevalonate kinase - Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia puctata |
|
|
|
Name 3-5 intracellular trafficking and processing defect disorders
|
- Menkes disease
- Wilsons disease - hemochromatosis - alpha-1-antitrypsin dificiency - congenital disorders of glycosylation |
|
|
|
Name 3-5 inborn errors of cholesterol synthesis disorders:
|
- Smith=Lemli-Opitz syndrome
- Hypercholesterolemia, AD - Apolipoprotein E deficiency - Tangier disease - Desmosterolosis |
|
|
|
What is the most useful test to examine for disorders of amino acid metabolism?
|
BOTH:
** plasma amino acids ** urine organic acids |
|
|
|
How is PKU inherited?
What is defect and hat does it cause? |
** AR
** phenylalanine hydroxylase is defective so phenalyalanine cannot be converted to tyrosine - build up of phenylalanine |
|
|
|
You see an infact with vomiting, irritability, eczematoid rash, mousy/wolf like/musty odor ---
What do you suspect? what is causing the odor? |
PKU
Odor: phenylacetic acid in urine |
|
|
|
What subset of children with hyperphenylalaninemia will present with severe neurological disease, even with dietary treatment that mains normal phenylalanine levels?
|
defect in synthesis or recycling of bioprterin - neuro sxs that progress in spite of dietary tx that maintains norm phenylalanine levels
What is the treatmetnt for those children since dietary restrictions don't work? |
Tx phenylalanine restriction and biopterin supplements and biogenic amine precursors such as 5-hydroxytryptophan and dopa
|
|
|
In patients with hyperphenylalaninemia, defect in tetrahydrobioterin is also a cofactor for the hydroxylation of tryptophan and tyrosine -- in tern it interferes with synthesis of ____, ____, and ____
|
*Serotonin
* Dopa * NE |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of a patient with hyperphenylalaninemia?
|
- Drooling
- posturing - hypotonia - spasticity - psychomotor delay |
|
|
|
What is tyrosinemia and what is the inheritance pattern of Tyrosemia Type I, II and III?
|
** group of disorders with common theme of ELEVATED tyrosine levels in body fluids
* AR |
|
|
|
Type I tyrosinemia
|
0 deficiency of fumarylacetoacetate hydroxylase
- accumulation of succinylacetone - early --> death; some progress slowly - FTT, hepatomegaly, hepatoblastoma * NOT MR - renal tubular acidosis like Faconi, XR like rickets |
|
|
|
How do you treat liver failure and Faconi syndrome of hepatorenal tyrosemia?
|
** NTBC
- 2-(butri-4-trifuoro-methyl-benzolyl-1, 3-cyclohexanedione |
Blocks tyrosine breakdown --> high tyrosine
|
|
|
Tyrosinemia Type II
|
- deficiency of tyrosine aminotransferase
- corneal ulders or dendritic keratosis, red papular or keratotic lesions on palms and soles - 50% MR - skin and eye lesions due to deposition of tyrosine |
|
|
|
Tyrosinemia Type III
|
Extremely rare!!!!
- deficiency of 4-hydroxyphenypyruvate dioxygenase - MR |
|
|
|
What is Alkaptonuria?
|
** deficiency in homogentisic acid dioxygenase (3rd step in tyrosien metabolism)
- tyrosine NOT elevated - excretion of dark colored urine |
|
|
|
What happens to the urine of kids with alkaptonuria?
|
** fresh urine = norm
** sits and alkalinizes -- oxidation of homogentistic acid --> dark-brown/black pigement (?brick dust) |
|
|
|
What happens to the ears and sclera in adult (30s+) patients with alkaptonuria?
|
deposition of pigment in ears and sclera =
** ochronosis |
|
|
|
What are the branched-chain amino acids?
|
** Lucine
** Isoleucine ** Valine How do you dx a defect? |
Urine organic acid test
** look for weird urine odor! |
|
|
Describe the sxs of Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)
|
** CNS disease early in infancy
** Urine (or hair/skin) smells liek maple syrup - sxs by day 3-5, death 2-4 weeks - feeding difficulty, irregular resp - loss of moro - sz, opisthotonos |
|
|
|
MSUD
|
** mapple urine
- rapid progression - defect in oxidative decarboxylation of ketoacids (= sweet smell) formed by catabolis of branched chain AA - AR |
|
|
|
How do you Dx MSUD?
