![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
311 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What percentage of the population lacks the CYP2D6 enzyme?
a. 10% b. 15% c. 20% d. 30% US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q1 |
a. 10%
|
|
|
Why is propoxyphene not recommended for use in elderly or chronic pain patients?
a. It is more potent than codeine b. Propoxyphene offers no additional benefit to acetaminophen alone and may cause adverse effects c. Norpropoxyphene may accumulate and cause cardiac toxicity and arrhythmias d. b and c US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q2 |
d. b and c
|
|
|
Which is true of morphine?
a. It is used more than any of the other opioids because it causes the least number of side effects b. M3G contributes to analgesia c. Accumulation of M6G may lead to sedation and respiratory depression in patients with advanced renal impairment d. It has the fastest onset of analgesia of all the opioids US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q3 |
c. Accumulation of M6G may lead to sedation and respiratory depression in patients with advanced renal impairment
|
|
|
Which is the advantage of using Fentanyl?
a. It acts selectively at the mu receptor, leading to an improved side effect profile b. It has a very fast onset of action c. It has no pharmacologically active metabolites and is one of the safest options for patients with renal failure d. All of the above US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q4 |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
Which is an appropriate indication for Meperidine?
a. Pain due to pancreatitis b. Intermittent intravenous dosing for a patient allergic to morphine or hydromorphone c. Intramuscular administration for postoperative pain d. Oral Meperidine use for a patient with chronic pain US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q5 |
b. Intermittent intravenous dosing for a patient allergic to morphine or hydromorphone
|
|
|
Patients taking methadone should consider that:
a. Methadone may prolong the QTc interval and cause cardiac arrhythmias b. Methadone has a stable equianalgesic dose for all other opioids c. Methadone has a long half-life and may cause delayed sedation and respiratory depression d. a and c US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q6 |
d. a and c
|
|
|
Which factor has limited the use of mixed agonist-antagonist opioids for severe or chronic pain?
a. They exhibit a ceiling effect for analgesia b. They may cause withdrawal in patients who already take pure opioids c. They may cause psychotomimetic effects d. All of the above US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q7 |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
Which is an acceptable method of administration?
a. Splitting tablets of Oxycontin, Opana ER, and MS Contin b. Using morphine sustained-release tablets rectally c. Using large volumes for subcutaneous administration d. Intramuscular injection US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q8 |
b. Using morphine sustained-release tablets rectally
|
|
|
Which patient is the best candidate for starting treatment with the Fentanyl transdermal patch?
a. A patient with acute postoperative pain b. A patient with a life expectancy of <24 hours c. A patient taking two Lortab 5/500 mg tablets per day for three days d. A patient who has been taking morphine 60 mg once daily for three weeks US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q9 |
d. A patient who has been taking morphine 60 mg once daily for three weeks
|
|
|
Which statement regarding transmucosal or buccal administration of Fentanyl is true?
a. The Fentanyl buccal tablet and transmucosal lozenge are indicated for the relief of acute postoperative pain b. The Fentanyl buccal tablet and transmucosal lozenge have a faster onset than oral short-acting opioids c. A patient who has never taken opioids should be started on the lowest strength of either formulation d. Doses of the Actiq lozenges and Fentora buccal tablets are interchangeable US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q10 |
b. the Fentanyl buccal tablet and transmucosal lozenge have a faster onset than oral short-acting opioids
|
|
|
What does the APS recommend when initiating treatment with a sustained-release opioid?
a. Treat patients for 48 hours with an immediate-release opioid, then convert two thirds of the estimated daily requirement to a sustained-release regimen b. Sustained-release products should be tried on an as-needed basis before switching to a scheduled regimen c. When starting sustained-release regimens, always use the lowest dose available d. When starting sustained-release regimens, eliminate use of the immediate-release prn opioid US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q11 |
a. Treat patients for 48 hours with an immediate-release opioid, then convert two thirds of the estimated daily requirement to a sustained-release regimen
|
|
|
For patients on sustained-release opioid regimens, immediate-release as-needed rescue doses should be what percentage of the total daily requirement?
a. 3 to 15% b. 10 to 15% c. 25 to 50% d. 30 to 50% US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q12 |
b. 10 to 15%
|
|
|
Which statement should a pharmacist consider when converting opioid doses?
a. When converting morphine from the oral to intravenous route, doses should be reduced by 30% to 50% to account for incomplete cross-tolerance b. When converting from one opioid to another, doses should be reduced by 30% to 50% to account for incomplete cross-tolerance c. Conversion to methadone should be handled like any other opioid d. Most opioids have equivalent doses for oral and intravenous routes US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q13 |
b. When converting from one opioid to another, doses should be reduced by 30% to 50% to account for incomplete cross-tolerance
|
|
|
Which approach may be used to manage opioid-induced side effects?
a. Changing opioid schedule b. Changing opioid route c. Opioid rotation d. All of the above US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q14 |
d. All of the above
|
|
|
Which side effect does not decrease with tolerance?
a. Sedation b. Constipation c. Pruritus d. Respiratory depression US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q15 |
b. Constipation
|
|
|
Which regimen should be added for a patient who takes chronic opioid therapy?
a. Stool softener as monotherapy b. Stimulant laxative such as senna or bisacodyl c. Bulk-forming laxative such as Metamucil d. Any of the above US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q16 |
b. Stimulant laxative such as senna or bisacodyl
|
|
|
Which opioid is safe for use in renal failure?
a. Codeine b. Morphine c. Methadone d. Propoxyphene US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q17 |
c. Methadone
|
|
|
Which opiod is the best choice for a patient with an anaphylactic morphine allergy?
a. Hydrocodone b. Hydromorphone c. Oxycodone d. Fentanyl US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q18 |
d. Fentanyl
|
|
|
Which of the following is a true statement?
a. Patients who are physically dependent on an opioid are also addicted b. The risk of tolerance to analgesia increases the longer an opioid is used, and opioids must be rotated every six months to prevent this phenomenon c. The risk of addiction is low for patients who have no history of substance abuse d. Patients who clock-watch and hoard opioids are addicted US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q19 |
c. The risk of addiction is low for patients who have no history of substance abuse
|
|
|
Which percentage represents the prevalence of reported addiction in patients treated with opioids in chronic pain centers?
a. Less than 0.01% b. Between 2% and 5% c. Between 3.2% and 18.9% d. Between 35.7% and 65.4% US Pharmacist Opioid Quiz q20 |
c. Between 3.2% and 18.9%
|
|
|
Opioids may be rationally administered to facilitate sleep is the patient is experiencing:
a. Cough b. Pain c. Chronic insomnia d. a and b e. All of the above |
d. a and b
|
|
|
Morphine is often used as the prototype opioid analgesic because it:
a. is the most potent b. is very efficacious c. exhibits the fewest side effects and toxicities d. has a long duration of action e. can be given by oral, IV, and epidural routes 2007 exam 2 q1 |
b. is very efficacious
|
|
|
While euphoria is mediated by the _____opioid receptor, dysphoria is mediated by the ____opioid receptor
a. Mu/Kappa b. Mu/Sigma c. Kappa/Sigma d. Kappa/Delta e. Mu/Delta 2007 exam 2 q2 |
a. Mu/Kappa
|
|
|
Addition of a methyl moiety at position 3 of morphine to produce codeine:
a. increases potency b. increases oral bioavailability c. increases efficacy d. a and b e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q3 |
b. increases oral bioavailability
|
|
|
This drug is a partial agonist:
a. codeine b. methadone c. nalbuphine d. Fentanyl e. etorphine 2007 exam 2 q4 |
c. nalbuphine
|
|
|
The effect of morphine on cardiovascular function is beneficial after:
a. myocardial infarct b. ischemic stroke c. hemorrhagic stroke d. a and b e. none of the above 2007 exam 2 q5 |
a. myocardial infarct
|
|
|
Opioid effects on the smooth muscle of the gut to produce constipation result from:
a. Relaxing circular (segmenting) smooth muscle and increasing tone of the longitudinal (propulsive) smooth muscle b. Contracting circular (segmenting) smooth muscle and increasing tone of the longitudinal (propulsive) smooth muscle c. Relaxing circular (segmenting) smooth muscle and decreasing tone of the longitudinal (propulsive) smooth muscle d. Contracting circular (segmenting) smooth muscle and decreasing tone of the longitudinal (propulsive) smooth muscle 2007 exam 2 q6 |
b. Contracting circular (segmenting) smooth muscle and increasing tone of the longitudinal (propulsive) smooth muscle
|
|
|
Although a high degree of tolerance develops to the analgesic action of opioids, no appreciable tolerance develops to:
a. pupillary effects b. constipation c. urinary retention d. a and b e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q7 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Although the analgesic dose of morphine and methadone is 10 mg IM in naïve patients, the spectrum and degree of side effects (respiratory depression, constipation, nausea and vomiting) would be:
a. less for methadone b. less for morphine c. the same for morphine and methadone d. cannot be stated because of patient related variable of sensitivity to opioid effects 2007 exam 2 q8 |
c. the same for morphine and methadone
|
|
|
The analgesic effect of opioids is supra-additive when combined with:
a. aspirin b. NSAIDs as ibuprofen c. acetaminophen d. a and b e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q9 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
The antitussive effect of codeine and the nonopioid dextromethorphan is via the ______and _____receptors, respectively:
a. Mu/kappa b. Mu/delta c. Kappa/sigma d. Mu/sigma e. Delta/kappa 2007 exam 2 q10 |
d. Mu/sigma
|
|
|
Opioids may be rationally administered to facilitate sleep if the patient is experiencing:
a. cough b. pain c. chronic insomnia d. a and b e. All of the above 2007 exam 2 q11 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
Nalmephene is approved for treatment of:
a. opioid overdose b. reversal of opioid anesthesia c. treatment of alcohol dependence d. a and b e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q12 |
d. and b
|
|
|
Nor-metabolites of this drug have convulsant properties:
a. Meperidine b. propoxyphene c. methadone d. a and b e. b and c 2007 exam 2 q13 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
This drug combination is a rational strategy to prevent abuse
a. diphenoxylate with atropine b. pentazocine with naloxone c. buprenorphine with naloxone d. a and b e. b and c 2007 exam 2 q14 |
e. b and c
|
|
|
This drug should not be administered to MI patients because it may increase cardiac work:
a. morphine b. methadone c. butorphanol d. nalbuphine e. dihydromorphone 2007 exam 2 q15 |
c. butorphanol
|
|
|
Of the partial agonist analgesics this one exhibits the greatest potency and longest duration of action:
a. nalbuphine b. buprenorphine c. butorphanol d. pentazocine 2007 exam 2 q16 |
b. buprenorphine
|
|
|
This medication should be labeled as paregoric to avoid accidental overdose:
a. camphorated tincture of opium b. opium tincture c. deodorized opium tincture d. diluted tincture of opium 2007 exam 2 q17 |
a. camphorated tincture of opium
|
|
|
This product is NOT combined with atropine:
a. difenoxin b. diphenoxylate c. loperamide d. a and b e. b and c 2007 exam 2 q18 |
c. loperamide
|
|
|
Pain that is stimulus-independent and triggered by light touch or a nonpainful stimulus is referred to as:
a. hyperalgesia b. paresthesia c. allodynia d. μ-receptor-dependent 2007 exam 2 q19 |
c. allodynia
|
|
|
This is a non-opioid which is metabolized to an active metabolite with greater mu receptor affinity and potency than morphine. It also blocks the reuptake of NE and 5HT:
a. remifentanil b. methotrimeprozine c. clonidine d. tramadol 2007 exam 2 q20 |
d. tramadol
|
|
|
Which of the following agents is indicated for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia?
