![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
135 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the layers of the skin?
|
Epidermis
Dermis Subcutaneous (hypodermis) |
|
|
What is responsible for water-proofing the skin?
|
Keratin
|
|
|
What gives skin its pigment? What cells produce it?
|
Melanin ; melanocytes
|
|
|
Lack of melanin production
|
Albinism
|
|
|
What skin disorder might you have if you have no protection against the sunlight?
|
Albinism
|
|
|
If you have lack of melanocytes, what skin disorder would you have?
|
Albinism
|
|
|
If your melanocytes lose the ability to produce melanin what disorder would you have?
|
Vitiligo
|
|
|
Small areas of hypopigmentation is called
|
Vitiligo
|
|
|
Patches of darker skin is called
|
melasma
|
|
|
Connective tissue contains both __________and ________fibers.
|
elastic and collagen fibers
|
|
|
Which section of the skin contains melanocytes
|
Basal layer of the epidermis
|
|
|
Which layer contributes the most to the flexibility and strength of the skin?
|
Dermis
|
|
|
Which layer of the skin contains the nerves and blood vessels?
|
Dermis and hypodermis
|
|
|
Which layer of the skin includes sensory receptors for pressure, touch, pain, and temperature?
|
Dermis (Meissner's and Pacinian corpuscles)
|
|
|
A loss of turgor in the skin would likely indicate
|
Dehydration
|
|
|
Which layer within a hair follicle does mitotic growth occur?
|
Stratum basale
|
|
|
What is the muscle associated with hair follicles? What type of nerve innervation caused it to contract?
|
Arrector pili muscle ; sympathetic NS
|
|
|
Which gland produces sebum? When does this secretion begin?
|
Sebum ; at puberty
|
|
|
What type of sweat glands are all over your body?
|
Eccrine
|
|
|
What type of sweat glands are found in axillae, scalp, face, and external genitalia?
|
Apocrine (ducts open into canal or hair follicles)
|
|
|
Which layer of the skin contains connective tissue?
|
Dermis and hypodermis
|
|
|
Which layer of the skin contains fat cells?
|
Hypodermis (subcutaneous)
|
|
|
Which layer of the skin contains fibroblasts?
|
Hypodermis
|
|
|
Which layer of the skin contains macrophages?
|
Hypodermis
|
|
|
Which layer of the skin contains nerves?
|
Dermis and hypodermis
|
|
|
What type of muscle is the arrector pili muscle?
|
Smooth
|
|
|
What does you skin synthesis with ultraviolet stimulation? What is this required for?
|
Vitamin D ; absorption of calcium in the intestinal mucosa
|
|
|
Name two ways in which your skin regulates your body temperature.
|
1- vasodilation (warming)
2- evaporation of sweat (cooling) |
|
|
Give an example of a systemic disorder which might cause a skin lesion
|
Liver disease
|
|
|
Give an example of a systemic infection which would cause skin lesions
|
Chickenpox
|
|
|
What is another name for itching of the skin?
|
Pruritus
|
|
|
Small, flat circumscribed lesion of a different color than the normal skin
|
Macule
|
|
|
Small, firm (solid) elevated lesion
|
Papule
|
|
|
Thin walled, raised, fluid filled lesion
|
vesicle or blister
|
|
|
Cavity in the tissue
|
Ulcer
|
|
|
Firm, raised, deep lesion
|
Nodule
|
|
|
Raised, filled with pus lesion
|
pustule
|
|
|
slightly elevated, flat "scaly like" lesion
|
plaque
|
|
|
Crack in the lesion
|
Fissure
|
|
|
Pruritus could be caused by
|
Allergic reaction
chemical irritation (due to insect bite) Parasites, like scabeis |
|
|
What might pruritus interdigitally indicate?
|
Scabies
|
|
|
Although the exact mechanism for pruritus is not fully understood, we know _________ is released
|
Histamine
|
|
|
Infection resulting from pruritus is usually due to
|
Breaking the skin barrier by scratching
|
|
|
What treatments is recommended for pruritus?
