![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Suspect congenital anomalies if >3 minor or 1 major. What are the major and minor anomalies?
|
Minor: 2-3 toe syndactyly, hypertelorism (eyes far apart), preauricular ear tag, epicanthal folds
Major: cleft lip/palate, CHD, brain anomalies, omphalocele, limb absence |
|
|
What diseases are children with trisomy 21 at risk for?
|
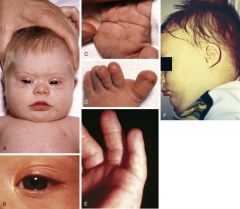
CHD, duodenal atresia, leukemia, Hirschprung's disease, MR. Hypotonia is one of the most common abnormalities in babies who have DS, occurring in up to 90%.
|
|
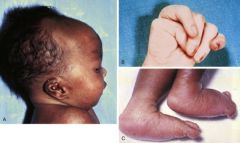
Rocker bottom feet, hand clenching-chromosomal abnormality?
|
Edward's syndrome (trisomy 18) Usually fatal in first year of life. 95% spontaneously lost before delivery.
|
|
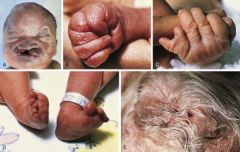
Clef palate, holoprosencephaly, chromosomal abnormality?
|
Patau syndrome (trisomy 13), clinically severe, usually death in first year of life, 20% of cases are due to unbalanced translocation (parents have inc recurrence risk).
|
|
|
Mom's risk of having another child with chromosomal abnormality?
|
1% added to mom's maternal age risk.
|
|
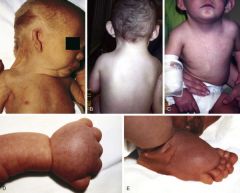
Nuchal webbing, puffy hands/feet (pedal edema), CHD (coarctation), short stature, no periods/infertile (gonadal dysplasia?
|
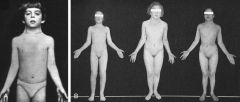
Turner syndrome (45, X). This is the one of the only chromosomal abnormalities not related to maternal age.
|
|
|
Tall stature, small testes, gynecomastia, learning/behavioral problems?
|
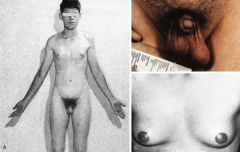
Klinefelter (47, XXY). Can have more than 2 X chromosome-increased risk for neuro issues.
|
|
|
What study looks for microdeletion syndromes?
|
FISH
|
|
|
What does CATCH 22 stand for?
|
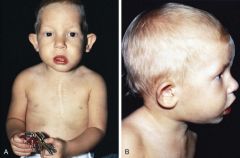
cardiac defects/conotruncal, abnormal facies, T cell deficit, cleft palate, hypocalcemia
22q Microdeletion syndrome/DeGeorge/Velocardiofacial CHD and MR-think about this deletion, can also be missing thymus |
|
|
Shrill cry, low broad nose, hypertelorism (not necessarily distinct characteristic features?
|

5p- syndrom/Cri du chat (deletion of short arm of chromosome 5), most are sporadic but 10-15% are due to translocation
|
|
|
Greek helmet appearance (middle part of nose pushed forward)?
|

4p-/Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome)
|
|
|
What does WAGR stand for?
|
Wilms tumor, Aniridia (absence of the iris), GU anomalies, mental Retardation.
Chromosomal deletion syndrome, AD |
|
|
Male to male transmission (excludes all x linked and mitochondrial transmission), both sexes are equally affected, in every generation, 50% chance of giving it to their offspring
|
AD
|
|
|
Diagnostic criteria for Marfan syndrome?
|
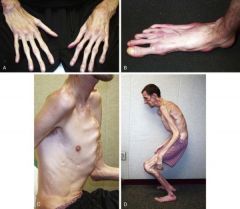
AD, 25% due to new mutation
-Skeletal changes (tall/thin, scoliosis, pectus deformities, long fingers) -Eyes (myopia, dislocated lens**) -Heart (aortic dilation**, dissections) -Not common-learning disorders If no family hx-major criteria in at least 2 organ systems and invovlement of third system. If positive family hx-one major criteria in at least 1 organ system and involvement of second system |
|

Paucity of bile ducts, triangular face?