|
** Dx: inc amt of leucine, isoleucine and valine in plasma and urine
*** finding alloisoleucine = abnorm AA = DX |
|
|
|
What metabolic disease can be mistaken for child abuse?
|
Glutaric aciduria type I
What can it cause? |
** Subdural hematomas
** retinal hemorrhages |
|
|
What are the lens findings in Marfan syndrome vs homocystinuria??
|
Lenticular subluxation
** downward and medial (low IQ) = homocystineuria ** upward (nomral IQ) = marfan |
|
|
|
What is the clinical picture of someone with Homocystinura?
|
cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency
** Marfanoid habitus ** DD / MR ** ** lens dislocation ** inc riks of thromboembolism in arteries and vins *** subluxation/dislocation of ocular lense |
|
|
|
If you see a neonate with intractable seizures (or sz and apnea requiring intub) and h/o hiccups in utero with large amounts of glycine in body fluids what do you think of?
|
Nonketotic hyperglycemia
- AR - Dx by comparing CSF and plasma glycine levels |
|
|
|
What molecule is the problem in all urea cycle disorders?
Where does the Urea cycle occur? |
** AMMONIA (NH₄⁺) is problem
** ususally borken into glycine, glutamine, carbamyl phosphate periportal hepatocytes (mito) of liver |
|
|
|
Describe the urea cycle....
|
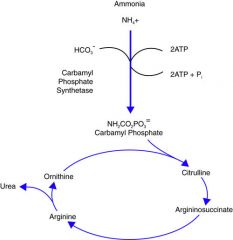
NH₄⁺ --> Carbamolyl phosphate --> Citrulline --> argininosuccinate --> argine --> urea into urine
|
|
|
|
Name 2-6 urea cycle disorders
What is the inheritance pattern of all except 1? |
- N-acetyle synthetase deficiency (NAGS deficiency)
- Carbamoly phosphate synthetase I (CPS deficiency) ** Orthine transcarbamolyase deficiency (OTC - most common and X-linked!!) - Arginosuccinate synthase deficiency (Citrullinemia) - Arginosuccinate lyase deficiency (argininoscuccinic aciduria) - Arginase deficiency (argininemia) ** AR except OTC = X-linked |
|
|
|
At what level of ammonia does grain edema occur? How does hyperammonia present?
|
** 100-200 umol/L
** lethargy, vomiting, confusion ----> coma *** ammonia and elevated CSF glutamine = toxic |
|
|
|
if the urea cycle defect is more (proximal or distal), it causes more severe symptoms?
|
** Proximal
CPS and OTC are the worst! |
|
|
|
You see an infant with elevated ammonia, no liver abnorm, and mild/no ketoacidosis. What defect should you consder?
|
** Urea cycle
** also low BUN and resp alkalosis |
|
|
|
you see blood gas... respiratory alkalosis what you think of??
|
**** Urea cycle defect!
|
|
|
|
Which urea cycle defect do you think of if you have:
- progressive spastic diplegia/quad - tremor - ataxia - choreathetosis |
Argininemia
|
|
|
|
Which urea cycle defect do you think of if you have:
- porgressive spastic diplegia/quad - retinal depigmentation - chorioretinal thinkking |
HHH = hyperorthithinemia, hyperammonemia, homocitrullineura = mitorchondrial ornithine transporter ORNT1
|
|
|
|
Which urea cycle defect do you think of if you have:
- interstitaial PNA (d/t pulm alveolar proteinosis - glomerulonephritis - osteoporosis - underlying immune deficiency |
LPI = Lysinuric protien intolerance = amino acid transporter gene SLC7A7
|
|
|
|
Which urea cycle defect do you think of if you have:
- Trichorrhexis nodosa (node like appearance of fragile hair_ episodic coma |
Arininosuccinic aciduria
|
|
|
|
What does the citrulline level tell you?
|
** absent/low - d/o proximally - OTC, CPS
How do you differentiate between the two? |
** Check Urine orotic acid level
- elevated = OTC - norm/low = CPS and NAGS |
|
|
Which urea cycle defect is plasma arginiene concentration NOT low??
|
*** argininemia
|
|