|
topical agents to reduce itch sensation
antihistamine glucocorticoids |
|
|
Cryosurgery is a treatment for which type of skin lesion?
|
Precancerous lesions
|
|
|
What type of inflammatory disorder would be caused by exposure to an antigen?
|
Contact dermatitis
|
|
|
Does direct chemical or mechanical irritation involve an immune response?
|
NO (only inflammatory response)
|
|
|
What is another name for hives?
|
Urticaria
|
|
|
What is the cause of urticaria? Where other than the skin can it occur?
|
Ingestions of substances that results in a type I hypersensitivity; in the pharyngeal mucosa
|
|
|
What should you check for if a patient has urticaria? What risk is involved?
|
Swelling around the mouth
Check airway Urticaria often leads to anaphylatic shock! |
|
|
What is another name for atopic dermatitis?
|
Eczema
|
|
|
Diagnose.
Erythematous rash with serous exudate on the face, chest, and shoulders |
Infant eczema (atopic dermatitis)
|
|
|
Diagnose.
Dry, scaly, pruritic rash on the knees and inner elbows |
Adult eczema (atopic dermatitis)
|
|
|
Chronic inflammation resulting from a response to allergens (eosinophilia and increased serum IgE levels)
|
Eczema (atop dermatitis)
|
|
|
What is the treatment for atopic dermatitis?
|
Antihistamines, glucocorticoids
|
|
|
when is the typical onset of psoriasis?
|
Teen years
|
|
|
Rash that results from abnormal T-cell activation
|
Psoriasis
|
|
|
In which inflammatory disorder is there an excessive keratinocyte proliferation?
|
Psoriasis
|
|
|
Itching or burning lesions on the face, scalp, knees, and elbows are characteristic of which skin disorder?
|
Psoriasis
|
|
|
During psoriasis exacerbation, skin lesions are (wet/dry)
|
wet
|
|
|
During psoriasis remission, skin lesions are (wet/dry).
|
Dry
|
|
|
An example of a plaque
|
Psoriasis,during remission
|
|
|
Which inflammatory skin disorder is a symptom of an auto immune disorder?
|
Pemphigus
|
|
|
What is the problem in pemphigus?
|
Autoantibodies disrupt the cohesion between epidermal cells (often causing the epidermis to separate from the basal layer)
|
|
|
Pemphigus causes which of the following to form?
1- Blisters (bullae) 2- Plaque 3- Nodules |
1- Blisters (bullae)
|
|
|
After the skin sheds in pemphigus, what might the patient experience?
|
Pain, and risk of secondary infection due to open area
|
|
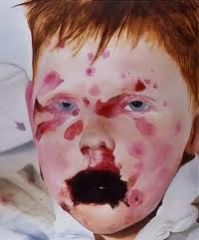
Diagnose.
This is an extensive case of which skin disorder? What other factors might contribute? |
Steven-Johnson syndrome.
Extensive form of pemphigus. Often secondary to allergic reactions to medications. |
|
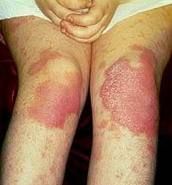
Diagnose.
Which stage is this in? |
Psoriasis.
Exacerbation |
|
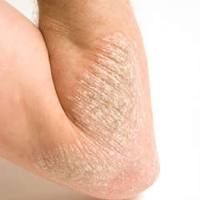
Diagnose.
What does this result from? How would you treat? |
Eczema (in an adult- flexor surface)
Eosiniphilia and increased serum IgE levels (due to allergens) Glucocorticoids and antihistamines |
|
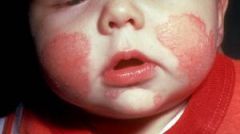
Diagnose.
