![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name 5 skin lesions well associated with tuberous sclerosis complex. |
1. Hypomelanotic macules 2. Facial angiofibromas (adenoma sebaceum) 3. Shagreen patch 4. Forehead patch 5. Periungual or subungual fibromas |
|
|
1. What are facial angiofibromas?
2. Where do they typically appear?
3. Where might they spread?
4. At what age do they generally appear? |
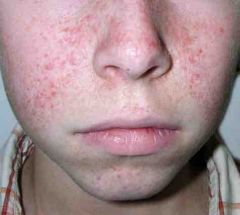
1. They are benign tumors appearing as small reddish spots or bumps.
2. They are first to be seen across the cheeks and nose.
3. They can spread to the lower lip or chin.
4. Typically appear as the child reaches 4-5 years of age (but can be seen at birth.) |
|
|
1. Name 2 features of the shagreen patch.
2. Name 2 places where the patch is likely to be found. |
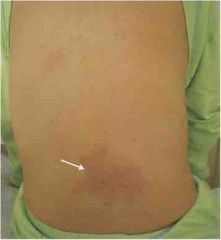
1. Description shagreen patch a. A connective tissue nevis similar in color to surrounding skin b. Tougher and dimpled like orange peel
2. Usually on (a) lower back or (b) nape of neck. |
|
|
What is the forehead patch of tuberous sclerosis complex? |
It resembles the shagreen patch but is found on the forehead or scalp. |
|
|
1. Where are the periungual or subungual fibromas of tuberous sclerosis complex found?
2. When do they appear in the disease? |
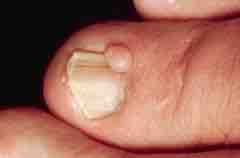
1. They appear around the fingernails or toenails
2. They usually first appear well beyond the pediatric age group. |
|
|
Name 3 distinguishing features of the hypomelanotic macules seen with tuberous sclerosis complex. |
1. They simply need to have less pigment than surrounding skin.
2. The classic form is "ash-leaf," but they are allowed any shape or size.
3. Three of them are required to constitute a major criterion for diagnosis. |
|
|
Name 6 brain lesions seen in individuals with tuberous sclerosis complex. How many are apt to be seen in any one patient? |
1. Cortical tubers 2. Subependymal nodules 3. SEGA-subependymal giant cell astrocytomas 4. Cortical dysplasias 5. Neuronal migration lines 6. Cortical astrocytomas
A patient may have any, all, or none at all! |
|
|
What are the 2 characteristic optic lesions in the tuberous sclerosis complex? |
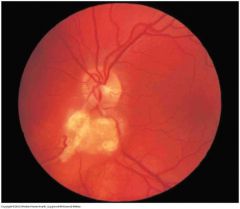
1. Retinal nodular hemartomas
2. Retinal achromic patches |
|
|
Name 2 oral lesions connected to the tuberous sclerosis complex. |
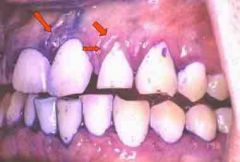
1. Multiple randomly distributed pits in dental enamel 2. Gingival fibromas |
|
|
What GI lesion is connected with tuberous sclerosis complex? |
Hamartomatous rectal polyps (but these are not unique to tuberous sclerosis complex) |
|
|
There are 11 major features and nine minor features of tuberous sclerosis complex. How many criteria from which list are needed to make a presumptive diagnosis of:
1. "Definite" tuberous sclerosis (TSC) 2. "Probable" TSC 3. "Possible" TSC |
1. Definite TSC: 2 major features alone OR 1 major feature with 2 minor features
2. Probable TSC: 1 major feature and one minor
3. Possible TSC: 1 major feature alone or 2 or more minor features alone |
|
|
List 11 major features of tuberous sclerosis complex |
1. Facial lesions: angiofibromas and or forehead plaques 2. Ungual or periungual fibroma 3. Hypomelanotic macules (3 or more) 4. Shagreen patch 5. Multiple renal nodular hamartomas 6. Cortical tuber 7. Subependymal nodule 8. Subependymal giant cell astrocytomas 9. Cardiac rhabdomyoma, single or multiple 10. Lymphangiomyomatosis 11. Renal angiomyolipoma |
|
|
Name the cardiac lesion associated with tuberous sclerosis complex. |
Cardiac rhabdomyoma, single or multiple |
|
|
Name 2 renal lesions found in tuberous sclerosis complex. |
1. Renal angiomyolipoma 2. Multiple renal nodular hamartomas |
|
|
List 9 minor diagnostic criteria for tuberous sclerosis complex. |
1. Multiple randomly distributed pits in dental enamel 2. Hamartomatous rectal polyps 3. Bone cysts 4. Cerebral white matter migration lines 5. Gingival fibromas 6. Non-renal hamartomas 7. Retinal achromic patch 8. "Confetti" skin lesions 9. Multiple renal cysts |
|
|
Name the 2 genes associated with tuberous sclerosis complex. Name the chromosome on which each one is located |
1. |

