![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Oculomotor does what
|
Pupillary sphincter (parasump), levator palpebrae, sup / med, inf rectus, inf oblique (elevation and abduction)
|
|
|
Trochlear does what
|
Superior oblique (abducts and depresses)
|
|
|
Abducens does what
|
motor to lateral rectus
|
|
|
Trigeminal Opthalmic
|
Sensory to dorehead, conjunctiva, upper eyelid
|
|
|
Trigeminal maxillary
|
sensory to lower eyelid, cheek, upper teeth, hard palate
|
|
|
Trigeminal mandibular
|
Sensory to skin over jaw and temple, ant 2/3 tongue, motor to muscles of mastication
|
|
|
Facial nerve
|
facial expression, taste to anterior 2/3, secretomotor
|
|
|
Facial goes through
|
internal acoustic meatus
|
|
|
Vestibulocochlear
|
Internal acoustic meatus
|
|
|
Glossopharyngeal
|
Sensory to orthopharynx, secretomotor to parotid
|
|
|
Vagus
|
Motor to palate, pharynx, larynx, sensory to larynx and resp, fore- and midgut GI tract below airway; parasympathetic to foregut and midgut thoracic and most abdominal viscera; somatic sensory to external acoustic meatus
|
|
|
Accessory
|
Sternomastoid and trapezius
|
|
|
Hypoglossal
|
Tongue
|
|
|
Four air sinuses
|
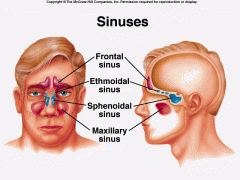
|
|
|
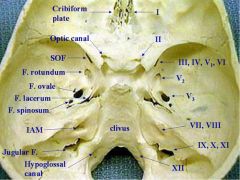
Distribution of cranial nerves through skull, names of foraminae
|
1 / 2 / 3, 4, 5a, 6 / b / c / 7, 8 / 9, 10, 11 / 12
Crib / Optic canal / SOF / Rotundum / Ovale / IAM / Jug foramen / Hypoglossal canal COSplayers ROw In Joggers and Heels |
|
|
|
|
|
From outside of skull to inside:
|
Skull, Periostrum, bone, dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
|
|
|
Foramen spinosum
|
Middle meningeal artery
|
|
|
Jugular foramen
|
4, 5a, 6 and internal jugular vein
|
|
|
foramen magnum
|
spinal cord, vertebral artery
|
|
|
carotid canal
|
carotid artery and symp plexus
|
|
|
sup and inf orbital fissures
|
opthalmic veins as well as 3/4/5a/6
|
|
|
IAM
|
7, 8, laberynthine artery
|
|
|
Basics of the circle of willis
|
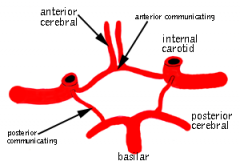
|
|
|
Lacrinal gland innervated by
|
parasymp facial nerve
|
|
|
Blink reflex
|
Opthalmic nerve
|
|
|
Blink, afferent and efferent, muscle
|
afferent - opthalmic. Efferent - facial to orbicularis oculi
|
|
|
What is cornea, what is schlera?
|
Cornea is covering of eye at iris, schlera is covering everywhere else
|
|
|
Directions of gaze
|
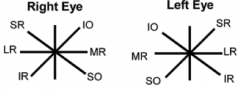
|
|
|
Where do opthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular divisions of V. C2-C4 supplies where?
|
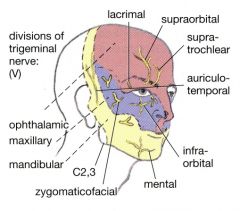
|
|
|
Forehead block
|
infiltration above the line of the eyebrows, from the midline, to just lateral to the mid-pupillary line.
|
|
|
Infraorbital nerve block
|
The approach is a line that runs between the first and second premolars at apex of the superior vestibule of the mouth.
