![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
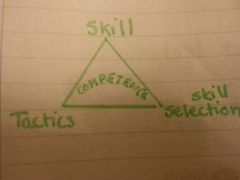
What are the key concepts?
|
Competence
Peformance Creativity Healthy active lifestyle. |
|
|
|
Competence
|
The relationship between skill, the selection of skills tactics and compositional ideas and the readiness of mind and body to cope with physical activity.
|
|
|
|
Peformance
|
Using physical competance and knowledge to produce an effective outcome
|

|
|
|
Creativity
|
Exploring and experimenting with ideas to produce an effective outcome.
|

|
|
|
Healthy, Active Lifestyle
|
Understanding that regular physical activity can improve your physical and mental health.
|
|
|
|
Name the 5 key processes (things you do) DEMDD
|
Developing skills
Evaluating and improving Making informed choices about HAL Decision Making Developing Physical and Mental capacity |
|
|
|
Developing skills and technique and example
|
Refine and adapt skills into techniques
eg In tennis throwing the ball up when serving and hitting the ball. |
|
|
|
Evaluating and Improving and example
|
Being able to identify strengths and weaknesses in physical activity.
eg Recognising you are weak at shooting in football and planning to improve your shooting in training. |
|
|
|
Making informed decisions about HAL and example
|
Choosing an activity or role that is best suited to you and your level of fitness.
eg choosing an activity that may help strengthen your heart like long distance running spinning or an aerobic class. |
|
|
|
Name the 6 fundamental motor skills
|
Running
Throwing Jumping Kicking Catching Hitting |
|
|
|
Name the 5 components of health related fitness and the test to go with it.
|
Cardiovascular Endurance- 12 minute cooper run
Muscular Endurance- Abdominal curl Strength- Hand grip strength test Flexibility- Sit and Reach Tesy Speed- 30 metre sprint test. |
|
|
|
Define and give a everyday and practical example for cardiovascular endurance or stamina
|
The ability to continue to work aerobically for long periods of time.
Walking up the stairs To last the whole of the hockey match. |
|
|
|
Define and give an everyday and practical example for Muscular Endurance
|
The ability of the muscle or group of muscles to repeatedly contract or keep going without rest.
Brushing your hair Rowing along a lake continually for 1 hour |
|
|
|
Define Speed give an everyday example and a practical example
|
The ability of the body to move quickly.
running out the way of a car coming in your direction In hockey running to get the ball before the opposition gets it. |
|
|
|
Define flexibility give an everyday example and a practical example.
|
The amount or range of movement that you can have around a joint.
The ability to bend down to put your socks on. A gymnast peforming the splits. |
|
|
|
Define Strength give an everyday example and a practical example.
|
The ability of tje muscular system to exert force for a short period of time.
Pick up the shopping and putting it in the car. Using resistance bands. |
|
|
|
Give 3 reasons to warm up and to cool down
|
Warm up:
To increase body (muscle) temperature To raise oxygen uptake increasing flow to the muscles. To improve performance and technique. Cool Down: Prevent blood pooling Gradually deacreases body temperature and heart rate. Psychological benefits, calms you down. |
|
|
|
Name the 5 characteristics of a skill full peformer and describe. (P-Face)
|
Pre-Determined - The peformer already knows what they are going to do.
Fluent- Smooth flow link movement without being ''jerky'' Aesthetic- Its pleasing to the eye. Co-ordinated - The ability to use more than one limb at a time. Efficency- A peformer who can complete the task with minimum outlay of time energy or both. |
|
|
|
What does a Peformance Goals relate to and give an example.
|
Technique/ skills and how we can carry out these skills.
eg to improve my v-drags in hockey so I can then outwit my opponent and pass to a supporting player. |
|
|
|
what does a outcome goal relate to and give an example.
|
The result of an activity
To beat my swimming personal best. |
|
|
|
Name 5 health screening measurements.
|
BMI
Blood pressure Cholesterol level Resting Heart Rate Hydration |
|
|
|
What does BMI measure and who does the BMI not apply to?
|
BMI measures body composition.
