![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is SUDI? |
Sudden unexpected death in infancy is an unexpected death in a child under 1 year of age All unexpected deaths in infancy should be referred to the Coroner Autopsy demonstrates some abnormality Autopsy fails to demonstrate an abnormality SIDS |
|
|
What are causes of infant mortality? |
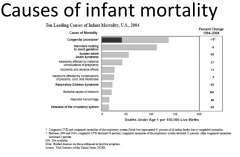
|
|
|
What racial groups are infant death most common in? |
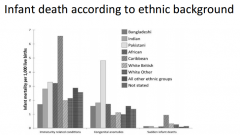
|
|
|
What parent occupations have the highest risk of infant related mortality? |
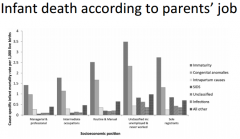
|
|
|
What were the relative causes of infant death in 1998? |
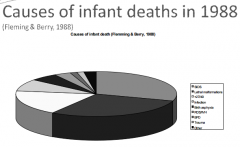
|
|
|
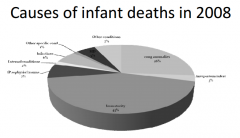
What were the relative causes of infant death in 2008? |
|
|
|
What are causes of babies being found dead in the cot? |
Congenital heart disease Respiratory infections CNS infections Septicaemia Intoxication Seizure disorders Unexplained (SIDS) Suffocation and NAI |
|
|
What are causes of instantaneous death in babies? |
Cause is obvious: Accident or trauma
Cause is not apparent but may be: Cardiac malformation - TPGA, PTA Coronary arteritis/fibromuscular dysplasia of coronary arteries or myocarditis Cardiomyopathy Arrhythmia Respiratory foreign body or laryngeal cyst |
|
|
What is Reye's syndrome? |
Reye syndrome or Reye's syndrome is a potentially fatal syndrome that has numerous detrimental effects to many organs, especially the brain and liver, as well as causing a low blood sugar.[1] The classic features are a rash, vomiting, and liver damage. The exact cause is unknown and, while it has been associated with aspirin consumption by children withviral illness, it also occurs in the absence of aspirin use. |
|
|
What are causes of rapid death due to recognised illness? |
Respiratory infections - bronchopneumonia, meningitis, CNS infections Gastroenteritis Other infections Reye’s syndrome CNS haemorrhage Congenital adrenal hyperplasia Kidney - DIC Congenital centronuclear myopathy |
|
|
What is Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome? |
Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome (WFS) or hemorrhagic adrenalitis or Fulminant meningococcemia, is defined as adrenal gland failure due to bleeding into the adrenal glands, caused by severe bacterial (or rarely viral) infection (most commonly the meningococcus Neisseria meningitidis).[1] The bacterial infection leads to massive hemorrhage into one or (usually) both adrenal glands.[2] It is characterized by overwhelming bacterial infection meningococcemia leading to massive blood invasion, organ failure, coma, low blood pressure and shock, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) with widespread purpura, rapidly developing adrenocortical insufficiency and death. |
|
|
Why is a post-mortem carried out in SIDS? |
To establish whether death was natural or not To elucidate the cause of death To provide basis for counselling Accurate certification of death for epidemiological and research purposes |
|
|
What is the definition of SIDS? |
The sudden unexpected death of an infant under 1 year of age, which remains unexplained after a thorough case investigation, including a complete autopsy, examination of the death scene and review of the clinical history |
|
|
What are some features of SIDS? |
Commonest between 4 and 20 weeks Commoner in winter Baby found dead in cot or co-sleeping Death occurs silently during sleep SIDS while awake Resuscitated SIDS |
|
|
What are risk factors for SIDS? |
Social class IV or V Unmarried mother Young mother High parity High birth order Short inter pregnancy interval City dweller Co-sleeping Maternal smoking Maternal opiate addiction Maternal infection in pregnancy Low birth weight Preterm IUGR Twins Minor malformations |
|
|
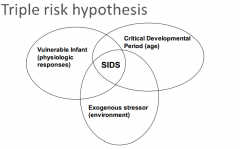
What is the triple risk hypothesis? |
|
|
|
What are features of the critical development period? |
Developmental immaturity Rapid changes between 1 and 5 months Abnormalities in arcuate nucleus of brainstem suggests delayed development of arousal, cardiorespiratory control or cardiovascular control and thermal regulation Laryngeal spasm with GOR Autoresuscitation from apnoea |
|
|
What factors make an infant vulnerable? |
Long QT syndrome Abnormality of the serotoninergic network (including arcuate nucleus) Slower responses to changes (increase in heart rate or breathing) |
|
|
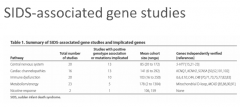
What are features of SIDS gene studies? |
|
|
|
What are external stressors for neonates? |
Minor URTI Prone position Bed-sharing Overheating Hyperthermia |
|
|
What are typical external findings in babies? |
Body apparently well developed and well nourished Frothy fluid around nose (often bloodtinged) Cyanosis of lips and nail-beds |
|
|
What are typical internal findings in babies? |
“Large” thymus with petechiae Petechiae pleura Epicardial petechiae Full expansion of lungs Liquid heart blood Empty bladder Prominent LN & Peyer’s patches |
|
|
What are microscopic findings in neonates? |
Pulmonary congestion and oedema Mild inflammation of upper respiratory tract Focal fibrinoid necrosis of vocal cords Persistent haemopoiesis in the liver |
|
|
How do you differentiate between SIDS and suffocation? |
Controversial cases Missed genetic or metabolic disease? Consider suspicious circumstances Better to call “unascertained” if not sure |
|
|
What are mimics of abuse in young babies? |
Fractures Sometimes (rare) seen in vaginal delivery Osteopenia of prematurity Vitamin D deficiency especially in breast fed babies Resuscitation (especially in VDD and OP) SDH 25-46% of asymptomatic newborns Retinal haemorrhages 34% of newborns (clear up to 2 months?) |
|
|
What religious considerations must you make with neonatal death? |
All religions: respect for the deceased Christianity – relics kept Islam - teaching, society (Cairo fatwa 1986) Judaism – orthodox reformed Others |