a. Topiramate b. Gabapentin c. Carbamazepine d. Phenytoin 2007 exam 2 q21 |
c. Carbamazepine
|
|
|
Which of the following antidepressants is most effective in the treatment of neuropathic pain?
a. amitriptyline b. fluoxetine c. paroxetine d. citalopram 2007 exam 2 q22 |
a. amitriptyline
|
|
|
The mechanism of action of drugs efficacious in treatment of neuropathic pain is thought to include all of the following EXCEPT:
a. blockade of sodium channels b. blockade of calcium channels c. blockade of glutamate receptors d. blockade of potassium channels e. depletion of Substance P receptors 2007 exam 2 q23 |
d. blockade of potassium channels
|
|
|
Adverse effects on infants born to methadone maintained mothers include:
a. low birth weight b. withdrawal symptoms c. fetal alcohol-like syndrome d. a and b e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q24 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
A person who develops physical dependence as a result of continued prescription narcotic use for analgesia:
a. is addicted and should be referred to an addiction treatment center b. is chemically dependent and needs to see a psychiatrist for assessment c. is physically dependent but not addicted d. is addicted but not psychologically dependent 2007 exam 2 q25 |
c. is physically dependent but not addicted
|
|
|
The first effect of alcohol on human function:
a. impair judgment and reasoning b. impair speech c. impair reflexes d. induce poor coordination 2007 exam 2 q26 |
a. impair judgment and reasoning
|
|
|
A 150-pound person’s blood alcohol level is determined to be 200mg% (0.200 grams%) measured by breath sample analysis 1 hour after the last drink; This person:
a. is probably female b. can drive safely after waiting about 3 hours c. is legally impaired d. can lower his or her blood level by eating a meal e. none of the above 2007 exam 2 q27 |
c. is legally impaired
|
|
|
When an alcohol abuser overdoses the likely toxic effects may include which of the following?
a. cardiovascular collapse b. respiratory depression c. seizure d. all of the above e. a and b only 2007 exam 2 q28 |
e. a and b only
|
|
|
Disulfiram (Antabuse) and Naltrexone (ReVia) are used to treat alcoholism. Pick the best statement that describes their comparative effects
a. Disulfiram punishes people who drink while taking it; Naltrexone produces positive reinforcement when it is consumed b. After daily consumption of Naltrexone a person can experience a pleasurable effect of alcohol after two days of non-compliance, whereas a person would have to wait 10 to 14 days after stopping Disulfiram to drink alcohol without experiencing discomfort c. Disulfiram and Naltrexone have essentially the same mechanism of action so there is little if any difference between them d. Because of its opioid receptor activity, discontinuation of Naltrexone is more discomforting than discontinuation of Disulfiram 2007 exam 2 q29 |
b. After daily consumption of Naltrexone a person can experience a pleasurable effect of alcohol after two days of non-compliance, whereas a person would have to wait 10 to 14 days after stopping Disulfiram to drink alcohol without experiencing discomfort
|
|
|
When considering treatment for a patient at risk for alcohol withdrawal the preferred treatment approach is:
a. Use a withdrawal assessment scale and treat signs and symptoms as they emerge b. Treat prophylactically with benzodiazepines to prevent withdrawal distress c. Use phenytoin to control seizure occurrences d. Administer anti-psychotic drugs to protect against delirium tremors (DTs) e. All of the above 2007 exam 2 q30 |
b. Treat prophylactically with benzodiazepines to prevent withdrawal distress
|
|
|
How long after the last drink is the risk of seizure the greatest during alcohol withdrawal?
a. 1 to 5 hours b. 7 to 12 hours c. 18 to 36 hours d. 2 to 3 days e. 3 to 5 days 2007 exam 2 q31 |
c. 18 to 36 hours
|
|
|
Which of the following best describes the pharmacokinetics of alcohol?
a. first order absorption and zero order elimination b. peak blood level in about 30 to 45 minutes c. elimination rate enhanced by caffeine or water administration d. all of the above e. a and b only 2007 exam 2 q32 |
e. a and b only
|
|
|
The probability of physical dependence in depressant substance abusers is estimated by considering the:
a. dose of drug consumed on each day of drug use b. frequency of days of use in the past 30 days c. duration (days, weeks, months) of continuous (daily) use d. All of the above e. a and c only 2007 exam 2 q33 |
d. All of the above
|
|
|
Ativan (lorazepam) would be preferred over Valium (diazepam) in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal when:
a. a rapidly absorbed oral medication is needed b. the patient has significant liver dysfunction c. the patient has kidney damage d. the patient is allergic to benzodiazepines e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q34 |
b. the patient has significant liver dysfunction
|
|
|
Naltrexone (Trexan and Revia) is used to treat both alcoholism and narcotics addiction because Naltrexone:
a. blocks the “high” associated with the effects of both alcohol and opiates. b. when taken regularly, will create an unpleasant reaction if someone drinks alcohol or ingests narcotics. c. has a general effect on drug abusers that takes away their desire to get high. d. satisfies patients’ craving for either alcohol or opiates 2007 exam 2 q35 |
a. blocks the “high” associated with the effects of both alcohol and opiates
|
|
|
Which of the following would be likely to reduce the number of drug seeking heroin addicts in Baltimore City?
a. expanded treatment capacity (treatment on demand) b. offer new needles for old ones (needle exchange) c. provide “safe houses” for heroin injectors d. all of the above e. a and b only 2007 exam 2 q36 |
a. expanded treatment capacity (treatment on demand)
|
|
|
Methadone maintenance works by:
a. keeping the addict “high” thereby satisfying the psychological drive for intoxication b. creating cross tolerance to opioids thereby reducing the reinforcing effect of heroin use c. blocking narcotic receptors thus making agonist effects difficult to achieve d. all of the above e. a and b only 2007 exam 2 q37 |
b. creating cross tolerance to opioids thereby reducing the reinforcing effect of heroin use
|
|
|
Advantage(s) of methadone in the treatment of opioid addiction:
a. it lacks cross- tolerance with other opioids b. it is effective when orally administered c. avoidance of a reservoir in the body because it has a short half life d. it is an agonist with no abuse potential e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q38 |
b. it is effective when orally administered
|
|
|
Buprenorphine is:
a. able to suppress narcotic withdrawal symptoms in a patient in mild opioid withdrawal b. effective as a detoxification medication for the treatment of heroin withdrawal c. likely to produce withdrawal distress if given to an opioid intoxicated person with a high level of opioid tolerance d. all of the above e. a and b only 2007 exam 2 q39 |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
Which of the following distinguishes methadone from buprenorphine?
a. Methadone is an agonist, buprenorphine is an antagonist b. Methadone is a full mu agonist, buprenorphine is a partial mu agonist c. Methadone is approved for maintenance, buprenorphine is approved only for detoxification d. A single methadone dose provides 24-hour relief from withdrawal, buprenorphine must be administered 2 to 3 times daily 2007 exam 2 q40 |
b. Methadone is a full mu agonist, buprenorphine is a partial mu agonist
|
|
|
The recent increase in heroin abuse and dependence among young people is attributable to which of the following:
a. increased heroin purity allows new route of administration (intranasal) which makes heroin experimentation more acceptable. b. heroin produces physical dependence insidiously and the person may not recognize their growing dependence until it is well developed. c. increased acceptability of heroin use among teens. d. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q41 |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
Cannabis
a. is non-addicting b. produces no physical dependence c. disrupts ego function d. all of the above e. b and c only 2007 exam 2 q42 |
e. b and c only
|
|
|
Since delta –9- THC is highly lipid soluble:
a. it concentrates in the brain b. it sustains a reservoir in lipid tissue c. it follows a two-compartment kinetic model d. all of the above e. b and c only 2007 exam 2 q43 |
e. b and c only
|
|
|
When a cannabis abuser overdoses, the likely toxic effects include which of the following?