BMI is calculated by taking a person's weight and dividing it by there height squared. BMI does not apply to elderly people, pregnant women or highly trained athlete. |
|
|
|
Give the function of carbohydrates
|
An energy source for the body. Especially in high intensity exercise it is stored as glycogen.
|
|
|
|
Give the differences of the different carbohydrates.
|
Simple sugars- quick energy release-eg sugar jam and fruit juice
Complex Starches- Slower release in energy- eg pasta cereal and bread. |
|
|
|
Give the protein function
|
Growth and repair
Also can be used as an energy source if fatd snd carbohydrates are in short supply. |
|
|
|
Give function for fats
|
Major source of producing a lot of energy
also is used for insulation. |
|
|
|
what is calciums function
|
for stong bones and teeth
found in milk and cheese |
|
|
|
what is irons function
|
for haemoglobin in the red blood cells
found in green vegetable |
|
|
|
what is vitamin c function
|
for healthy skin and gums and to help heal wounds
found in oranges |
|
|
|
what is vitamin d function
|
For strong bones and teeth (cannot absorb calcium without it)
sourced from sun |
|
|
|
What is the function of vitamins in general
|
vital in the production of energy and functioning our metabolism as well as preventing disease.
|
|
|
|
what is the function of fibre
|
for bowel movement reduces constipation , piles
|
|
|
|
what is the function of water
|
water carries nutrients around the body, helps regulate body temp and helps remove waste products. Maintains hydration.
|
|
|
|
Describe the characteristics of a balenced diet
|
not too much alcohol
not too much sugar not too much salt eat breakfast sufficient minerals sufficient vitamins sufficient water |
|
|
|
What will happen to the boys weight of his energy input is the same as his energy output
|
his weight weight will stay the same
|
|
|
|
What will happen to the boys weight if his energy input is more as his energy output
|
He will gain weight
|
|
|
|
What will happen to the boys weight if his energy input is less than his energy output?
|
He will lose weight
|
|
|
|
What is health
|
Health is a state of complete physical mental and social well being.
|
|
|
|
Name 5 benefits of a HAL
|
live longer
cope with stress good self esteem aviods obesity You are able to socialise. |
|
|
|
how much exercise should you do a week
|
1 hour 5 times a week.
|
|
|
|
Name 3 possible effects of over eating and under eating
|
over eating:
participation decreases low self esteem decreases flexibility high cholesterol under eating: Tiredness slows growth and development Become weak so struggle to do some things. |
|
|
|
Name 5 effects of smoking
|
cigerettes contain tar, nicotine, carbon monoxide and other irritants that cause coughing.
Reduce fitness level- damage to lungs Raised blood pressure - nicotine releases hormones which make our heart beat faster Life Expectancy Appetite Lowered resistance to illness- chest infections |
|
|
|
Name 5 effects of alcohol
|
Reduce co-ordination slower reaction time
Dehydration Lower muscle glycogen levels Rapid loss of heat Longer injury recovery time Reduced size of arteries Thinking, judgement and vision/ hearing are also affected |
|
|
|
Name 5 positive effects of performance enhancing drugs.
|
Can increase peformance
More strength Can increase your power and speed Control anxiety Reduce weight Lower heart rate Speed up reaction time Increase your confident |
|
|
|
Name 4 side effects of steroids.
|
Increased aggression
Impotence (cant have children) Development of breast for men For women development of male features eg hair growth ect |
|
|
|
Name 5 negative effects of performance enhancing drugs.
|
You can experience withdrawal symptoms if you stop
High blood pressure Anxiety depression and lower self esteem can occur Can lead to more injury through over training Can lead to being banned, fined or disqualified. |
|
|
|
Negative effects of blood doping on health
|
Risk of blood infection or AIDS
Increased blood pressure Heart failure Kindney failure |
|
|
|
Name the 5 methods of training
|
Circuit Training
Aerobics Spinning Pilates Yoga Zumba/ dance exercises |
|
|
|
Measures and indicators of health and well being FLAPS
|
Frequency of positive and negative feelings
Level of participation in other activities Access to green space Positive Metal Health Satisfaction with life/ contentment |
|
|
|
Name 5 things that school curriculum offers
|
Being able to take part in sport after school
Fixtures Officiate Links to outside clubs improves fitness and social skills develop a passion for sport |
|
|
|
Name the 6 pathways to physical activity
|
Taking part in PE lessons and extra curriculum activists
Volunteering Taking part in community sport Take part as a peformer coach or official Getting to the highest possible standards you can Taking part in increasingly complex and challenging task. |
|