|
|
|
Mental nerve block
|
It supplies the skin of the lower lip and gum through the mental canal. This can be palpated in the mid-pupillary line,
|
|
|
Orbicularis oris
|
Surrounds the mouth, continuous with buccinator. Sphincter
|
|
|
Buccinator
|
Muscle of the cheek
|
|
|
Orbicularis oculi
|
Surrounds the eye
|
|
|
Bell's palsy
|
Damage to facial nerve in middle ear
|
|
|
Muscles of mastication supplied by
|
Mandibular branch of trigeminal
|
|
|
Masseter, temporalis, medial and lateral pterygoids
|
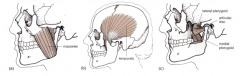
|
|
|
Taste innervated by
|
VII and IX
|
|
|
Lateral deviation and wasting of tongue after lesion of?
|
XII
|
|
|
Muscles of soft palate controlled by
|
pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve derived from the cranial accessory nerve
|
|
|
Function and sensory innervation of soft palate
|
Swallowing, gag reflex. Nerve IX
|
|
|
Transverse ligament of atlas
|
Around odontoid peg
|
|
|
Ligamentum flava, anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments?
|
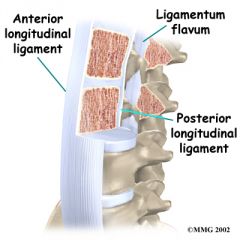
Between laminae of vertebrae
|
|
|
Hangman's fracture
|
The inferior articular process of C2 is broken allowing the axis to move forward on C3. The spinal cord is damaged at this level and so respiration is paralysed.
|
|
|
Scalenus anterior?
|
|
|
|
Sternomastoid?
|
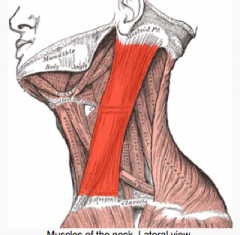
|
|
|
Termination of spinal cord in adult/newborn?
|
L1-2/L3-4
|
|
|
What layers does spinal anaesthesia pierce in what order?
|
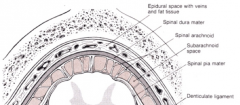
|
|
|
Spinal nerves exit through?
|
Intervertebral foraminae
|
|
|
Cauda equina syndrome
|
LOF of lumbar plexus due to CE damage. Lower motor neuron lesion.
|
|
|
Spinal anaesthesia
|
Local anaesthetic into the subarachnoid space, must be below L2 to avoid damage to spinal cord. Circulates in CSF.
|
|
|
role of coracoclavicular ligament
|
Prevents dislocation of acromioclavicular joint
|
|
|
Latissimus dorsi
|
Large back muscles, dorsal. Insert into anterior side of humerus
|
|
|
serratus anterior
|
superior external rotation of scapula, draws internally and forwards. Is along ribs on side of body, draws scapula from its medial part
|
|
|
What articulates the humerus to the radius / ulna?
What fossae do they go into? What's on the posterior side of the elbow? |
Capitulum / trochlea.
Radial / coronoid fossa Olecranon fossa into which olecranon goes |
|
|
Supracondular fracture can cause?
|
Damage to median nerve and brachial artery
|
|
|
Ligaments of elbow capsule?
|
First articular capsule, anular ligament of radius, radial and ulnar collateral ligaments to stop elbow adduction/abduction
|
|
|
Biceps brachii insertion / origins?
|
Radial tuberosity. Long head - supraglenoid tubercle of scapula, short head - coracoid process
|
|
|
Supinator is where?
|
Lateral part of proximal radius just after elbow
|
|
|
Triceps inserts
|
Olecranon process of ulna
|
|
|
Pronator originates / inserts
|
Medial epicondyle of humerus and coronoid process of ulna, inserts lateral radius
|
|
|
Dislocation of radius head caused by
|
Pull on pronated hands#
|
|
|
Colles' fracture
|
Falling onto outstretched arms, distal radius/ulna becomes dorsal to proximal
|
|
|
Contents of cubital fossa
|
Brachial artery, MCV, median nerve
|
|
|
Bones of wrist
|
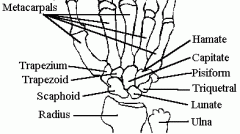
|
|
|
Wrist joint is?
|
Synovial
|
|
|
Flexor reticulatum?
|
Forms the tunnel of the carpal tunnel
|
|
|
What flexes wrist?
|
Flexor carpi radialis / ulnaris.
