![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
3 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
classifications of AF |
paroxysmal (self-terminating, usually <48h), persistent (>7d), permanent (>1y, when cardioversion has failed or is foregone)
valvular (e.g. rheumatic MV dz, prosthetic or repaired valve) v. nonvalvular
lone AF: <60y, no other cardiac dz (including HTN) |
|
|
etiologies of AF |
cardiac: HF, myo/pericarditis, ischemia, HTN crisis, cardiac surgery pulmonary: acute dz or hypoxia (e.g. COPD flare, PNA), PE, OSA metabolic: high catecholamine states (stress, infection, postop, pheo), thyrotoxicosis drugs: EtOH ("holiday heart"), cocaine, amphetamines, theophylline, caffeine neurogenic: SAH, ischemic stroke chronic: old age, HTN, ischemia, valve disease, CMP, hyperthyroid, obesity |
|
|
approach to acute AF |
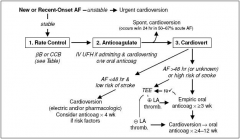
|

