![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
UG embryology
|
bladder derived from UG sinus (meso & endoderm)
urachus connects fetal bladder to umbilicus |
|
|
|
Ureter Developmental Abnormalities
|
Rare 2-3%
bifid ureter w/ or w/o double pelvis ureteropelvic junction obstruction (L side in males or pregnant females) congenital hyroureter or megaureter |
|
|
|
Urinary bladder abnormalities
|
Diverticula (acquired or congenital)
exstrophy (--> chronic inflammation --> adenocarcinoma) veisoureteral reflux congenital fistulae persistent urachus |
|
|
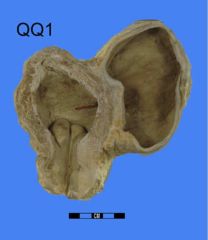
|
urinary bladder w/ diverticulum (congenital or acquired)
|
|
|
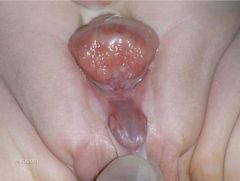
|
extrophy of bladder
|
--> chronic infections --> adenocarcinoma
|
|
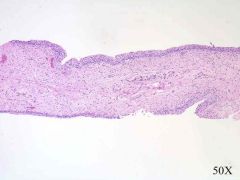
|
normal urothelium (5-7 cell layers thick)
|
|
|
|
UTI
|
lower tract infections are ascending (Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the exception)
Bacterial - coliforms (e. coli, proteus, klebsiella, enterobacter, chlamydia, mycoplasm) fungal - candida, cryptococcus virus - adenovirus, BK parasites - s. haematobium, t. vaginalis |
|
|
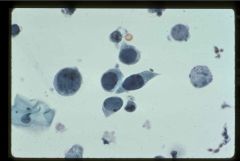
|
Polyoma or BK virus infection
"frosted glass" nuclear inclusions w/ clumped native chromatin |
|
|
|
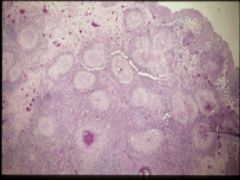
schistosomiasis
note granulomas |
|
|
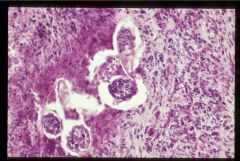
|
schistosomiasis
note granulomas |
|
|
|
UT inflammation
|
acute - frequency, abd pain, dysuria, PMN infiltrate, mucosal hyperemia, exudative or ulcerative
chronic - lymphoplasmacytic w/ fibrosis, follicular and eosinophilic variants acute or chronic cystitis may cause pyelonephritis |
|
|
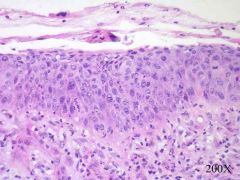
|
acute cystitis w/ exudate
|
|
|
|
Interstitial cystitis
|
chronic inflammation and fibrosis of all layers of the bladder wall, more common in women, associated w/ autoimmune dz
|
|
|
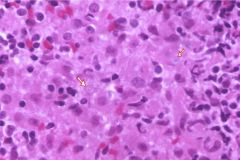
|
Malacoplakia
mucosal plaques containing foamy macrophages Michaelis-Gutmann bodies |
associated w/ immunocomp pts, e.coli, defects in phagosome activity
|
|
|
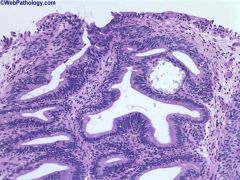
Cystitis glandularis
nests of downward growing urothelium, may become cystic, intestinal metaplasia may occur |
incr risk of adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
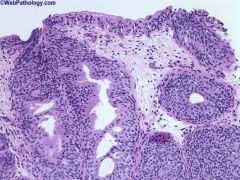
Cystisis cystica
nests of downward gorwing urothelium, may become cystic, extensive metaplasia |
incr risk adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
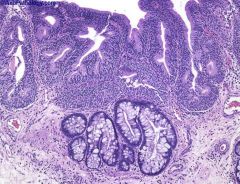
intestinal metaplasia
|
incr risk of adenocarcinoma w/ metaplasia
|
|
|
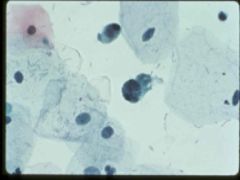
chemotherapy effect
enlarged cells, degenerative changes (cytoplasm fraying and nuclear smudging), crystals |
hemorrhagic cystitis associated w/ cyclophosphamide, radiation, adenovirus, causes gross hematuria