Ulnaris inserts around hook of hamate. |
|
|
What flexes fingers?
|
Flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus
|
|
|
What flexes thumbs?
|
Flexor pollicis longus and brevis
|
|
|
Finger flexor sheathes
|
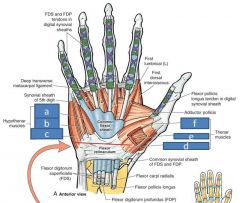
|
|
|
Extensors of wrist (4)
|
Extensor digitorum, extensor pollicis longus and brevis, abductor pollicis longus
|
|
|
Lumbericals do what?
|
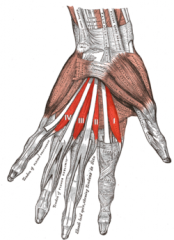
Flex metacarpophalangeal joints
|
|
|
Interossei do what?
|
Abduct / adduct fingers
|
|
|
Carpal tunnel syndrome
|
Compression of carpal tunnel, compression of median nerve. Numbness and pain
|
|
|
Ulnar nerve damage
|
causes clawing, cannot extend 4th and 5th digit
|
|
|
Upper limb arteries: subclavian, axillary, brachial, radial, ulnar, supericial and deep palmar arches
|
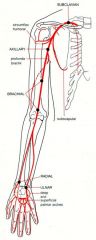
|
|
|
Supracondular fracture can cause damage to the
|
Brachial artery
|
|
|
Veins of upper limb - dorsal venous arch of hand, basilic, cephalic, median cubital, axillary and subclavian
|
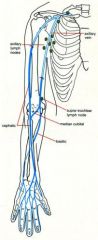
|
|
|
dermatomes of the arm
|
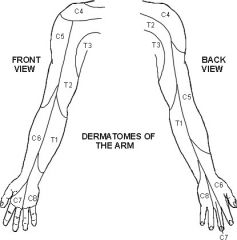
|
|
|
Lesion of upper brachial plexus
|
Erb's palsy - main loss will be of shoulder abduction and lateral rotation, and elbow flexion. Waiter's tip. Loss of sensation too
|
|
|
Lesion of lower brachial plexus
|
Damage to C8 and T1 would weaken the long flexors and extensors of the fingers, and all the intrinsic muscles of the hand
|
|
|
Horner's syndrome
|
Damage to T1 - sympathetic outflow to head. a constricted pupil, a drooping eyelid and hot , dry skin on the cheek or forehead of the affected side
|
|
|
Musculocutaneous nerve innervates
|
Elbow flexors
|
|
|
Median nerve innervates
|
most forearm flexors, thenar eminence, sensory to hand
|
|
|
Ulnar nerve supplies
|
Flexor dig profundus to ring and litle fingers, flexor carpi ulnaris, other snall muscles. Sensory to palm and dorsum
|
|
|
Axillary nerve supplies
|
deltoid, regimental badge skin. can be damaged by shoulder dissociation
|
|
|
Radial nerve supplies
|
Extensors of elbow, wrist, and fingers, sensory distribution esp dorsum of hand
|
|
|
Effect of damage by mid-shaft fracture of humerus
|
wrist drop
|
|
|
Ways to test for damage to C6/7/8 and ulnar / radial
|
tip of thumb C6 and median nerve,
tip of middle finger C7; tip of little finger C8 and ulnar nerve; dorsum of hand - radial nerve |