a. dangerous behaviors b. respiratory depression c. seizure d. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q44 |
a. dangerous behaviors
|
|
|
This is a reversible MAOI:
a. trazodone b. mertazepine c. reboxetine d. moclobemide e. phenelzine 2007 exam 2 q45 |
d. moclobemide
|
|
|
Consequences of TCA overdose that may lead to death include:
a. cardiac arrhythmias b. respiratory depression and apnea c. seizures d. metabolic acidosis e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q46 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
This drug may produce muscle problems referred to as Tardive Dyskinesia:
a. desipramine b. bupropion c. amoxapine d. tranylcypromine e. fluoxetine 2007 exam 2 q47 |
c. amoxapine
|
|
|
Suicidality in children and adolescents must be considered a risk with prescribing:
a. TCAs b. MAOIs c. SSRIs d. a and b e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q48 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
The “classical monoamine theory of depression” was based upon behavioral and neurochemical effects of:
a. phenelzine b. reserpine c. L-DOPA d. desipramine e. fluoxetine 2007 exam 2 q49 |
b. reserpine
|
|
|
The ultimate effect of traditional antidepressant efficacy (TCA’s, MAOI’s, SSRI’s) beyond receptor regulation that is thought to underlie clinical improvement is increased production of:
a. insulin-like growth hormone b. brain derived neurotrophic factor c. nitric oxide synthase d. a and b e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q50 |
b. brain derived neurotrophic factor
|
|
|
Patients should be counseled that it may produce priapism:
a. Amoxapine b. Maprotiline c. Bupropion d. Trazodone e. Cyclobenzaprine 2007 exam 2 q51 |
d. Trazodone
|
|
|
Should not be prescribed for bulimic patients:
a. Amoxapine b. Maprotiline c. Bupropion d. Trazodone e. Cyclobenzaprine 2007 exam 2 q52 |
c. Bupropion
|
|
|
Approved as a muscle relaxant instead of antidepressant:
a. Amoxapine b. Maprotiline c. Bupropion d. Trazodone e. Cyclobenzaprine 2007 exam 2 q53 |
e. Cyclobenzaprine
|
|
|
The analogue of a drug approved for treatment of schizophrenia:
a. Amoxapine b. Maprotiline c. Bupropion d. Trazodone e. Cyclobenzaprine 2007 exam 2 q54 |
a. Amoxapine
|
|
|
A selective NE uptake inhibitor that lowers threshold for seizures:
a. Amoxapine b. Maprotiline c. Bupropion d. Trazodone e. Cyclobenzaprine 2007 exam 2 q55 |
b. Maprotiline
|
|
|
Side effects of TCA’s are due mainly to:
a. blockade of H1 receptors b. blockade of alpha receptors c. blockade of muscarinic receptors d. a and b e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q56 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
The common side effects of TCA’s are also common side effects produced by:
a. benzodiazepines b. phenothiazines c. phenanthrenes d. a and b e. b and c 2007 exam 2 q57 |
b. phenothiazines
|
|
|
MAOI’s are associated with a high risk of neuroleptic-like syndrome when administered along with:
a. Meperidine b. L-Tryptophan c. pethidine d. a and b e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q58 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
T/F: Somatodendritic 5HT1a receptors are desensitized
2007 exam 2 q59 |
True
|
|
|
T/F: Postsynaptic 5ht1a receptors are sensitized
2007 exam 2 q60 |
True
|
|
|
T/F: Presynaptic 5ht1b/d receptors are sensitized
2007 exam 2 q61 |
False
|
|
|
T/F: Postsynaptic beta1 receptors are down regulated
2007 exam 2 q62 |
True
|
|
|
T/F: Postsynaptic 5ht2 receptors are down regulated
2007 exam 2 q63 |
True
|
|
|
T/F: Presynaptic alpha2 receptors are sensitized
2007 exam 2 q64 |
False
|
|
|
The biochemical correlate of Lithium’s antidepressant action is:
a. decreased formation of IP3/DAG b. uncoupling of GPCR c. blocks glutamate operated ion channels d. a and b e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q65 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
The parent drug has a half-life of 70 h and its active metabolite a half-life of 9-14 days
a. tranylcypromine b. fluoxetine c. desipramine d. loxapine e. propoxyphene 2007 exam 2 q66 |
b. fluoxetine
|
|
|
Because of their potential toxicity when TCAs are used in children, it is standard practice to monitor the:
a. electroencephalogram b. electrocardiogram c. urinary excretion of monoamine metabolites d. a and b e. all of the above 2007 exam 2 q67 |
b. electrocardiogram
|
|
|
The electrophysiologic basis of the antinociceptive of action of opioids results from:
a. increase gK b. decrease gCa c. increase gNa d. a and b e. b and c 2006 exam 2 q1 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
The antitussive action of opioids requires activation of the:
a. Mu receptor b. Kappa receptor c. Delta receptor d. Sigma receptor e. none of the above 2006 exam 2 q2 |
e. none of the above
|
|
|
All of the following are important transmitters of nociceptive stimuli EXCEPT:
a. substance P b. glutamate c. enkephalin d. norepinephrine e. c and d 2006 exam 2 q3 |
c. enkephalin
|
|
|
Opioids can be administered as sleep aids if the patient is experiencing:
a. pain b. cough c. delirium tremens d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q4 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
Heroin has less CNS penetration than morphine because heroin:
a. Is acetylated at two of the hydroxy groups b. Is methylated at one of the hydroxy groups c. Has dimethyl groups on the Nitrogen d. Has a N-allyl group e. Is methylated at two hydroxy groups 2006 exam 2 q5 |
a. Is acetylated at two of the hydroxy groups
|
|
|
The best oral bioavailability is exhibited by:
a. methadone b. diphenoxylate c. butorphanol d. morphine 2006 exam 2 q6 |
a. methadone
|
|
|
This opioid will precipitate abstinence when administered to patients taking high doses of morphine or methadone:
a. nalbuphine b. butorphanol c. buprenorphine d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q7 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Opioid effects on the smooth muscle of the gut to produce constipation are due to:
a. Relaxing circular (segmenting) smooth muscle and increasing tone of the longitudinal (propulsive) smooth muscle b. Contracting circular (segmenting) smooth muscle and increasing tone of the longitudinal (propulsive) smooth muscle c. Relaxing circular (segmenting) smooth muscle and decreasing tone of the longitudinal (propulsive) smooth muscle d. Contracting circular (segmenting) smooth muscle and decreasing tone of the longitudinal (propulsive) smooth muscle 2006 exam 2 q8 |
b. Contracting circular (segmenting) smooth muscle and increasing tone of the longitudinal (propulsive) smooth muscle
|
|
|
Nalmephene (Revex) is approved for treatment of:
a. opioid overdose b. reversal of opioid anesthesia c. treatment of alcohol dependence d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q9 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
This drug combination is a rational strategy to prevent abuse:
a. Diphenoxylate with atropine b. Pentazocine with naloxone c. Buprenorphine with naloxone d. a and b e. b and c 2006 exam 2 q10 |
e. b and c
|
|
|
b. methadone
|

These are time-effect curves for Morphine and ________?
a. codeine b. methadone c. buprenorphine d. nalbuphine e. pentazocine 2006 exam 2 q11 |
|
|
Which of the following antidepressants is most effective in the treatment of neuropathic pain?
a. Amitriptyline b. Fluoxetine c. Paroxetine d. Citalopram 2006 exam 2 q12 |
a. Amitriptyline
|
|
|
It has been shown that the molecular basis of opioid tolerance is ultimately dependent upon:
a. Retinoid-X-receptor b. CREB c. downregulation of tyrosine kinase receptors d. PPARgamma activated receptor e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q13 |
b. CREB
|
|
|
The principal enzyme responsible for the metabolism of methadone:
a. glucuronyl transferase b. plasma esterase c. N-demethylase d. phenylethylamine N-methyltransferase e. catechol-O-methyl-transferase 2006 exam 2 q14 |
c. N-demethylase
|
|
|
The principal enzyme responsible for the metabolism of dextropropoxyphene:
a. glucuronyl transferase b. plasma esterase c. N-demethylase d. phenylethylamine N-methyltransferase e. catechol-O-methyl-transferase 2006 exam 2 q15 |
c. N-demethylase
|
|
|
The principal enzyme responsible for the metabolism of meperidine:
a. glucuronyl transferase b. plasma esterase c. N-demethylase d. phenylethylamine N-methyltransferase e. catechol-O-methyl-transferase 2006 exam 2 q16 |
c. N-demethylase
|
|
|
The principal enzyme responsible for the metabolism of remifentanil:
a. glucuronyl transferase b. plasma esterase c. N-demethylase d. phenylethylamine N-methyltransferase e. catechol-O-methyl-transferase 2006 exam 2 q17 |
b. plasma esterase
|
|
|
The principal enzyme responsible for the metabolism of codeine:
a. glucuronyl transferase b. plasma esterase c. N-demethylase d. phenylethylamine N-methyltransferase e. catechol-O-methyl-transferase 2006 exam 2 q18 |
a. glucuronyl transferase
|
|
|
The fundamental pharmacological principle underlying methadone maintenance treatment of heroin addicts is:
a. Methadone maintenance doses produce a high degree of cross-tolerance to heroin b. Methadone maintenance doses produce a high degree of opioid physical dependence which maintains patient compliance in the program c. Methadone can produce psychological dependence similar to heroin to satisfy the addiction personality d. a and b e. All of the above 2006 exam 2 q19 |
a. Methadone maintenance doses produce a high degree of cross-tolerance to heroin.
|
|
|
The relationship between degree of physical dependence and naloxone ED50 for precipitating abstinence signs is:
a. Zero order b. Linear c. Direct d. Inverse 2006 exam 2 q20 |
d. Inverse
|
|
|
Patients receiving this opioid via transmucosal dosage form must be observed continuously by a clinician trained with administration of this preparation
a. hydromorphone b. buprenorphine c. Fentanyl d. nalmephine e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q21 |
c. fentanyl
|
|
|
Opium Tincture (Deodorized Opium Tincture) is ______ time more potent than Paregoric (Camphorated Tincture of Opium)?