How is this disorder different in infants and adults? |
Atopic Dermatitis (eczema)
In infants, usualyl erythrematous with serous exudate that occurs on face, shoulders, and chest. In adults, lichenificaiton (dry, scaly, pruritic) often on flexro surfaces |
|
|
Glucocorticoids, tar preparations, and anti-metabolites are treatments for which skin disorder?
|
Psoriasis
|
|
|
Glucocorticoids and immunosuppressants are treatments for which skin disorder?
|
Pemphigus
|
|
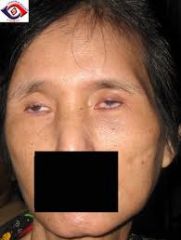
Diagnose.
What is present in all cases of this disorder? What could this lead to? |
Scleroderma.
Increased collagen deposition, inflammation and fibrosis with decreased capillary networks Renal failure, intestinal obstruction, respiratory failure due to distortion of the tissues. |
|
|
Scleroderma could occur as a skin disorder or ___________.
|
systemic, affecting viscera
|
|
|
What is the primary cause of scleroderma?
|
Unknown
|
|
|
diagnose.
Hard, shiny, tight immovable areas of the skin |
Scleroderma
|
|
|
Diagnose.
Impaired movement of mouth and eyes. |
Scleroderma
|
|
|
Cellulitis is an infection of the _____ and _______ tissues
|
dermis, subcutaneous
|
|
|
Another name for cellulitis
|
erysipelas
|
|
|
What does "iatrogenic" mean?
|
Complication arising from medical treatment (example= drug interaction)
|
|
|
Which skin infection is usually a secondary infection due to an injury or iatrogenic?
|
Cellulitis (erysipelas)
|
|
|
What is the most common causative agent in cellulitis? Second most?
|
Staph aureus ; Streptococcus
|
|
|
Where is cellulitis most commonly found?
|
In the lower trunks and legs
|
|
|
Diagnose.
Red streaks running along lymph vessels proximal to the infected area |
Cellulitis
|
|
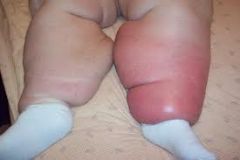
Diagnose.
What layers of the skin are infected? |
Cellulitis (erysipelas)
Dermis and Hypodermis |
|
|
Another name for a boil?
|
Furuncle
|
|
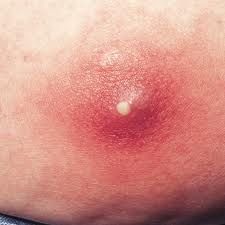
diagnose.
Causative agent? What is this filled with and what is meant by autoinoculation? |
Boil (furuncle)
S. aureus Filled with purulent exudate; if squeezed, it can result in the spread of infection to other areas of the skin. |
|
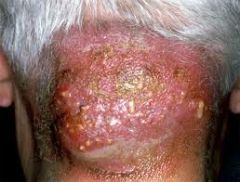
diagnose.
what is this a collection of? |
Carbuncle.
Collection of furuncles that coalesce to form a large infected mass. |
|
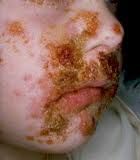
Diagnose.
What is causative agent? Other possibilities In which age group is this infection most common? |
Impetigo.
staph aureus (also streptococcis pyogenes and combination of staph or strep) Infants and children |
|
|
What skin infection is caused by one of the following agents?
Staph aureus Streptococcus pyrogenes combination of staph and strep |
Impetigo
|
|
|
what treatment is used for impetigo?
|
Topical antibiotics in the early stages. If lesions are extensive, systemic antibiotics are given
|
|
|
Infection caused by gram-positive, group A, beta-hemolytic streptococcus
|
Necrotizing Faciitis
|
|
|
In necrotizing faciitis, which type of bacteria are usually present, aneraobic, or aerobic?
|
combination of both
|
|
|
What allows streptococcus to breakdown tissue?
|
secretion of exotoxins
|
|
|
The history of a person with necrotizing faciitis usually includes...
|
minor trauma or infection in the skin and subcutaneous tissue of an extremity
|
|
|
Which is associated with necrotizing faciitis?
fever / no fever bradycardia / tachycardia hypotension / hypertension |
fever
tachycardia hypotension *also mental confusion, diorientation, and possible organ failure |
|
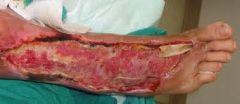
How would you treat this?