|
|
|
UT neoplasms
|
high M&M, 50k pts/yr
95% are urothelial (location % dependent on surface area) risk factors - tobacco, arylamines, chronic irritation, phenacetin, cyclophosphamide Chromosome 9 alterations - low grade, noninvasive (tumor suppressor gene) Chromosome 17 - p53, invasive lesions Chromosome 13 - Rb gene, invasive Chromosome 14 - flat and invasive |
|
|
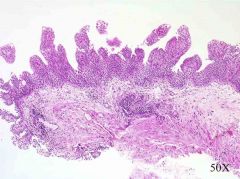
|
benign papilloma
papillary growth pattern, thin epithelium, orderly growth |
|
|
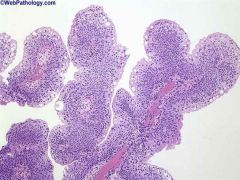
|
urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential
papillary architecture and foacl thickening of epithelium w/ areas of maturation |
|
|
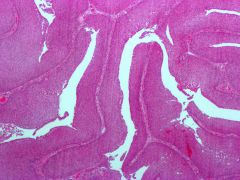
|
low grade urothelial carcinoma
complex branching architecture, epithelial thickening and crowding |
|
|
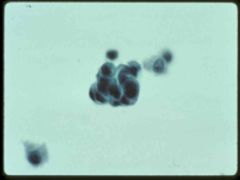
|
low grade urothelial carcinoma
crosded group of hyperchromatic cells clumped cells in urine = cancer |
|
|
|
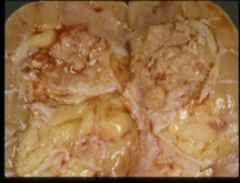
urothelial carcinoma of the renal pelvis
|
don't be fooled! its still the renal pelvis --> still urothelial
|
|
|
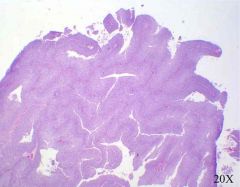
low grade urothelial carcinoma
papillae are beginning to fuse |
|
|
|
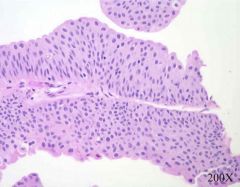
low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
epithelial thickness, lack of maturation, mitosis off bm |
|
|
|
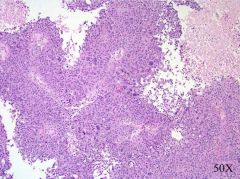
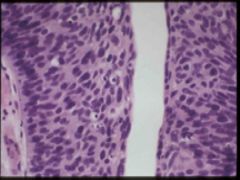
high grade urothelial carcinoma
pleomorphism, discohesion at edges, necrosis |
papillary, nodular, both
80% show invasion of muscularis, anaplasia, cellular discohesion, squamous or glandular differentiation ulceration may be present |
|
|
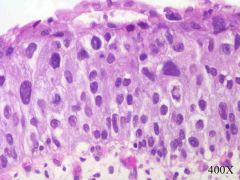
high grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
|
papillary, nodular, both
80% show invasion of muscularis, anaplasia, cellular discohesion, squamous or glandular differentiation ulceration may be present |
|
|
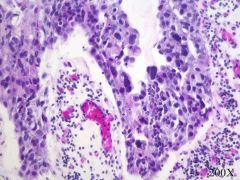
urothelial carcinoma in situ
|
|
|
|
urothelial carcinoma in situ
if you understand why or can see a basement membrane please enlighten me |
|
|
|
urothelial carcinoma
|
presents: PAINLESS hematuria, pyelonephritis or hyronephrosis (depending on location)
high rate of recurrence papillomas and low grade have 98% 10 yr survival high grade cancers have 40% 10 yr survival pure squamous cell is poor prognosis |
|
|
|
obstructive lesions
|
sclerosing retroperitoneal fibrosis - idiopathic, late/middle age
congenital narrowing, inflammatory stricture, fibrosis, contracture, compression, neurogenic |
|
|
|
urethral inflammation
|
gonococcal v. nongonococcal
associated w/ ascending cystitis |
|
|
|
urethral neoplasms
|
caruncle - inflammatory pseudotumor in older women (bleeds)
papillomas - viral, at meatus carcinoma - rare, older women, squamous near meatus, aggressive |
|