a. 5 b.10 c. 25 d. 50 e. 100 2006 exam 2 q22 |
c. 25
|
|
|
During reversal of opioid overdose (e.g., coma) with naloxone, the patient should:
a. receive a sedative (e.g., benzodiazepine) to prevent potential convulsions b. be restrained to avoid possible emergence violence c. receive intravenous fluids to counteract the diarrhea that will result d. a and b e. All of the above 2006 exam 2 q23 |
b. be restrained to avoid possible emergence violence
|
|
|
Patients taking Lithium may exhibit increased plasma Lithium concentrations leading to serious side effects when concurrently taking:
a. thiazide diuretics b. NSAID’s c. osmotic diuretics d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q24 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
Lithium is contraindicated in patients with:
a. hypertension b. diabetes c. “sick sinus” syndrome d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q25 |
c. “sick sinus” syndrome
|
|
|
SSRI’s are contraindicated with:
a. dextromethorphan b. L-tryptophan c. alcohol d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q26 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
Blockade of NE reuptake:
a. phenelzine b. sertraline c. reserpine d. protriptyline e. carbamazepine and valproic acid 2006 exam 2 q27 |
d. protriptyline
|
|
|
Sensitization of postsynaptic 5HT1A receptor:
a. phenelzine b. sertraline c. reserpine d. protriptyline e. carbamazepine and valproic acid 2006 exam 2 q28 |
d. protriptyline
|
|
|
Increased concentration of cytosolic NE and 5HT:
a. phenelzine b. sertraline c. reserpine d. protriptyline e. carbamazepine and valproic acid 2006 exam 2 q29 |
a. phenelzine
|
|
|
Depletion of vesicular transmitter
a. phenelzine b. sertraline c. reserpine d. protriptyline e. carbamazepine and valproic acid 2006 exam 2 q30 |
c. reserpine
|
|
|
Downregulation/desensitization of the following receptor is thought to contribute significantly to the ultimate therapeutic effect of antidepressant drugs
a. beta receptors b. somatodendritic 5HT1a receptors c. presynaptic 5HT1b/d d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q31 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
The common side effects of TCA’s are also common side effects produced by:
a. benzodiazepines b. phenothiazines c. phenanthrenes d. a and b e. b and c 2006 exam 2 q33 |
b. phenothiazines
|
|
|
These drugs are contraindicated with type-A MAOI’s:
a. Meperidine b. fluoxetine c. pethidine d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q34 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
When patients are receiving MAOIs Facts and Comparisons recommends that they report promptly the occurrence of:
a. rash b. nausea c. headache d. blurred vision e. dizziness 2006 exam 2 q35 |
c. headache
|
|
|
This drug should be avoided in subjects with history of seizures:
a. amoxepine b. maprotiline c. bupropion d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q36 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
The half-life of this drug is 70 hours and the half-life of its active metabolite is 9-14 days
a. bupropion b. fluoxetine c. duloxetine d. amoxepine e. venlafaxin 2006 exam 2 q37 |
b. fluoxetine
|
|
|
This antidepressant drug decreases the metabolism of methadone, which increases the likelihood of withdrawal symptoms if the antidepressant drug is discontinued
a. desipramine b. sertraline c. fluvoxamine d. tranylcypromine e. selegiline 2006 exam 2 q38 |
c. fluvoxamine
|
|
|
This drug is available as a patch for treatment of clinical depression:
a. sertraline b. duloxetine c. selegiline d. tranylcypromine e. imipramine 2006 exam 2 q39 |
c. selegiline
|
|
|
Management of opioid addiction:
a. Is primarily pharmacologically based, other non-pharmacological treatments are inconsequential b. Pharmacotherapy is an adjunct – counseling and other non-pharmacological treatments constitute the primary interventions c. Is greatly enhanced when pharmacotherapy and non-pharmacological treatments are combined d. a and c e. b and c 2006 exam 2 q40 |
e. b and c
|
|
|
Empirical evidence from clinical trials shows that methadone treatment:
a. Reduces injection drug use among opioid addicts b. Improves participation in neonatal programs by women who were previously daily heroin users c. Increases the likelihood that heroin addicts will make gains in other dimensions of their lives such as employment, interpersonal relationships, and crime reduction d. All of the above e. a and c only 2006 exam 2 q41 |
d. All of the above
|
|
|
Advantage(s) of methadone in the treatment of opioid addiction:
a. It lacks cross- tolerance with other opioids b. It is effective when orally administered c. Avoidance of a reservoir in the body because it has a short half life d. It is an agonist with no abuse potential e. All of the above 2006 exam 2 q42 |
b. It is effective when orally administered
|
|
|
Which of the following distinguishes methadone from buprenorphine?
a. Methadone is an agonist, buprenorphine is an antagonist b. Methadone is a full Mu agonist, buprenorphine is a partial Mu agonist c. Methadone is approved for maintenance, buprenorphine is approved only for detoxification d. A single methadone dose provides 24-hour relief from withdrawal, buprenorphine must be administered 2 to 3 times daily 2006 exam 2 q43 |
b. Methadone is a full Mu agonist, buprenorphine is a partial Mu agonist
|
|
|
Suboxone® is a buprenorphine sublingual tablet that contains naloxone. Naloxone is present in this product to:
a. Prevent oral abuse b. Precipitate withdrawal in opioid dependent individuals who take it sublingually c. Prevent an overdose of buprenorphine if a patient takes more than the recommended dose d. Prevent intravenous abuse of buprenorphine e. a and c only 2006 exam 2 q44 |
d. Prevent intravenous abuse of buprenorphine
|
|
|
T/F: Pharmacists require special licensing to dispense a prescription for buprenorphine sublingual tablets
2006 exam 2 q45 |
False
|
|
|
T/F: A physician authorized to prescribe under the provisions of the Drug Addiction Treatment Act may prescribe any opioid for the treatment of opioid addiction
2006 exam 2 q46 |
False
|
|
|
The current status of treatment availability for opioid dependence is:
a. America has an adequate supply of treatment b. Patients in the United States can get treatment on demand c. Current treatment capacity in the U.S. is sufficient for only about 15% of current heroin addicts d. Any private practice physician in America can offer opioid pharmacotherapy for heroin addicts e. A and B only 2006 exam 2 q48 |
c. Current treatment capacity in the U.S. is sufficient for only about 15% of current heroin addicts.
|
|
|
A chronic opioid abuser with a urine test positive for morphine (indicating recent heroin use) is given a dose of Naltrexone (Trexan) for addiction treatment. What would be his/her reaction?
a. S/He would experience immediate withdrawal distress b. S/He would get a “high” c. S/He would experience relief of withdrawal but would not get “high” d. S/He would experience no effect at all 2006 exam 2 q47 |
a. S/He would experience immediate withdrawal distress
|
|
|
Which of the following explains why maintenance pharmacotherapy is good for opioid addiction but not for alcohol addiction?
a. There is no cross tolerance between alcohol and benzodiazepines b. The margin of safety remains stable as opioid tolerance increases, but narrows as alcohol tolerance increases c. Patients on methadone are less likely to abuse heroin than alcoholic patients on maintenance benzodiazepines are to abuse alcohol d. Heroin addicts are more compliant patients generally than are alcoholic patients generally 2006 exam 2 q49 |
b. The margin of safety remains stable as opioid tolerance increases, but narrows as alcohol tolerance increases
|
|
|
A 150-pound person’s blood alcohol level is determined to be 200mg% (0.200 grams%) measured by breath sample analysis 1 hour after the last drink. This person:
a. Is probably female b. Can drive safely after waiting about 3 hours c. Is legally impaired d. Can lower his or her blood level by eating a meal e. None of the above 2006 exam 2 q50 |
c. Is legally impaired
|
|
|
There is a clear gender difference in blood alcohol levels in that even at the same body weight and amount of alcohol consumption a man will have a lower BAL than a woman. Why?
a. Because testosterone increases alcohol elimination. b. Because estrogen enhances alcohol absorption. c. Because men have more alcohol dehydrogenase in their livers than women have. d. Because men have more alcohol dehydrogenase in their stomachs than women have 2006 exam 2 q51 |
d. Because men have more alcohol dehydrogenase in their stomachs than women have
|
|
|
A person enters the emergency room at midnight with a blood alcohol level of 0.200. What is the earliest that his blood alcohol level would be zero (approximately)?
a. 2:00 a.m. b. 5:00 a.m. c. 10:00 a.m. d. 12:00 noon e. midnight the next day 2006 exam 2 q52 |
c. 10:00 a.m.
|
|
|
T/F: Disulfiram (Antabuse®) blocks alcohol metabolism and causes a toxic blood alcohol level with a very small amount of ingestion.
2006 exam 2 q53 |
False
|
|
|
T/F: Alcoholic patients who take Antabuse® regularly need not be referred for 12-step support in Alcoholics Anonymous
2006 exam 2 q54 |
False
|
|
|
When considering treatment for a patient at risk for alcohol withdrawal the preferred treatment approach is:
a. Use a withdrawal assessment scale and treat signs and symptoms as they emerge b. Treat prophylactically with benzodiazepines to prevent withdrawal distress c. Use phenytoin to control seizure occurrences d. Administer anti-psychotic drugs to protect against delirium tremors (DTs) e. All of the above 2006 exam 2 q55 |
b. Treat prophylactically with benzodiazepines to prevent withdrawal distress
|
|
|
Which of the following is a suitable choice for treating alcohol withdrawal?
a. Diazepam 10 to 20mgs every 4 to 8 hours. b. Chlordiazepoxide® 5 to 10mgs every 4 to 8 hours. c. Disulfiram 250mgs every day d. Naltrexone 50mgs daily 2006 exam 2 q56 |
a. Diazepam 10 to 20mgs every 4 to 8 hours.
|
|
|
Regarding marijuana use:
a. It causes an acute and potentially fatal physical toxicity b. CB2 receptors found in parts of the brain that control vital functions are related to the toxic effects of marijuana c. THC accumulates in the brain at levels that are 5 to 10 times the level found in the blood d. Cannabinoid receptors in macrophages of the spleen & immune cells are thought to have relevance for anti-inflammatory & immunosuppressive activity e. b and d only 2006 exam 2 q57 |
d. Cannabinoid receptors in macrophages of the spleen & immune cells are thought to have relevance for anti-inflammatory & immunosuppressive activity.
|
|
|
Which of the following regarding marijuana is true?
a. high doses can cause the release of unconscious material b. five “joints” are equal to one pack of cigarettes c. causes little change in blood pressure d. only a & c e. all of the above 2006 exam 2 q58 |
d. only a & c
|
|
|
Methamphetamine and Cocaine differ in which of the following ways:
a. Methamphetamine has a longer half-life than cocaine b. Cocaine is significantly more addictive than methamphetamine c. Methamphetamine is less likely to produce paranoid psychosis d. Methamphetamine is usually snorted while cocaine is usually injected e. All of the above 2006 exam 2 q59 |
a. Methamphetamine has a longer half-life than cocaine
|
|
|
Regarding cocaine abuse:
a. The most effective clinical treatments for cocaine abuse do not involve pharmacotherapy b. Medications are clinically in use that block cocaine induced euphoria and reverse cocaine toxicity c. Tricyclic anti-depressants are effective in reversing post-cocaine withdrawal depression d. The risk for relapse to cocaine use following a binge episode is 1 to 4 weeks after the last use e. None of the above 2006 exam 2 q60 |
a. The most effective clinical treatments for cocaine abuse do not involve pharmacotherapy.
