![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In the case of cancer, accumulation of mutations as it progresses will result in _________ and _________. |
invasion; spread
|
|
|
These proteins keep the cells attached to one another.
|
E-cadherins.
Tumors down-regulate E-cadherins |
|
|
The basement membrane is composed of two key molecules, namely _______ and _______. |
(1) Collagen IV
(2) Laminin |
|
|
After disattachment of tumor cells, they attach to the laminin in the basement membrane and destroy it by acquiring a ____________.
|
type IV collagenase
|
|
|
Once a tumor cell is out in the extracellular matrix it will attach itself to __________. After that, it can __________.
|
fibronectin; spread locally and enter lymphatics or blood vessels.
|
|
|
Carcinomas tend to spread via the __________.
|
lymphatics
|
|
|
The place where you would expect to see carcinomas is in the _______________.
|
regional draining lymph nodes
|
|
|
Sarcomas tend to spread via the __________.
|
blood
|
|
|
Some carcinomas spread hematogenously. Which ones?
|
(1) Renal cell carcinomas (renal vein)
(2) Hepatocellular carcinoma (hepatic vein) (3) Follicular carcinoma of thyroid (4) Choriocarcinoma |
|
|
Why does choriocarcinoma logically like to invade the blood and not the lymphatics (as it "should")?
|
Choriocarcinoma is a malignancy of placental tissue, in particular the cells that line the villi of the placenta (trophoblasts). Choriocarcinoma is malignancy of trophoblasts. Trophoblasts are designed by nature to find blood vessels and invade blood vessels.
|
|
|
This carcinoma characteristically spreads by seeding body cavities. What carcinoma is it? What is a term used to describe a property of this seeding when cutting through the mass.
|
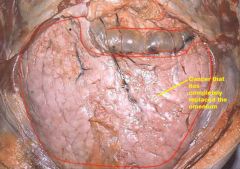
Ovarian carcinoma. Often involves the omentum of the abdomen. When you cut through it it has the consistency of cake. Another term to describe this is 'omental caking'.
|