|
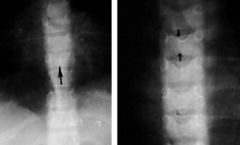
Alagille syndrome. AD
-Paucity of bile ducts, cardiac defects (PS), eye anomalies, butterfly vertebrae |
|
|
Achondroplasia-what is inheritance pattern?
|
AD, 80% new mutations, more severe if get 2 mutations
|
|
|
What is CHARGE syndrome?
|
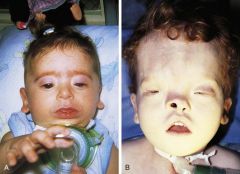
AD, generally sporadic
C-coloboma/CNS dz H-heart defects- A-choanal Atresia R-retardation of growth G-GU anomalies E-ear anomalies or deafness |
|
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta
|
AD
-See osteopenia, multiple fracture, blue/grey sclera, dental abnormalities, hearing loss, short stature |
|
|
AR
|
-2 mutatant alleles for the same gene, males and females equally affected, 25% recurrent risk of parents of affected, an unaffected sibling has a 2/3 chance of being a carrier, consanguinity increases the rsk
|
|
|
Examples of AR conditions
|
CF, hemoglobinopathies, metabolic conditions
|
|
|
X linked inheritance
|
-50% chance of females transmitting to sons, no male to male transmission, all daughters of affected males are obligate carriers, males severely affected
|
|
|
Examples of X linked disorders?
|
Duchenne Muscular dystrophy/DMD
Incontinentia Pigmenti (X linked dominant, see females with dz, men tend to die as fetuses) G6PD deficiency Rett syndrome (x linked dominant as well, females develop normally and then drop off, microcephaly) Alport syndrome (women have milder dz, kidney failure/deafness/abnormal eye exam) Aicardi syndrome |
|
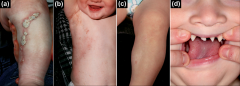
Peg shaped teeth,linear blistering rash (no erythema) that scabs?
|
Incontinentia pigmenti
|
|
|
What diseases can result from 15q11-13 chromosome deletion?
|
Prader Willi syndrome-from the dad's side
Angelman syndrome-from the mom's side |
|
|
Angelman syndrome
|

Severe MR, ataxic gait with jerky arm movements, seizure EEg abnormalities, inappropriate laughter, blond hair/blue eyes
|
|
|
Prader Willi syndrome
|
Hypotonic infant, FTT/difficulty feeding infant. Then at 2-4 years of age begans rapidly eating--see obesity, small hands/feet, short stature, hypogonadism
|
|
|
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
|

Macroglossia, ear lob pits/creases, macrosomia, hemihypertrophy, omphalocele, risk for embryonal tumors, imprinting vs AD
|
|
|
Fragile X
|
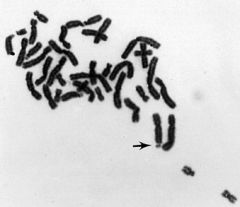
-Trinucleotide repeat expansion (size of repeat correlates with severity and age of onset)
-Increasing # of repeats in successive generation-anticipation -Most common inherited form of MR (most common chromosomal cause is Down's) -MR, large ears, generalized overgrowth |
|
|
Risk of multifactorial inheritance to siblings (ie cleft lip/palate)?
|
2-6%
|
|
|
Cornelia de Lange syndrome
|
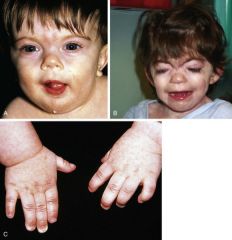
AD, Poor growth, IUGR, skeletal/limb abnormalities, short upturned nose, unibrow
|
|
|
Noonan syndrome
|
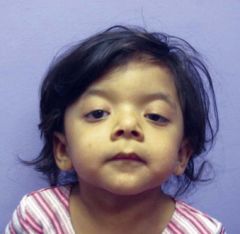
AD, short stature, hypertelorism, low set ears, lymphedema, delayed puberty/ cryptochordism, heart defects (pulmonary valve stenosis), normal intelligence
|
|
|
Williams syndrome
|
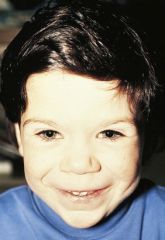
microdeletion (FISH), short stature/FTT, short nose, puffy eyelids, full mouth into a big smile!, MR, behavioral phenotype (talk a lot without saying anything), supravalvular aortic stenosis (get test for syndrome if has this)
|
|
|
Most common cause of bone marrow failure, abnormal thumbs/radial defects?
