![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
posterior teeth? |
the enamel rods at the cervix slope occlusally, unlike in permanent teeth where these rods slope cervically. |
|
|
Teething? |
drooling, desire to bite or chew, mild pain. No evidence of high fever, diarrhea or sleep problems. Patterns of eruption. Eruption problems. |
|
|
Eruption patterns of primary teeth |
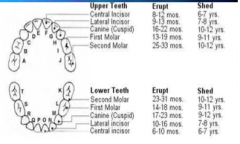
sequence more important than timing. symmetrical pattern. mandibular erupt first. 6, 11, 15, 19, 23, 27 months 1 tooth, 4 teeth, 8 teeth, 12 teeth, 16 teeth, 20 teeth. |
|
|
Eruption cyst and eruption hematoma |
eruption cyst- results from a fluid accumulation within the follicular space of an erupting tooth. eruption hematoma- with trauma, blood appears within the tissue space. |
|
|
difference with crown of primary teeth? |
shorter, narrower occlusal table, constricted in cervical portion, thinner enamel and dentin layers, enamel rods in cervical area directed occlusally, broad and flat contacts, color is usally lighter |

