![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Perspective drawings |

They appear to the eye or from you perspective (Not drawn to scale) |
|
|
Oblique drawings |

One surface drawn orthographically (true shape and size) can be drawn to scale ONLY ONE ANGLE Receding, edges, drawn, parallel normally at 45 degrees |
|
|
Isometric drawings |

Horizontal planes always recede at 30 degrees MORE THEN ONE ANGLE Advantage of showing all directions made to scale |
|
|
Arrow head leader line |
Points to applicable area or part |
|
|
Solid dot leader line |
When surface area is referenced |
|
|
Conventional dimensioning |
Each dimension is adjacent to the next |
|
|
Baseline dimensioning |
Taken from a common extenison line |
|
|
Running dimensions |
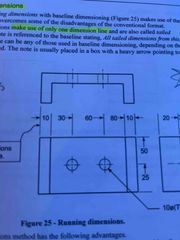
Make use of only one dimension line |
|
|
Orthographic projection |

Method of describing the true shape of an object using two or more views |
|
|
Orthographic views |
Used to describe any shape in sufficient detail to permit fabrication |
|
|
Unidirectional |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Aligned |

(Must align yourself) |
|
|
Concentric circles |
Have a common centre |
|
|
Eccentric circles |

Have different centres |
|
|
Parallelogram |
Four sided figure the opposite size of which are parallel and equal |
|
|
Trapezoid |
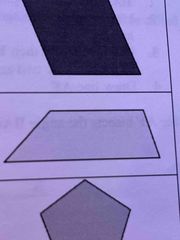
A four sided figure with two parallel sides, two non-parallel sides |
|
|
Hexagon |
A polygon of six equal size and six equal angles |
|
|
Pentagon |
A polygon of five equal sides, and five equal angles |
|
|
Acute angle |

Less then 90 degrees |
|
|
Obtuse angle |
More than 90 degrees |