|
|
|
This antidiarrheal agent should not be administered to infants or children:
a. Paregoric b. Loperamide c. diphenoxylate d. a and b e. all of the above 2003 exam 3 q67 |
c. diphenoxylate
|
|
|
Combination of Type A-MAOIs with the following may produce hypertensive crisis:
a. tyramine b. ephedrine c. L-dopa d. a and b e. all of the above 2003 exam 3 q68 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Advantage of methadone in the treatment of opioid addiction:
a. it lacks cross-tolerance with other opioids b. it is effective when orally administered c. avoidance of a reservoir in the body because it has a short half life d. it is an agonist with no abuse potential e. all of the above 2003 exam 3 q69 |
b. it is effective when orally administered
|
|
|
Blockade of 5HT/NE transporter:
a. imipramine b. Lithium c. electroconvulsion d. phenelzine e. paroxetine 2003 exam 3 q70 |
a. imipramine
|
|
|
Causes uncoupling of receptor and G-protein:
a. imipramine b. Lithium c. electroconvulsion d. phenelzine e. paroxetine 2003 exam 3 q71 |
b. Lithium
|
|
|
Desensitization of Somatodendritic 5HT1A receptor and Presynaptic 5HT1B/D receptor
a. imipramine b. Lithium c. electroconvulsion d. phenelzine e. paroxetine 2003 exam 3 q72 |
e. Paroxetine
|
|
|
Although this opioid is widely prescribed as an analgesic, it is no more efficacious than aspirin
a. dextropropoxyphene b. butorphanol c. codeine d. a and b e. all of the above 2002 exam 3 q70 |
a. dextropropoxyphene
|
|
|
This drug combination is considered to be a rational combination in Dr. Moreton’s opioin:
a. codeine and aspirin b. pentazocine and naloxone c. diphenoxylate and atropine d. a and b e. all of the above 2002 exam 3 q71 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
The acute toxicity associated with MDMA (ecstasy) abuse is probably caused by:
a. adrenergic overstimulation b. cholinergic rebound c. appetite suppression d. serotonergic nerve degeneration 2002 exam 3 q72 |
a. adrenergic overstimulation
|
|
|
Inhibitors of MAO type A when used alone and/or in combination with other drugs or food have the potential to cause hypertensive crisis by all of the following mechanisms except:
a. prevent the metabolism of dopamine which is subsequently converted to NE b. prevent the metabolism of indirect acting sympathomimetics c. down regulate central Presynaptic alpha2 receptors that regulate central sympathetic outflow d. enhance the release of NE by tyramine e. A-type MAOIs are converted to direct acting alpha adrenergic receptor agonists (amphetamine and methamphetamine) 2001 exam 3 q70 |
e. A-type MAOIs are converted to direct acting alpha adrenergic receptor agonists (amphetamine and methamphetamine)
|
|
|
This drug is a phenothiazine analgesic which lacks dependence liability; it is contraindicated in children with flu symptoms
a. nalbuphine b. dezocine c. Tramadol d. methotrimeprazine e. buprenorphine 2001 exam 3 q71 |
d. methotrimeprazine
|
|
|
Fentanyl has a short duration of action because it:
a. is rapidly hydrolyzed b. is rapidly N-demethylated to an inactive metabolite c. is rapidly redistributed from CNS d. undergoes rapid binding to plasma proteins e. undergoes rapid renal clearance via filtration and tubular secretion 2001 exam 3 q72 |
c. is rapidly redistributed from CNS
|
|
|
Select the INCORRECT statement. When used in place of methadone in opioid maintenance treatment programs, LAAM is advantageous because it:
a. produces cross-tolerance to injected heroin b. has a longer duration of action than methadone c. is a prodrug that produces active opioid metabolites d. must not be given more than three times a week (every other day) e. will not produce respiratory depression in overdose 2001 exam 3 q73 |
e. will not produce respiratory depression in overdose
|
|
|
Addiction to cannabis:
a. is marked by compulsive use of marijuana b. is as disruptive to a person’s life as addiction to alcohol c. is not associated with physical dependence d. all of the above e. a and c only 2001 exam 3 q75 |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
The pain transmitter in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord is:
a. glutamate b. substance P c. CGRP d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 quiz 3 q1 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
A modulator of pain transmission in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord is:
a. NO b. prostaglandin c. enkephalin d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 quiz 3 q2 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
The mechanism of action of opioids to decrease pain transmission in the spinal cord is via:
a. increased K+ conductance b. decreased Ca++ conductance c. increased Cl- conductance d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 quiz 3 q3 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
Codeine has greater bioavailability than morphine because codeine:
a. Is acetylated at one of the hydroxyl groups b. is methylated at one of the hydroxyl groups c. Is N-demethylated d. has an N-allyl group e. is methylated at two hydroxyl groups 2006 quiz 3 q4 |
b. is methylated at one of the hydroxyl groups
|
|
|
The antitussive action of opioids requires activation of the:
a. Mu receptor b. kappa receptor c. delta receptor d. sigma receptor e. none of the above 2006 quiz 3 q5 |
e. none of the above
|
|
|
Naloxone (Narcan) is approved for treatment of:
a. opioid overdose b. reversal of opioid anesthesia c. treatment of alcohol dependence d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 quiz 3 q6 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
The IM or SC dose of morphine for analgesia in a naïve patient is:
a. 0.1 mg b. 1 mg c. 10 mg d. 50 mg e. 100 mg 2006 quiz 3 q7 |
c. 10 mg
|
|
|
This opioid is metabolized to an active metabolite that may produce convulsions:
a. Methadone b. Meperidine c. propoxyphene d. a and b e. b and c 2006 quiz 3 q8 |
e. b and c
|
|
|
This drug combination is an irrational strategy to discourage drug abuse:
a. diphenoxylate with atropine b. pentazocine with naloxone c. buprenorphine with naloxone d. a and b e. a and c 2006 quiz 3 q9 |
a. diphenoxylate with atropine
|
|
|
Paregoric is most often prescribed for:
a. infants and children b. nursing mothers c. the elderly d. patients allergic to opioids e. rapid metabolizers 2006 quiz 3 q10 |
a. infants and children
|
|
|
Methadone achieves its pharmacotherapeutic effect by virtue of:
a. cross-tolerance b. antagonism of the narcotic receptor c. making patients sick if they inject heroin on top of their methadone d. a and c 2006 quiz 4 q2 |
a. cross tolerance
|
|
|
Which of the following predicts the likely severity of alcohol withdrawal?
a. early onset of withdrawal b. high dose, long duration, daily alcohol use c. severe withdrawal in the past d. all of the above e. b and c only 2006 quiz 4 q4 |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
Buprenorphine abused by a methadone maintenance patient taking 100 mg/day of methadone will produce what effect?
a. the added opioid will produce euphoria b. methadone will completely block buprenorphine-induced euphoria c. the combination could induce an overdose state d. the patient will experience narcotic withdrawal distress e. the patient will experience buprenorphine induced seizures 2006 quiz 4 q5 |
d. the patient will experience narcotic withdrawal distress
|
|
|
The relatively low toxicity of marijuana in humans reflects:
a. a lack of cannabinoid receptors in vital function areas of the brain b. low potency marijuana in current street markets c. poor absorption of cannabinoids when smoked d. all of the above 2006 quiz4 q6 |
a. a lack of cannabinoid receptors in vital function areas of the brain
|
|
|
Cocaine addiction is marked by
a. extreme physical dependence b. bouts of binge and crash cycles of use c. low psychological dependence d. few negative consequences on one’s social functions 2006 quiz 4 q7 |
b. bouts of binge and crash cycles of use
|
|
|
Which of the following best describes the state of pharmacological treatments for cocaine addiction?
a. most antidepressants are effective b. only SSRI antidepressants have been shown to be effective in reversing cocaine rebound depression c. effective dopamine receptor blocking agents are clinically in use d. effective pharmacotherapy for cocaine addiction has been elusive 2006 quiz4 q8 |
d. effective pharmacotherapy for cocaine addiction has been elusive
|
|
|
The treatment of choice for exogenous depression is:
a. ECS b. TCA c. MAOI d. Lithium e. benzodiazepine 2006 quiz 5 q1 |
e. benzodiazepine
|
|
|
Subjects with bipolar disorder respond best to:
a. carbamazepine b. phenelzine c. reboxetine d. imipramine 2006 quiz 5 q2 |
a. carbamazepine
|
|
|
The acute effects of antidepressant drugs depend mainly upon elevation of synaptic concentration of:
a. norepinephrine b. serotonin c. dopamine d. a and b e. b and c 2006 quiz 5 q3 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
The therapeutic effect of antidepressant drugs is thought to depend ultimately upon action of:
a. BDNF b. glutamate c. cortisol d. IP3/DAG e. GABA 2006 quiz 5 q4 |
a. BDNF
|
|
|
The common side effects of TCAs are also common side effects produced by:
a. benzodiazepines b. phenothiazines c. phenanthrenes d. a and b e. b and c 2006 quiz 5 q5 |
b. phenothiazines
|
|
|
The most dangerous drug class in acute overdose is:
a. MAOIs b. SSRIs c. TCAs 2006 quiz 5 q6 |
c. TCAs
|
|
|
This drug is contraindicated with aged cheese, aged sausage and Chianti wine:
a. reboxetine b. sertraline c. imipramine d. tranylcypromine e. moclobemide 2006 quiz 5 q7 |
d. tranylcypromine
|
|
|
These drugs are contraindicated with type-A MAOIs:
a. Meperidine b. fluoxetine c. pethidine d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 quiz 5 q8 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Downregulation/desensitization of the following receptor is thought to contribute significantly to the ultimate therapeutic effect of antidepressant drugs:
a. beta receptors b. Somatodendritic 5HT1A receptors c. postsynaptic 5HT1A receptors d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 quiz 5 q9 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
A cardinal sign of the “Serotonin Syndrome” is:
a. hyperthermia b. cerebral edema c. acute liver failure d. acute renal failure e. convulsions 2006 quiz 5 q10 |
a. hyperthermia
|
|
|
The so-called “cheese effect” results from blockade of Type-A MAO in the:
a. gut b. liver c. sympathetic nerve d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 quiz 5 q11 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
Regardless of the pharmacotherapeutic agent employed, the onset of clinical efficacy of antidepressant drugs is usually:
a. 2-3 days b. 2-3 weeks c. 2-3 months d. 2 days to 2 weeks e. 2 weeks to 2 months 2006 quiz 5 q12 |
b. 2-3 weeks
|
|
|
Which of the following regarding marijuana is true?
a. high doses can cause the release of unconscious material b. three joints are equal to one pack of cigarettes c. causes little change in blood pressure d. a and c e. all of the above 2003 quiz 4 q1 |
d. a and c
|
|
|
Ecstasy is:
a. a schedule I drug b. heightens male sexual response c. causes long-term decreases in 5-HT d. a and c e. all of the above 2003 quiz 4 q2 |
d. a and c
|
|
|
Evidence shows that ecstasy causes:
a. decreased impulsivity b. poor memory of past information c. no effect on memory of new information d. b and c e. all of the above 2003 quiz 4 q3 |
d. b and c
|
|
|
Which of the following regarding buprenorphine is true?
