![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Basal cell carcinoma
|
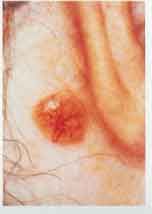
Diagnosis?
|
|
|
inflammed brachial cleft ear
|
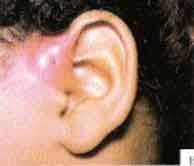
Diagnosis?
|
|
|
brachial cleft in ear
|
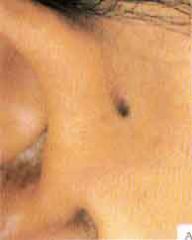
What is this?
|
|
|
chondrodermatitis helicis
|
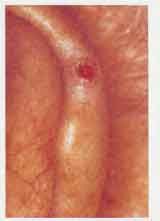
Diagnosis?
|
|
|
cutaneous cyst
|
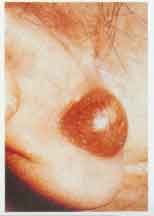
Diagnosis?
|
|
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
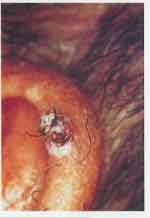
Diagnosis?
|
|
|
Tophi
|
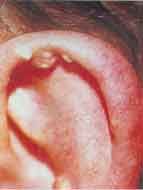
Diagnosis?
|
|
|
tympanic membrane
|
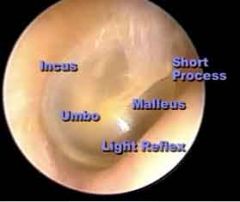
what is this. take a good look at all labels
|
|
|
Prebyscusis
|
Hearing loss associated with aging >50 yo
|
|
|
What are the 4 D’s to the the auricle examination?
|
Discharge, displacement, discoloration, Deformity
|
|
|
Upon examination of the ear what does discharge signify?
|
Otitis externa, OM with perforation, foreign body.
|
|
|
Upon examination what can displacement of ear signify?
|
Displacement away from the skull can signify mastoiditis, parotiditis, cellulites of the pinna, angioedemmaM
|
|
|
What is the umbo?
|
Where the malleous meets the tympanic membrane.
|
|
|
Par flaccida
|
Above the short processes of the malleous
|
|
|
Pars Tensa
|
Inferior, most of the short process
|
|
|
What are the malleolar folds?
|
They separate the pars flaccids from the tensa
|
|
|
What is the conductive phase of hearing?
|
The first part of hearing as sound goes from external ear to the middle ear
|
|
|
What is the sensorineural phase
|
Second part involves the choclea and nerves
|
|
|
What us BAER
|
Universally used in most American hospitals before infants are discharged
|
|
|
What type of hearing loss is the most common in the elderly
|
Sensorineural hearing loss
|
|
|
What are some of the clues to basilar skull fx
|
Hemotympanum , and other signs of trauma
|
|
|
What is a preauricular cyst?
|
brachial cleft remnants with an overlying surface dimple vulnerable to infection
|
|
|
In the weber test what does it mean of a the sound/vibrations did not lateralize equally to both ears
|
The sound lateralized to the ear that has the damage
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the rinne test?
|
Compares air conduction with bone conduction
|
|
|
What is a normal finding in the Rinne test?
|
AC> BC, 2:1
|
|
|
What are the signs and symptoms of otitis externa
|
Ear cannal inflamed, infected. Pain when auricle is moved, purulent discharge from ear
|
|
|
How does the tympanic membrane present when there is an otitis media
|
Eardrum is red, full loses landmarks and light reflex.
|
|
|
What is the most common bacterial pathogen of otitis media?
|
Strep
|
|
|
In pediatrics what is the most common OM pathogens
|
Strep pneumoniae 45-55%
|
|
|
What is bolus Myringitis?
|
Infections with painful hemorrhagic vesicles on the TM.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of bullous myrigitis?
|
Earache, blood tinged discharge, hearing conductive loss
|
|
|
How long does it that for a perforated tympanic membrane to close?
|
4-6 weeks
|
|
|
What is tympanosclerosis?
|
A deposition of hyaline material within the layers of the tympanic membrane following ear infections or perforations
|
|
|
Cutaneous cyst in ear
|
Often arises from sebaceous cyst; benign firm sac lies in the dermis. Attached to epidermis but mobile. Can become infected
|
|
|
Basal cell carcinoma
|
Raise nodules; note telangectasia and lustrous surface. Slow growing rarely metastasizes. Ulceration may occur
|
|
|
Chodrodermatitis helices
|
Chronic inflammatory lesion start as painful, tender papules on helix or antehelix. Must differentiate btw this and carcinoma
|
|
|
tophi
|
Deposits of uric acid characteristics of topaceous gout; hard nodules in the helix or antihelix. Discharge chalky white
|

