![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
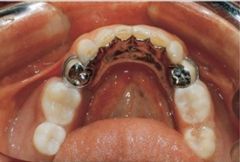
What are the two main types of mandibular major connectors?
|
Lingual Bar and Lingual Plate (linguoplate)
|
|
|
Which mandibular major connector is half-pear shaped in longitudinal section with the thinnest part around the teeth and the thickest part near the apex of the teeth?
|
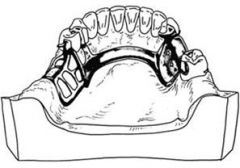
Lingual bar
|
|
|
What should you do when you want to place a lingual bar but there is a torus in the way?
|
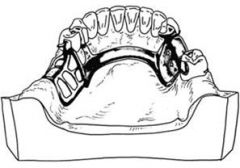
Remove the torus if it is too high or do NOT use a lingual bar
|
|
|
What happens if a lingual bar is placed superior to a torus?
|
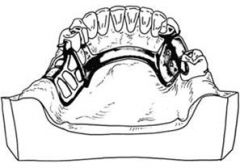
The denture base may settle and the lingual bar will descend into contact with the thin mucosal covering of the torus and the effect is very painful
|
|
|
What type of mandibular major connector is the one of choice for the routine prosthesis which has no unusual requirements?
|
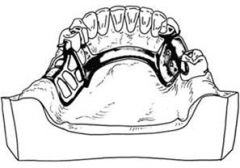
Lingual Bar
|
|
|
Where does a lingual bar get its strength from?
|
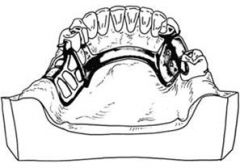
The thickness and the half-pear shaped cross section
|
|
|
How far below the gingival margin of all the teeth should the superior border of a lingual bar be?
|
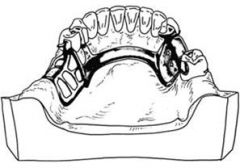
3-4 mm
|
|
|
Can you place a lingual bar if the gingiva is exposed and recedes on the lingual?
|
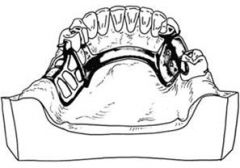
No, because you don't have a proper amount of gingiva
|
|
|
When should you use a lingual plate?
|
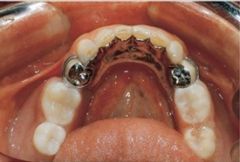
When you don't have enough gingiva for the lingual bar
|
|
|
What gives the lingual plate its strength?
|
Its Width
|
|
|
Where does the lingual plate extend up to?
|
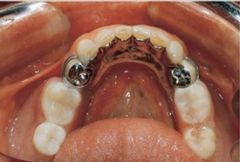
Lingual plate extends up to the contact point on the lingual surface
|
|
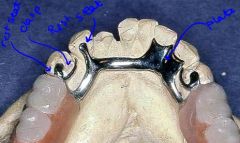
How far apart should the minor connectors be in this clasp?
|
Minimum of 5mm apart for Combination bar and plate
|
|
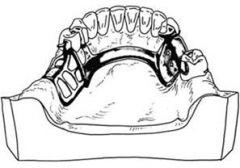
Where is the inferior border of the lingual bar in relationship to the gingival margin?
|
6-7mm below the gingival margin
|
|
What is the width of the lingual bar?
|
Usually 3mm
|
|
|
T/F
Mandibular major connectors don't touch the tissue |
True they are not form fitted
|
|
|
Which major connectors are form-fitted to the tissue?
|
Maxillary major connectors
|
|
|
Which major connectors don't touch the tissue?
|
Mandibular Major connectors
|
|
|
How far below the gingival margin should the maxillary major connectors be?
|
5-6 mm below the gingival margin
|
|
|
What could happen if a maxillary major connector is closer than 5-6 mm below the gingival margin?
|
Could strangle the tissue around the roots of the teeth
|
|
|
What are the five types of Maxillary Major Connectors?
|
Palatal Bar
AP bar (anterior posterior) Palatal Strap Full palate Horseshoe (U-shaped) |
|

What does the cross section of a palatal bar look like?
|
Half moon
|
|

When would you want to use a palatal bar?
|
Don't want to use this too often unless it is a really small partial
|
|