a. its effects on cAMP are stronger than other opiates creating more intense withdrawal distress b. buprenorphine is metabolized by the kidneys and may accumulate in patients with renal failure c. buprenorphine is a more potent antagonist than naloxone d. only exhibits agonist activity 2003 quiz 4 q4 |
c. Buprenorphine is a more potent antagonist than naloxone
|
|
|
Regarding ultra-rapid detoxification from heroin:
a. naloxone is given to precipitate withdrawal b. the process takes about 3 days c. patients receive general anesthesia d. patients are discharged with prescriptions for buprenorphine e. a and c 2003 quiz 4 q5 |
e. a and c
|
|
|
During alcohol withdrawal:
a. the risk of intention tremors occurs at 18-36 hours b. the risk of seizure is greatest at 18-36 hours c. short acting agents are preferred over long-acting agents d. lorazepam should be administered in doses of 10 mg q6h x 4 doses, then 5 mg q6h x 8 doses e. a and d 2003 quiz 4 q7 |
b. the risk of seizure is greatest at 18-36 hours
|
|
|
Acute effects of cocaine can cause:
a. systemic vasodilation when snorted b. stroke c. increased blood pressure due to arteriolar constriction d. enlarges nasal polyps 2003 quiz 4 q8 |
b. stroke
|
|
|
“Kindling” with regard to cocaine is when:
a. psychosis becomes more probable b. seizure risk is increased c. crash phase begins d. all of the above e. a and b 2003 quiz 4 q9 |
e. a and b
|
|
|
The JAMA evidence-based practice guidelines for alcohol withdrawal concludes that:
a. beta blockers and clonidine are effective as monotherapy b. benzodiazepines are suitable for treating alcohol withdrawal c. treatment medication should be dosed individually d. neuroleptics are suitable as monotherapy as well as adjunct e. b and c 2003 quiz 4 q10 |
e. b and c
|
|
|
Metabolic transformation of morphine is by:
a. glucuronidation b. N-demethylation c. hydrolysis d. hydroxylation e. all of the above 2003 quiz 5 q1 |
a. glucuronidation
|
|
|
The analgesic action of full agonists is dependent mainly upon ___ receptors while the analgesic action of partial agonists is dependent mainly upon ___ receptors.
a. mu, kappa b. mu, delta c. delta, kappa d. mu, sigma e. kappa, sigma 2003 quiz 5 q3 |
a. mu, kappa
|
|
|
Codeine has higher oral bioavailability than morphine because codeine has a:
a. 3-methyl b. 6-glucuronide c. N-allyl d. 6-hydroxy e. 3-acetyl 2003 quiz 5 q4 |
a. 3-methyl
|
|
|
An overdose of this opioid may be associated with convulsions because it is metabolized to a normetabolite:
a. propoxyphene b. Meperidine c. pentazocine d. a and b e. all of the above 2003 quiz 5 q5 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
The following combinations of drugs represent a rational combination according to Dr. Moreton’s opinion:
a. pentazocine and naloxone b. Fentanyl and droperidol c. diphenoxylate and atropine d. a and b e. none of the above 2003 quiz 5 q6 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
The following opioids have a so-called “floor effect” (Dr. Moreton’s term for limited effect) on respiration:
a. butorphanol b. nalbuphine c. buprenorphine d. a and b e. all of the above 2003 quiz 5 q7 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Teenagers often abuse this opioid because it can be purchased at your pharmacy without a prescription:
a. codeine b. paregoric c. loperamide d. dextromethorphan e. diphenoxylate with atropine 2003 quiz 5 q8 |
d. dextromethorphan
|
|
|
The principal long-term receptor effects of MAOIs include:
a. desensitization of Somatodendritic 5HT1A receptors b. Desensitization of Presynaptic alpha2 receptors c. desensitization of postsynaptic 5HT1A receptors d. a and b e. all of the above 2003 quiz 5 q9 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
The principal long-term receptor effects of SSRIs include:
a. desensitization of Somatodendritic 5HT1A receptors b. Desensitization of Presynaptic 5HT1B/D receptors c. Downregulation/desensitization of Presynaptic 5HT2 transporter d. a and b e. all of the above 2003 quiz 5 q10 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
Blockade of 5HT/NE transporter:
a. imipramine b. lithium c. electroconvulsion d. phenelzine e. paroxetine 2003 quiz 6 q1 |
a. imipramine
|
|
|
Causes uncoupling of receptor and G-protein:
a. imipramine b. lithium c. electroconvulsion d. phenelzine e. paroxetine 2003 quiz 6 q2 |
b. Lithium
|
|
|
Desensitization of Somatodendritic 5HT1A receptor and Presynaptic 5HT1B/D receptor:
a. imipramine b. lithium c. electroconvulsion d. phenelzine e. paroxetine 2003 quiz 6 q3 |
e. paroxetine
|
|
|
Sensitizes postsynaptic 5HT1A receptor and down-regulates beta1 receptor:
a. imipramine b. lithium c. electroconvulsion d. phenelzine e. paroxetine 2003 quiz 6 q4 |
a. imipramine
|
|
|
The receptor-mediated action of opioids at the neuron is due to:
a. opening of K+ channels b. closing of Ca++ channels c. increasing cAMP d. decreasing cAMP e. all of the above 2002 quiz 4 q1 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Opioid receptor that mediates the action of opioids:
a. mu b. kappa c. delta d. sigma e. a, b, and c 2002 quiz 4 q2 |
e. a, b and c
|
|
|
Endogenous opioid peptides:
a. endorphins b. enkephalins c. dynorphins d. substance P e. a, b, and c 2002 quiz 4 q3 |
e. a, b and c
|
|
|
Full agonist analgesic:
a. naltrexone b. buprenorphine c. Meperidine d. dextromethorphan e. naloxone 2002 quiz 4 q4 |
c. Meperidine
|
|
|
Partial agonist analgesic with floor effect on respiration:
a. Fentanyl b. buprenorphine c. Meperidine d. dextromethorphan e. naloxone 2002 quiz 4 q5 |
b. buprenorphine
|
|
|
Pure antagonist:
a. Fentanyl b. buprenorphine c. Meperidine d. dextromethorphan e. naloxone 2002 quiz 4 q6 |
e. naloxone
|
|
|
High potency agonist:
a. Fentanyl b. buprenorphine c. Meperidine d. dextromethorphan e. naloxone 2002 quiz 4 q7 |
a. Fentanyl
|
|
|
Antitussive which teens may abuse:
a. Fentanyl b. buprenorphine c. Meperidine d. dextromethorphan e. naloxone 2002 quiz 4 q8 |
d. dextromethorphan
|
|
|
Rational or irrational combination?
Fentanyl and droperidol 2002 quiz 4 q9 |
rational
|
|
|
Rational or irrational combination?
diphenoxylate and atropine 2002 quiz 4 q10 |
irrational
|
|
|
Rational or irrational combination?
codeine and acetaminophen 2002 quiz 4 q11 |
rational
|
|
|
Rational or irrational combination?
pentazocine and naloxone 2002 quiz 4 q12 |
rational
|
|
|
When a maintenance drinker (physically dependent) stops alcohol use, how quickly does the blood alcohol concentration fall?
a. roughly 10 mgs% per hour b. Roughly 20 mgs% per hour c. Roughly 40 mgs% per hour d. quickly because the elimination half life of ethanol is only about 2 hours 2002 quiz 5 q1 |
b. Roughly 20 mgs% per hour
|
|
|
What is the risk for Delirium Tremens (DTs) in untreated alcohol withdrawal?
a. less than 5% b. 5 to 7% c. 10 to 15% d. 20 to 25% e. over 25% 2002 quiz 5 q2 |
b. 5 to 7%
|
|
|
Which of the following is a suitable choice for treating alcohol withdrawal?
a. diazepam 10-20mg q4-8 hr b. chlordiazepoxide 10-20mg q4-8 hr c. disulfiram 250mg every day d. naltrexone 50mg daily 2002 quiz 5 q4 |
a. diazepam 10-20mg q4-8hr
|
|
|
Effective pharmacotherapy for cocaine abusers includes which of the following?
a. antidepressants to reduce the intensity of the crash phase of withdrawal b. alcohol use to reduce agitation during the intoxication c. naloxone to reverse the effects of toxic overdose d. all of the above e. none of the above 2002 quiz 5 q5 |
e. none of the above
|
|
|
What forces are fueling the current increase in heroin use?
a. increased purity b. change from injection to snorting (intranasal) as a major route of administration c. increased experimentation by adolescents in rural counties d. all of the above e. none of the above 2002 quiz 5 q6 |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
What is the approximate cost savings when a single heroin addict stops using heroin and enrolls in a methadone maintenance program?
a. about $1,000 to $2,000 per year b. about $5,000 to $10,000 per year c. about $15,000 to $20,000 per year d. about $30,000 to $50,000 per year 2002 quiz 5 q7 |
c. about $15,000 to $20,000 per year
|
|
|
KEY:
I. down-regulation or desensitization of 5HT1A Somatodendritic receptor II. Desensitization of 5HT1B/D receptor III. Down-regulation of alpha2 presynaptic receptor IV. Down-regulation of beta1 receptor V. Sensitization of postsynaptic 5HT1A receptor SSRI: a. I, II b. I, III c. I, II, III d. IV, V 2002 quiz 6 q1 |
a. I, II
|
|
|
KEY:
I. down-regulation or desensitization of 5HT1A Somatodendritic receptor II. Desensitization of 5HT1B/D receptor III. Down-regulation of alpha2 presynaptic receptor IV. Down-regulation of beta1 receptor V. Sensitization of postsynaptic 5HT1A receptor MAOI: a. I, II b. I, III c. I, II, III d. IV, V 2002 quiz 6 q2 |
b. I, III
|
|
|
KEY:
I down-regulation or desensitization of 5HT1A Somatodendritic receptor II Desensitization of 5HT1B/D receptor III Down-regulation of alpha2 presynaptic receptor IV Down-regulation of beta1 receptor V Sensitization of postsynaptic 5HT1A receptor TCA: a. I, II b. I, III c. I, III, V d. III, IV, V 2002 quiz 6 q3 |
d. III, IV, V
|
|
|
Match the potentially serious drug-drug interaction. Meperidine leading to serotonin syndrome:
a. tranylcypromine b. imipramine c. fluoxetine d. Lithium Chloride 2002 quiz 6 q4 |
a. tranylcypromine
|
|
|
Match the potentially serious drug-drug interaction. Dextromethorphan leading to NMS-like syndrome:
a. tranylcypromine b. imipramine c. fluoxetine d. Lithium Chloride 2002 quiz 6 q5 |
a. tranylcypromine
|
|
|
Match the potentially serious drug-drug interaction. L-Tryptophan leading to serotonin syndrome:
a. tranylcypromine b. imipramine c. fluoxetine d. Lithium Chloride 2002 quiz 6 q6 |
a. tranylcypromine
|
|
|
Match the potentially serious drug-drug interaction. Thiazide diuretics leading to a paradoxical decreased renal clearance of this drug:
a. tranylcypromine b. imipramine c. fluoxetine d. Lithium Chloride 2002 quiz 6 q7 |
d. Lithium Chloride
|
|
|
Match the potentially serious drug-drug interaction. Clonidine leading to hypertensive crisis:
a. tranylcypromine b. imipramine c. fluoxetine d. Lithium Chloride 2002 quiz 6 q8 |
b. imipramine
|
|
|
Match the potentially serious drug-drug interaction. Ephedrine leading to hypertensive crisis:
a. tranylcypromine b. imipramine c. fluoxetine d. Lithium Chloride 2002 quiz 6 q9 |
a. tranylcypromine
|
|
|
Morphine is metabolized mainly by:
a. N-demethylation b. 3-O-methylation c. glucuronidation d. ester hydrolysis e. 3,6-O-sulfation 2005 exam 2 q3 |
c. glucuronidation
|
|
|
What is the metabolic step by which codeine is inactivated or activated?