|
Aggressive antimicrobial therapy, fluid replacement, excision of all infected tissue, amputation
|
|
|
Most common cause of cold sores or fever blisters?
|
HSV-1
|
|
|
Most common cause of genital herpes?
|
HSV-2
|
|
|
Where does herps virus remain latent? What triggers an exacerbation?
|
In the sensory ganglion ; stress, common cold, sun exposure
|
|
|
How is herpes spread?
|
With direct contact from fluid from the lesion
|
|
|
Name two complications of HSV when spread to other areas
|
Eye- keratitis
Finger- Herpetic whitlow (painful) |
|
|
Another name for warts?
|
verrucae
|
|
|
what are most common kind of warts? What is the causative agent of these?
|
Plantar warts ; HPV types 1-4
|
|
|
What causes genital verrucae?
|
HPV 6 and 11
|
|
|
What is another name for a fungal infection?
|
Mycoses
|
|
|
Most mycoses are superficial. When might it spread systemically?
|
In immunocompromised patients
|
|
|
Which fungal agent is associated with diabetic patients?
|
Candida
|
|
|
Tinea capitis
|
Fungal infection of the scalp
|
|
|
Tinea corporis
|
Fungal infection of the body, particularly non-hairy parts
|
|
|
Tinea pedis
|
Fungal infection of the foot
|
|
|
Tinea urguium
|
Fungal infection of the nails (usually toenails)
|
|
|
When do male and female scabies die?
|
males- after fertilizing female
females- after laying the eggs into epidermis |
|
|
Pediculus humanus corporis
|
body lice
|
|
|
Pediculus humanus capitis
|
head lice
|
|
|
Pediculus humanus pubis
|
pubic lice
|
|
|
Why do louse bite human host?
|
Suck blood for production of ova
|
|
|
What is excoriation
|
Break or damage of the skin
|
|
|
Why do excoriations occur in pediculosis?
|
From scratching
|
|
|
What are keratoses?
|
Benign lesions associated with aging or skin damage
|
|
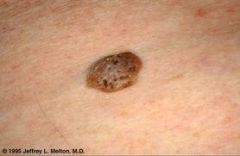
Diagnose.
What is this caused by? |
Seborrheic keratoses
Results from proliferation of basal cells (usually leads to an oval elevation that is smooth or rough and dark in color... usually looks like verruca, due to old age) |
|
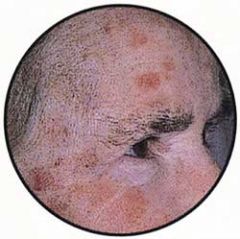
Diagnose.
What was this skin probably exposed to? |
actinic keratoses (AKs- "sunspots")
Ultraviolet radiation |
|
|
Painless, malignant tumor of the epidermis
|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
Where is squamous cell carcinoma most commonly found? Where else could it be found?
|
Face and neck
Base of tongue |
|
|
What is the typical prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma?
|
Good, if removed early
|
|
|
Highly metastatic form of skin cancer
|
Malignant melanoma
|
|
|
Where does Malignant melanoma develop?
|
Melanocytes
|
|
|
A newly-formed nevus could be an indication of what?
|
Malignant melanoma (nevus is a mole)
|
|
|
Multicolored lesion with an irregular border
|
Malignant melanoma
|
|
|
treatment for Malignant melanoma?
|
Surgical removal and radiation plus chemotherapy
|
|
|
Malignant melanoma is suspected in any nevus that shows:
|
A change in appearance
B change in border C change in color D change in diamter |
|
|
Lesions that occur in imunnocompromised patients (typically AIDS)
|
Kaposi's sarcoma
|
|
|
Kaposi's sarcoma may affect skin and ___________.
|
Viscera
|
|
|
Where are the malignant cells in Kaposi's sarcoma?
|
Endothelium of small blood vessels
|
|
|
Purplish macules, nonpruritic, nonpainful
|
Kaposi's sarcoma
|