|
Fanconi Anemia, AR, chromosomal instability
See pancytopenia (fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising), inc risk of AML, other physical abnormalities including cafe-au-lait spots, heart, ears, eyes and GU system. |
|
|
Ehlers Danlos syndrome
|

AD, connective tissue disorder, hypermobility form is most common, classic form = stretchy skin
|
|
|
VATER/VACTERL
|
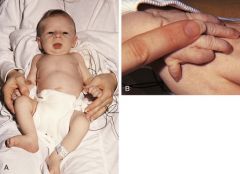
Vertebral abnormality
Anal atresia Cardiac TE fisulta Esophageal atresia Renal anomalies Limb anomalies |
|
|
Syndromes with severe neurological manifestations?
|
Meckel Gruber Sx (lethal)
Angelman/Prader Willi Sx Walker-Warburg Sx Sturge Weber sx Rett Sx (pictured above) |
|
|
SYndromes with thumb/radi defects and Hematological abnormalities?
|
Fanconi anemia (pancytopenai, hypoplastic thumb and radius, hyperpigmentation)
Diamond BlackFan Anemia (radial hypoplasia, anemia, CHD) Thrombocytopenia-absent radius syndrome (no radii, normal thumbs, low platelets/petechiae) Hold-Oram sx |
|
|
Syndromes with growth abnormalities?
|
Prader Willi
Angelmann Sx Sotos Sx Beckwith-Wiedemann sx Proteus sx |
|
|
Syndromes with short stature
|
Cornelia de lange
Dubowitz sx Noonan sx Williams sx |
|
|
The combination of tetralogy of Fallot, hypoplastic thumbs, cleft palate, and a renal abnormality described for the infant in the vignette is highly suspicious for?
|
22q11 deletion syndrome
|
|
|
Treacher Colin Syndrome
|
TCS is an autosomal dominant condition that is highly variable and is caused by spontaneous gene mutations in 60% of affected individuals. Unusual features associated with TCS include downslanting eyes with lower lid coloboma (notching) and absent eyelashes medial to the notch, malar hypoplasia, hypoplastic/malformed external ears with conductive and/or sensorineural hearing loss, and microretrognathia that has the potential to compromise the airway.
|
|
|
Most metabolic disorders are what type of inheritance?
|
AR
Exceptions: Hunter's sx (X linked), mitochondrial disorders, OtC (x linked) |
|
|
Most common disorder of amino acid metabolism? Inc frequency in Irish descent?
|
PKU, phenylalanine is not broken down, normal at birth but severe damage by 8 weeks of age.
Presentation: seizures, autism, musty odor. Goal is to start treatment by 2 weeks of age. Dx: Elevated plasma phenylalanine level, on all newborn screens (no TPN), low plasma tyrosine level TX: low phenylalanine intake |
|
|
Abnormal metabolism of methionine?
|
Homocystinuria
Clinical features: marfanoid habitus, DD, gross motor delays, ataxia. Increase in homocysteine and methionine Tx: Pyridoxine |
|
|
Succinylacetone buildup is cause of symptoms in this amino acid disorder?
|
Tyrosinemia Type 1
|
|
|
In utero hiccups, neonate presents with seizures and apnea?
|
Nonketotic Hyperglycinemia-glycine encephalopathy.
Dx by comparing CSF and plasma glycine levels. |
|
|
Hyperammonemia, increased glutamine, no ketoacidosis, respiratory alkalosis, mild or no liver dysfunction?
|
Urea cycle defect disorders. High ammonia is what causes symptoms. Start seeing CNS symptoms around 100-200. No Ketones in the urine (unlike organic acid syndromes)
-CPS1 (normal/low orotic acid) -NAG (normal/low orotic acid) -OTC deficiency (X linked, elevated orotic acid) -Citrullinemia (high citrulline, normal orotic acid) -Argininosuccinic Aciduria/ASA (hair thing-trichorrhexis nodosa, high citrulline, high ASA) -Arginase deficiency (only one that does not present with high ammonia-->spastic quadriplegia, ataxia) |
|
|
How do you treat urea cycle disorders?
|
Give Phenylbutyrate, arginine or citrulline; protein restriction; and increase caloric intake; use HD for hyperammonemia if necessary
|
|
|
High anion gap, metabolic acidois, ketonuria-what type of metabolic disorders?
|
Organic Acidurias. Buildup of ketoacids. Have elevated urine organic acids, hypoglycemia
TX: low protein diet, extra biotin and carnitine |
|
|
Organic Aciduria disorder (with elevated valine, isoleucine, leucine and alloisoleucine in plasma and urine?
|
Maple Syrup Urine disease.