a. glucuronidation b. O-Demethylation to active hydroxyl metabolite c. N-Demethylation to active metabolite d. N-Demethylation to inactive metabolite e. ester hydrolysis 2005 exam 2 q4 |
b. O-Demethylation to active hydroxyl metabolite
|
|
|
What is the metabolic step by which remifentanil is inactivated or activated?
a. glucuronidation b. O-Demethylation to active hydroxyl metabolite c. N-Demethylation to active metabolite d. N-Demethylation to inactive metabolite e. ester hydrolysis 2005 exam 2 q5 |
e. ester hydrolysis
|
|
|
What is the metabolic step by which methadone is inactivated or activated?
a. glucuronidation b. O-Demethylation to active hydroxyl metabolite c. N-Demethylation to active metabolite d. N-Demethylation to inactive metabolite e. ester hydrolysis 2005 exam 2 q6 |
d. N-Demethylation to inactive metabolite
|
|
|
What is the metabolic step by which meperidine is inactivated or activated?
a. glucuronidation b. O-Demethylation to active hydroxyl metabolite c. N-Demethylation to active metabolite d. N-Demethylation to inactive metabolite e. ester hydrolysis 2005 exam 2 q7 |
c. N-Demethylation to active metabolite
|
|
|
Identify the agents effective in treatment of opioid overdose:
a. naloxone b. nalmephene c. ipecac d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q8 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
Tolerance develops to the following effects of opioids:
a. respiratory depression b. pupillary constriction c. constipation d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q9 |
a. respiratory depression
|
|
|
Higher than recommended therapeutic doses of this drug may produce psychotomimetic effects:
a. pentazocine b. nalbuphine c. dextromethorphan d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q12 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
This opioid will precipitate abstinence when administered to patients taking high doses of morphine or methadone:
a. nalbuphine b. butorphanol c. buprenorphine d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q13 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
A sustained release preparation of an opioid that is currently widely abused is:
a. dextromethorphan b. oxycodone c. hydrocodone d. hydromorphine e. a and b 2005 exam 2 q14 |
b. oxycodone
|
|
|
In patients with renal disease, chronic administration of this drug may lead to convulsions because of production of the normetabolite:
a. Meperidine b. dextromethorphan c. methadone d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q15 |
a. meperidine
|
|
|
This drug behaves as a partial agonist:
a. nalorphine b. nalbuphine c. butorphanol d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q16 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
A pharmacist received a prescription for DTO 0.7 mL PO q4h for baby Smith for opiate withdrawal resulting from birth to an opiate-dependent mother. What product would you dispense?
a. diluted tincture of opium b. deodorized opium tincture c. camphorated opium tincture d. paregoric e. none of the above 2005 exam 2 q17 |
e. none of the above
|
|
|
The transmitter whose release is decreased by morphine is:
a. substance P b. bradykinin c. serotonin d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q18 |
a. substance P
|
|
|
Select the INCORRECT statement. The action of enkephalin or morphine may decrease pain transmission via action on the Presynaptic mu receptor to cause it to:
a. open K+ channels b. close Ca++ channels c. dimerize with kappa or delta receptors d. uncouple from Gs protein e. inhibit adenylyl cyclase via Gi protein 2005 exam 2 q19 |
d. uncouple from Gs protein
|
|
|
This drug is a phenothiazine analgesic that lacks dependence liability; it is contraindicated in children with flu symptoms:
a. nalbuphine b. methotrimeprazine c. buprenorphine d. fentanyl e. tramadol 2005 exam 2 q20 |
b. methotrimeprazine
|
|
|
Experimental animal findings with antidepressants that correlate with their clinical efficacy are:
a. reversal of reserpine-induced “depression” b. reversal of forced-swim learned helplessness c. anticonvulsant activity in electroshock-induced seizures d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q21 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
Over the years, TCAs have been largely replaced with SSRIs because:
a. SSRIs produce a response in a greater proportion of the population b. SSRIs are more efficacious than TCAs in those patients who respond to SSRIs c. SSRIs are generally safer and produce fewer serious side effects than TCAs d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q22 |
c. SSRIs are generally safer and produce fewer serious side effects than TCAs
|
|
|
Subjects taking SSRIs should avoid:
a. dextromethorphan b. tyramine c. meperidine d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q23 |
a. dextromethorphan
|
|
|
The following are approved for bipolar disorder EXCEPT:
a. lithium b. valproate c. carbamazepine d. duloxetine e. c and d 2005 exam 2 q24 |
d. duloxetine
|
|
|
Blockade of NE reuptake:
a. tranylcypromine b. citalopram c. reserpine d. reboxetine e. lithium 2005 exam 2 q25 |
d. reboxetine
|
|
|
Inhibition of 5HT reuptake:
a. tranylcypromine b. citalopram c. reserpine d. reboxetine e. lithium 2005 exam 2 q26 |
b. citalopram
|
|
|
Increased concentration of cytosolic NE and 5HT:
a. tranylcypromine b. citalopram c. reserpine d. reboxetine e. lithium 2005 exam 2 q27 |
a. tranylcypromine
|
|
|
Depletion of vesicular transmitter:
a. tranylcypromine b. citalopram c. reserpine d. reboxetine e. lithium 2005 exam 2 q28 |
c. reserpine
|
|
|
MAO-A inhibitors may produce hypertensive crisis when patients taking them ingest foods or drugs containing:
a. tyramine b. ephedrine c. L-tryptophan d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q30 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
MAO-A inhibitors may produce the “Serotonin Syndrome” or neuroleptic malignant-like syndrome when given in combination with:
a. SSRIs b. TCAs c. meperidine d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q31 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
TCAs are problematic for patients with:
a. history of seizures b. urinary retention c. glaucoma d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q33 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Bupropion should not be prescribed to patients with:
a. agranulocytosis b. bulimia c. porphyria d. cardiac arrhythmias e. paralytic ileus 2005 exam 2 q34 |
b. bulimia
|
|
|
Venlafaxine is a good addition to the antidepressant armamentarium because it:
a. exhibits relatively few side effects due to lack of binding affinity for monoamine receptors b. lacks sensitivity for inhibition of NE and 5HT reuptake like many of the TCAs c. in overdose cases, lacks the cardiac toxicity seen with overdoses of TCAs d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 35 |
d. a and b
|
|
|
All of the following EXCEPT ___ may account for the therapeutic action of lithium:
a. decreases DAG formation b. decreases IP turnover c. decreases cAMP formation d. inhibits NE-sensitive adenylyl cyclase e. inhibits 5HT-sensitive adenylyl cyclase 2005 exam 2 36 |
e. inhibits 5HT-sensitive adenylyl cyclase
|
|
|
All of these maneuvers produce demonstrable improvement in depressed patients except:
a. sleep deprivation for one night b. electroconvulsive shock c. hypothermia-induced hibernation d. transcranial electromagnetic stimulation e. c and d 2005 exam 2 37 |
e. c and d
|
|
|
Methadone maintenance works by:
a. keeping the addict “high” therby satisfying the psychological drive for intoxication b. creating cross tolerance to opioids therby reducing the reinforcing effect of heroin use c. blocking narcotic receptors thus making agonist effects difficult to achieve d. all of the above e. a and b 2005 exam 2 q39 |
b. creating cross tolerance to opioids, thereby reducing the reinforcing effect of heroin use
|
|
|
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act passed by the US Congress in 2000 authorizes:
a. any physician to prescribe any opiate for the treatment of opioid dependence b. any physician to dispense buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid dependence c. Specially trained physicians to prescribe certain buprenorphine formulations for the treatment of opioid dependence d. Any pharmacist to dispense buprenorphine prescribed by an authorized physician for the treatment of opioid dependence e. c and d 2005 exam 2 q41 |
e. c and d
|
|
|
Suboxone is a buprenorphine sublingual tablet that contains naloxone. Naloxone is present in this product to:
a. prevent oral abuse b. precipitate withdrawal in opioid-dependent individuals who take it sublingually c. prevent an overdose of buprenorphine if a patient takes more than the recommended dose d. prevent intravenous abuse of buprenorphine e. a and c 2005 exam 2 q42 |
d. prevent intravenous abuse of buprenorphine
|
|
|
T/F: Disulfiram (Antabuse) blocks alcohol metabolism and causes a toxic blood alcohol level with a very small amount of ingestion
2005 exam 2 q43 |
false
|
|
|
T/F: Alcoholic patients who take Antabuse regularly are highly motivated and not in need of other non-pharmacological treatments
2005 exam 2 q44 |
false
|
|
|
The effect of alcohol on neuronal transmission:
a. depresses the activity of all excitable tissue b. makes nerve cells more resistant to firing c. alters chloride, calcium, and sodium flux d. all of the above e. a and c 2005 exam 2 q45 |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
Which of the following is(are) a risk factor(s) for the development of delirium tremens (DTs)?