What is the thickness of a palatal bar?
|
3-4mm
|
|
|
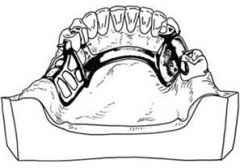
What is the AP Bar a combination of?
|
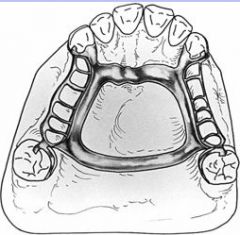
Anterior Bar and Posterior Strap or vice versa
|
|
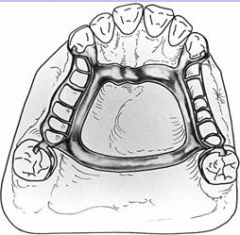
What shape is the bar in an AP bar in cross section?
|
Half-pear shaped
|
|
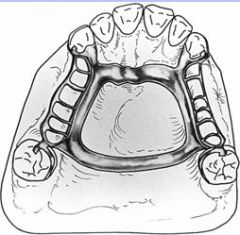
How wide must the strap be in an AP bar?
|
at least 8mm wide
|
|
|
What connector would you use to avoid palatal tori?
|
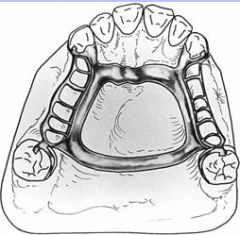
AP bar
|
|
|
How far back can you have a AP bar on the palate?
|
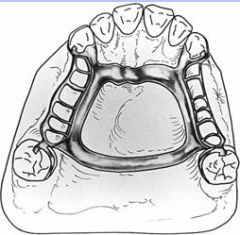
Anterior to the vibrating line, it cannot go to the post dam
|
|
|
What are the dimensions required for a palatal strap?
|
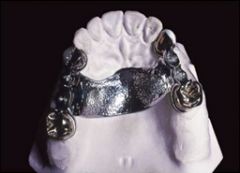
Must be at least 8mm in width and 1mm thick (any smaller and it is considered a bar)
|
|
|
What is a relatively smooth strap that goes across the palate?
|
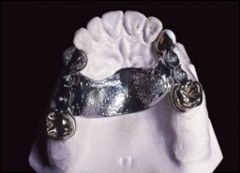
Palatal Strap
|
|
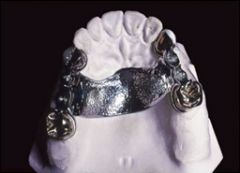
Why are palatal straps well accepted by the patient?
|
They are ~1mm thick, which is not very bulky
|
|
|
Which maxillary partial denture provides the maximum support for a partial?
|
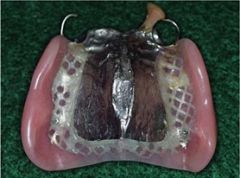
Full Palate
|
|
|
Which partial denture major connector provides a snow shoe effect?
|
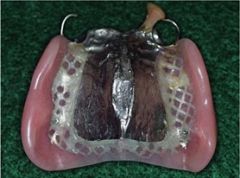
Full Palate - force is exerted on it and is fully supported by the tissue
|
|
|
Which partial extends all the way back to the vibrating line, so you must cut in a post dam?
|
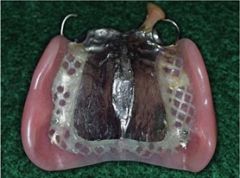
Full Palate
|
|
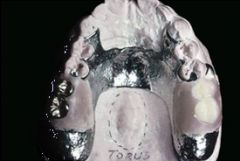
What is a Horseshoe (U-shaped) partial good for?
|
Avoiding palatal Torus - especially good in medically compromised people who cannot withstand a torus surgery.
|
|
|
What properties must major connectors possess to be considered permanent?
|
Rigidity and Cross arch stabilization
|
|
|
What part of the partial goes from the major connector to the terminus?
|
Minor connector
|
|
|
What are the dimensions of minor connectors?
|
~2.5mm - 1.5mm tapering wider from the major connector to thinner to the terminus
|
|
|
What major connectors are useful for avoiding tori?
|
Horseshoe (U-shaped)
AP Bar |

