![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In pressure overload, the predominant heart alteration seen is _________.
|
hypertrophy
|
|
|
In ___________ overload, chamber dilation is the predominant alteration.
|
volume
|
|
|
In end stage heart failure, which morphologic changes are usually seen?
|
both - hypertrophy and dilation
|
|
|
Changes to cells in concentric hypertrophy
|
-cells become wider, but not longer
-wall becomes thicker (hypertrophy not dilation) |
|
|
Sarcomere arrangement in concentric hypertrophy
|
more sarcomeres are produced and arranged in parallel
|
|
|
Changes to cells in eccentric hypertrophy
|
-cells become wider AND longer
-chamber dilates in proportion to increased thickness (wall thickness may be normal or even below normal) |
|
|
How can you measure dilation?
|
Heart weight (since wall thickness may be normal or below normal)
|
|
|
Sarcomere arrangement in eccentric hypertrophy
|
-more are produced and arranged in series
|
|
|
Hypertensive heart disease would primarily result in what kind of hypertrophy?
|
concentric
|
|
|
Cor Pulmonale (Isolated Right Heart failure) would result in what? What causes it?
|
right ventricular dilation - due to pulmonary hypertension
|
|
|
What changes would result from mitral valve insufficiency?
|
left atrial dilation
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of heart failure?
|
ischemic heart disease
|
|
|
In addition to elements of both dilation and hypertrophy, what changes would you see in ischemic heart disease?
|
atherosclerosis of coronary arteries and perhaps old areas of infarct
|
|
|
Normal heart weight
|
250-350g
|
|
|
The greatest increase in heart mass would result from what two abnormalities?
|
aortic regurgitation or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
|
|
|
Three main classes of cardiomyopathies
|
-dilated
-hypertrophic -restrictive |
|
|
What is the most common type of cardiomyopathy?
|
dilated
|
|
|
What is the least common cardiomyopathy?
|
restrictive
|
|
|
Dilated cardiomyopathy is characterized by a dilated ________________ and ____________ dysfunction.
|
ventricular chamber; systolic
|
|
|
It typically becomes apparent between the ages of ________.
|
20-50
|
|
|
Five possible etiologies of DCM
|
-genetic
-myocarditis -alcohol -pregnancy -idiopathic (many may be myocarditis) |
|
|
Most common cause of DCM
|
genetic (20-50%)
|
|
|
What kinds of gene mutations can cause DCM?
|
-mutations in genes involving cytoskeletal proteins
-mutations in mitochondrial DNA |
|
|
X-Linked DCM is caused by a dysfunction in what gene
|
dystrophin (a cytoskeletal protein)
|
|
|
What kind of genetic mutations are the most common cause of DCM presenting in childhood?
|
mitochondrial DNA mutation
|
|
|
In myocarditis, the cause of injury is what?
|
inflammation
|
|
|
Acute myocarditis will present with what symptoms?
|
fatigue, dyspnea, palpitations, fever, precordial pain
|
|
|
Type of cardiomyopathy caused by alcohol and chemotherapeutic agents
|
toxic cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
When in pregnancy does peripartum cardiomyopathy present?
|
third trimester or first 6 months post-partum
|
|
|
What is the most common outcome?
|
spontaneous recovery
|
|
|
Genetic condition in which the ventricle (right more commonly than left) is severely thinned (myocyte loss) and replaced by fatty infiltration and interstitial fibrosis
|
Arrythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
An individual with a "banana-shaped" LV showing asymmetric septal hypertrophy may have what?
|
HCM/HOCM/IHSS
|
|
|
What is HCM/HOCM/IHSS?
|
Hypertrophic (obstructive) cardiomyopathy or idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis - left ventricular hypertrophy without systemic disease causing it (a primary cardiomyopathy)
|
|
|
Mutations in genes responsible for what cause HOCM?
|
proteins of the contractile unit - the sarcomere
|
|
|
The most common genetic mutation responsible for HOCM is what?
|
mutation in the beta-myosin heavy chain
(other common mutations - in toponin-T and myosin binding protein C) |
|
|
What histological changes may be seen in HOCM?
|
-disorganization of the myocytes and contractile elements within the cells
-extreme myocyte hypertrophy -interstitial fibrosis (due to ischemia) |
|
|
Describe the involvement of the mitral valve in HOCM
|
-increased blood flow pulls the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve into the aortic outflow tract, increasing the obstruction already there due to the hypertrophic septum (IHSS)
|
|
|
Restrictive cardiomyopathy causes ________ dysfunction
|
diastolic (ventricles stiff and can't fill appropriately)
|
|
|
Describe the ventricular, atrial and microscopic findings of restrictive cardiomyopathy
|
-normal or slightly enlarged ventricles with no dilation
-bilateral atrial dilation (blood backs up) -patchy or diffuse interstitial fibrosis microscopically |
|
|
Small, semitranslucent "drops of wax" on the atrial endocardial surfaces, particularly on the left, is typical of what restrictive cardiomyopathy?
|
cardiac amyloidosis
|
|
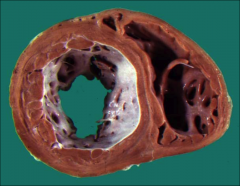
Endomyocardial disease associated with other anomalies that is most common in first two years of life and usually occurs in the left ventricle only, that presents as shown
|
endocardial fibroelastosis
|
|
|
Endomyocardial disease of unknown etiology which affects ventricles only and is found in children in tropical areas
|
endomyocardial fibrosis
|
|
|
Loeffler endomyocarditis is caused by damage by what cells?
|
eosinophils
|
|
|
What are two general causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy?
|
-endomyocardial diseases
-amyloidosis |
|
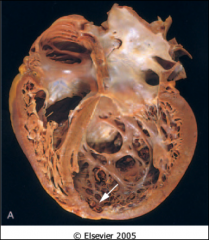
A large, heavy, floppy heart with mural thrombi as shown is characteristic of what?
|
DCM (dilated)
|