a. binge drinking b. past experience of DTs c. blackouts when drinking d. drinking despite known adverse consequences e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q47 |
b. past experience of DTs
|
|
|
In general, which of the following principles accurately guide the selection of pharmacotherapy of alcohol withdrawal:
a. long-acting agents contribute to a smoother withdrawal with fewer rebound symptoms b. short acting agents may have a lower risk of oversedation c. long acting agents are less effective in preventing withdrawal distress d. all of the above e. a and b 2005 exam 2 q49 |
e. a and b
|
|
|
Antabuse (disulfiram) and ReVia (naltrexone):
a. cause discomfort when patients drink alcohol b. reduce the risk of relapse to alcohol use when taken compliantly c. have good records of patient adherence for up to 12 months of outpatient prescription therapy d. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q52 |
b. reduce the risk of relapse to alcohol use when taken compliantly
|
|
|
T/F: Marijuana smoke contains more tar and carcinogenic material than cigarette smoke
2005 exam 2 q53 |
true
|
|
|
T/F: since marijuana produces no physical dependence, addiction to marijuana is practically nonexistent
2005 exam 2 q54 |
false
|
|
|
Pharmacologically, cannabis differs from depressants and stimulants in which of the following ways:
a. the contribution to the drug effect of “set” and “setting” are sustained throughout the dose/effect curve b. toxicity is mainly related to behavior rather than overt effects on vital functions c. specific receptors have not been identified to explain its pharmacologic effect d. all of the above e. a and b 2005 exam 2 q55 |
e. a and b
|
|
|
Which of the following is untrue regarding MDMA?
a. has been shown in animal models to produce serotonergic nerve damage b. is a natural product derived from tropical fungi c. has been shown in human studies to produce serotonergic nerve damage d. is associated with fatal toxicity from hyperthermia and kidney failure 2005 exam 2 q56 |
b. is a natural product derived from tropical fungi
|
|
|
Based on the pharmacological effect of cocaine and the “amine depletion” theory of post-cocaine withdrawal depression,
a. like opioid abusers, cocaine abusers can avoid fatigue and other rebound effects by continuing high dose administration b. therapists should expect a robust anti-depressant response to most antidepressants c. therapists can predict a natural gradual return to normal mood only after the brain has replenished its presynaptic amine stores d. all of the above e. a and c 2005 exam 2 q57 |
c. therapists can predict a natural gradual return to normal mood only after the brain has replenished its presynaptic amine stores
|
|
|
Effective pharmacotherapy for cocaine abusers include(s) which of the following:
a. antidepressants to reduce the intensity of the crash phase of withdrawal b. alcohol use to reduce agitation during the intoxication c. naloxone to reverse the effects of toxic overdose d. all of the above e. none of the above 2005 exam 2 q58 |
e. none of the above
|
|
|
Regarding cocaine abuse:
a. medications are clinically in use that block cocaine-induced euphoria and reverse cocaine toxicity b. tricyclic antidepressants are effective in reversing post-cocaine withdrawal depression c. there is no effective pharmacotherapy treatment for cocaine abuse d. 6-10 weeks after the last use of cocaine, addicts are at high risk of relapse e. c and d 2005 exam 2 q59 |
e. c and d
|
|
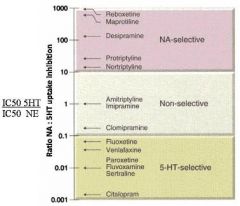
From the figure above, one can conclude that:
a. imipramine and desipramine are low potency blockers of the NE and 5HT transporter b. among the NE reuptake blockers, reboxetine is the most selective c. of all the drugs listed, citalopram is the lease efficacious d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q32 |
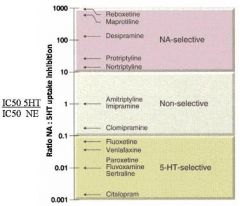
b. among the NE reuptake blockers, reboxetine is the most selective
|
|
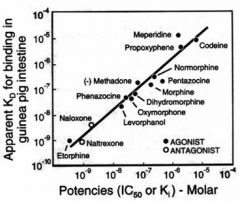
MOUSE HOT PLATE ANALGESIA
This graph demonstrates that: a. all opioids are potent antidiarrheal agents b. all opioid antagonists are more potent than opioid agonists c. there is a high correlation between in vitro and in vivo opioid activity d. a and b e. all of the above 2005 exam 2 q1 |
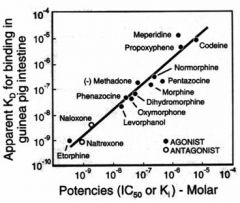
c. there is a high correlation between in vitro and in vivo opioid activity
|
|
|
A person who develops physical dependence as a result of continued prescription narcotic use for analgesia:
a. is addicted and should be referred to an addiction treatment center b. is chemically dependent and needs to see a psychiatrist for assessment c. is physically dependent but not addicted d. is addicted but not psychologically dependent 2007 exam 3 q77 |
c. is physically dependent but not addicted
|
|
|
Subjects taking irreversible type MAOIs should avoid:
a. tyramine b. L-tryptophan c. ephedrine d. dextromethorphan e. all of the above 2006 exam 3 q71 |
c. ephedrine
|
|
|
Patients with bipolar disorder may benefit from administration of:
a. lithium carbonate b. carbamazepine c. valproate d. a and b e. all of the above 2006 exam 3 q72 |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Disulfiram blocks what enzyme as its primary mechanism of action?
a. aldehyde dehydrogenase b. glutamic acid decarboxylase c. alcohol dehydrogenase d. choline acetyltransferase e. adenylyl cyclase 2005 exam 3 q73 |
a. aldehyde dehydrogenase
|
|
|
The pathophysiology of neuropathic pain includes which of the following?
a. It is an injury to either the peripheral or central nervous system b. It may occur in the absence of ongoing tissue damage c. It is mediated in the central nervous system by cyclic AMP d. Both A and B US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q1 |
d. both a and b
|
|
|
Pain symptoms characteristic of neuropathy may be reported by the patient as:
a. burning b. tingling c. stabbing d. all of the above US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q2 |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
The treatment of neuropathic pain requires a multidisciplinary approach. Physical rehabilitation for the patient is important for which of the following reasons?
a. rehabilitation assists the patient in carrying out activities of daily living b. the patient will be able to avoid the use of opioids c. rehabilitation provides a cure for the neuropathic pain syndrome d. the physical therapist will find employment for the patient US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q3 |
a. rehabilitation assists the patient in carrying out activities of daily living
|
|
|
The multidisciplinary team identifies and treats which of the following problems associated with neuropathic pain?
a. depression b. sleep disturbances c. substance abuse d. all of the above US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q4 |
d. all of the above
|
|
|
Management strategies for treating the patient with neuropathy include which of the following?
a. using high-dose acetaminophen b. informing the patient that a pain-free condition may not be achieved c. using opioids only on an “as needed” basis d. following up on the treatment plan with only the primary care physician US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q5 |
b. informing the patient that a pain-free condition may not be achieved
|
|
|
Methadone is an opioid useful in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Each of the following is true except:
a. Methadone has been proven in many clinical trials to be superior in producing pain relief compared with the tricyclic antidepressants b. Methadone is a N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist c. Caution is advised in converting the patient from an existing opioid to methadone d. Side effects include nausea and constipation US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q6 |
a. Methadone has been proven in many clinical trials to be superior in producing pain relief compared with the tricyclic antidepressants
|
|
|
Which of the following relates to interventional or invasive therapies for the treatment of neuropathic pain?
a. Epidural and intrathecal use of clonidine b. Chemical neurolysis using polyethylene glycol c. They have a limited role as therapies, providing only short- to medium-term pain relief d. Both A and C US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q7 |
d. Both A and C
|
|
|
Dosing of tramadol in the treatment of neuropathic pain is to be titrated up to:
a. 100 to 1,000 mg/day b. 100 to 400 mg/day c. 400 mg three times a day d. 400 mg every six hours US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q8 |
b. 100 to 400 mg/day
|
|
|
Underlying etiologies associated with neuropathic pain may include which of the following?
a. Phantom limb pain b. Ischemia due to peripheral vascular disease c. Nerve compression due to tumor growth d. All of the above US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q9 |
d. All of the above
|
|
|
Pain that is stimulus-independent and triggered by light touch or a nonpainful stimulus is referred to as:
a. Hyperalgesia b. Paresthesia c. Allodynia d. Mu receptor-dependent US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q10 |
c. Allodynia
|
|
|
Which of the following medications is/are FDA approved for postherpetic neuralgia?
a. Gabapentin b. Amitriptyline c. Lidocaine patch 5% d. Both A and C US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q11 |
d. Both A and C
|
|
|
Which of the following agents is indicated for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia?
a. Topiramate b. Gabapentin c. Carbamazepine d. Phenytoin US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q12 |
c. Carbamazepine
|
|
|
The maximum number of lidocaine 5% patches that should be applied at one time is:
a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q13 |
b. 3
|
|
|
Which of the following antidepressants is most effective in the treatment of neuropathic pain?
a. Amitriptyline b. Fluoxetine c. Paroxetine d. Citalopram US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q14 |
a. Amitriptyline
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is true regarding the role of serotonin reuptake inhibitors in neuropathic pain?
a. Serotonin reuptake inhibitors are more effective than tricyclic antidepressants b. Serotonin reuptake inhibitors are better tolerated than tricyclic antidepressants c. All serotonin reuptake inhibitors work by affecting levels of norepinephrine and serotonin d. None of the above US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q15 |
b. Serotonin reuptake inhibitors are better tolerated than tricyclic antidepressants
|
|
|
Approximately what percentage of the US population is affected by neuropathic pain?
a. 1.5% b. 3% c. 5% d. 10% US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q16 |
a. 1.5%
|
|
|
Which of the following tricyclic antidepressants has demonstrated benefit for central post-stroke pain?
a. Amitriptyline b. Imipramine c. Nortriptyline d. Doxepin US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q17 |
a. Amitriptyline
|
|
|
Dosage adjustments of gabapentin may be necessary in which of the following situations or populations?
a. The elderly b. Renal impairment c. Hepatic impairment d. Both A and B US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q18 |
b. renal impairment
|
|
|
Each of the following is true regarding central neuraxial therapy except:
a. It is the administration of a drug into the epidural or intrathecal space b. Baclofen is effective for the treatment of phantom limb pain when administered intrathecally c. Very high doses of morphine are required for intrathecal administration d. Morphine may be administered intrathecally US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q19 |
c. Very high doses of morphine are required for intrathecal administration
|
|
|
Opioids are recommended for patients whose neuropathic pain is considered to be:
a. Mild to moderate b. Moderate c. Moderate to severe d. Intermittent US pharmacist neuropathic pain quiz q20 |
c. Moderate to severe
|

