![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
lactational changes in breast |
increase in # of acini, but no increase in # of cell layers |
|
|
common symptoms of breast disease |
lumpiness, pain (mastalgia or mastodynia), palpable mass (>2cm), nipple discharge (galactorrhea = benign, bloody, unilateral = worrisome) |
|
|
breast lump: <35 yo |
fibroadenoma, mastitis, fat necrosis, carcinoma |
|
|
breast lump: 35-50 yo |
fibrocystic changes, carcinoma, fibroadenoma, fat necrosis, mastitis, papilloma |
|
|
breast lump: >50 yo |
carcinoma, FCC, fat necrosis, Paget's, mastititis, papilloma |
|
|
congenital nipple inversion |
common, corrected spontaneously during pregnancy; clinically significant DDx = cancer, infl. dz of nipple |
|
|
accessory axillary breast tissue |
prophylactic mastectomy may remove entire breast but not all breast epithelium |
|
|
milk line remnants (supernumerary nipples/breasts) |
may be functional (changes w/ menstrual cycle); persistent epidermal thickenings |
|
|
acute mastitis |
1st mo of breastfeeding; causes = Staph (localized), Strep (diffuse) -> lead to neutrophil infiltration or abscess formation; Rx = ABs, surgical drainage |
|

|
acute mastitis |
|
|
squamous metaplasia of lactiferous ducts |
causes = smoking, Vit A deficiency keratin becomes trapped, accumulates; if duct ruptures, inflammatory response to keratin results in erythematous painful mass - may result in fistula tract |
|
|
duct ectasia (dilated ducts) |
5th-6th decade, multiparous; poorly defined palpable periareolar mass; chronic granulomatous infl., macrophages; thick debris in duct |
|

|
duct ectasia |
|
|
fat necrosis |
painless, palpable mass, skin thickening or retraction; see density or calcifications on mam (mimic carcinoma); history of trauma or prior surgery |
|

|
fat necrosis |
|
|
non-proliferative breast changes |
fibrocystic change |
|
|
fibrocystic change |
20-40 years; most common disorder of breast; can have cyst formation, fibrosis, or adenosis; lumpy-bumpy breasts |
|
|
how cysts form in breasts |
dilation and unfolding of lobules -> cystic lobules coalesce -> rupture -> reactive fibrosis |
|

|
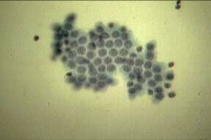
apocrine metaplasia - fibrocystic change |
|

|
apocrine cytology - fibrocystic change |
|
|
benign ductal epithelium metaplasia |
|
|
usual ductal hyperplasia |
proliferative breast dz w/o atypia; incr. ductal epithelial cell layers |
|

|
usual ductal hyperplasia (mild) |
|
|
florid usual ductal hyperplasia |
proliferative breast dz w/o atypia; >4 cell layers; ducts and lobules expanded, irregular lumens at periphery |
|

|
usual ductal hyperplasia - florid |
|
|
sclerosing adenosis |
proliferative breast dz w/o atypia; cancer mimic; glandular crowding & stromal fibrosis; lots of acini |
|

|
sclerosing adenosis |
|
|
radial scar (complex sclerosing lesion) |
proliferative breast dz w/o atypia; poorly circumscribed, radiating out (mimics cancer); see spokes of fibrotic tissue & small glands |
|
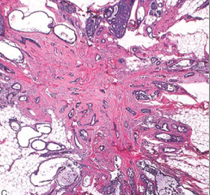
|
radial scar (complex sclerosing lesion) |
|
|
intraductal papilloma |
proliferative breast dz w/o atypia; solitary lesion in major ducts near nipple; 40-50 y/o; most common cause of bloody nipple discharge; see frond-like projections of stroma covered by ductal epithelium |
|

|
intraductal papilloma |
|
|
gynecomastia |
male breast enlarged due to excess estrogen (puberty, old age, Klinefelter's, Leydig cell tumor, cirrosis) and drugs (alcohol, marijuana, heroin, antiretroviral therapy, anabolic steroids) |
|

|
gynecomastia |
|
|
atypical ductal hyperplasia |
proliferative breast dz w/ atypia; resembles DCIS |
|
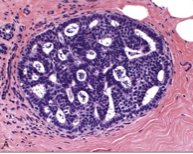
|
atypical ductal hyperplasia |
|
|
LCIS vs atypical lobular hyperplasia |
LCIS = dyshesive, uniform cells filling & distending >50% of spaces in TDLU ALH = no distention of acinar spaces (>50%) |
|
|
fibroadenoma |
proliferative breast dz w/o atypia; common in reproductive age; stromal & glandular hyperplasia; firm, rubbery, painless & mobile; no sig. incr. risk of malignancy; change w/ menstrual cycle, preg. and menopause |
|
|
fibroadenoma |
stromal tumor w/ smooth capsule and fleshy cut surface; slit-like ducts and loose fibrous stroma |
|

|
fibroadenoma |
|
|
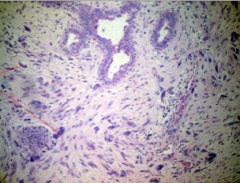
Phyllodes tumor |
stromal tumor; develop from intralobular stroma, larger than fibroadenoma, 10-20 years later than FA, more cellular stroma; most benign; stromal component can metastasize |
|

|
Phyllodes tumor |
|
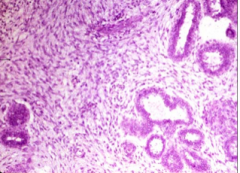
|
benign phyllodes tumor - higher power |
|
|
malignant phyllodes tumor |