Presents with CNS disease, normal baby who deteriorates at 3-4 days of life, feeding difficulties, irregular respirations, loss of Moro reflex. Abnormal odor of "maple syrup" -inc frequency in Mennonites |
|
|
Organic Aciduria commonly precipitated by infection, can also see osteoporosis?
|
MMA and propioic acidemia.
Propionic: ketotic hyperglycemia, AG metabolic acidosis, hyperammonemia, thrombocytopenia |
|
|
Liver disease, jaundice, cataracts, E Coli sepis, presents with vomiting and diarrhea?
|
Galactosemia-deficiency in GALT.
Dx-NbS, positive urine reducing substances Tx: Soy formula |
|
|
Presents at about 6 month of age (with fruit/fruit juices), jaundice, abnormal LFTs, severe hypoglycemia?
|
Hereditary fructose intolerance/HFI.
Inc incidence in Europe. |
|
|
FTT, low blood sugar, lactic acidosis, hypotonia, myopathy?
|
Fatty Acid Oxidation defects.
Dx difficult (some on Nbs). May require skin/muscle biopsy. Cannot fast as fatty acid oxidation is responsible for energy during fasting. Get hypoketotic hypoglycemia, acidosis, hepatomegaly. Low glucose can be a late finding. |
|
|
Most common form of fatty acid oxidation defect?
|
MCAD, Presents in first 2 years of life, stress/fasting can induce illness. Can cause SIDS.
FTT, low blood sugar, lactic acidosis, hypotonia, myopathy, cannot fast! low ketones Tx: frequent feedings, carnitine Other types: VLCAD, LCHAD, SCAD |
|
|
Problems manifest during fasting. See hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, protuberant abdomen, inc LFTs, increased ketones, "doll like facies,?
|
Glycogen Storage Disease. Defect in G6P in liver, kidney and intestine. Cannot convert glycogen to glucose.
Dx: Gene analysis TX: Cornstarch, allopurinol |
|
|
Muscle cramps with exercise in young adults/teens, urine turns brown (myoglobinuria), elevated CK levels even at rest, elevated lipids, second wind phenomenon?
|
GSD V/McArdle's disease.
|
|
|
Glycogen accumulates in the lysosomes -either presents in an infant with cardiomegaly or later on in life as a myopathy?
|
GSD Type 2/Pompe's disease (lysosomal storage disease)
|
|
|
Accumulation of sulfate presents with regressive development, dsymorphic syndromes, bone dysplasia or learning/developmental issues?
|
MPS/Mucopolysaccharidoses
Coarse facies, distinctive bone changes, joint stiffness, macrocephaly, hernias, corneal clouding. Examples include Hurler syndrome (AR). Hunter's syndrome (no vision problems/corneal clouding, X linked). Development for many children with an MPS disorder is initially normal, subsequently plateaus, and then regresses because of accumulation of metabolic by-products (glycosaminoglycans). Diagnostic screening includes urine testing for glycosaminoglycans and definitive testing for specific enzymes, depending on the findings on the urine test |
|
|
Common in Ashkenazi's Jewish population, cherry red spot, progressive CNS deterioration?
|
Tay-Sach's disease (sphingolipioses)
|
|
|
Erlenmeyer flask deformation fracture, hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, anemia, pain crises, can have normal development?
|
Gaucher's disease.
-Can present like leukemia with pancytopenia, organomegaly, FTT, and bone pain. Dx with glucocerebrosidase assay |
|
|
Peroxisomal disorder. Zellweger syndrome.
|
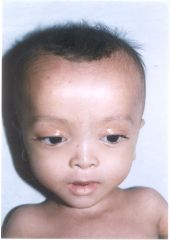
Patients can show craniofacial abnormalities (such as a high forehead, hypoplastic supraorbital ridges, epicanthal folds, midface hypoplasia, and a large fontanel), hepatomegaly (enlarged liver), chondrodysplasia punctata (punctate calcification of the cartilage in specific regions of the body), eye abnormalities, and renal cysts.[5] Newborns may present with profound hypotonia (low muscle tone), seizures, apnea, and an inability to eat
|

