![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
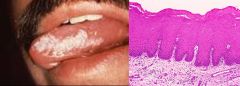
55 year old man visited his dentist for a routine dental exam. Dentist noticed lesions with the clinical and histological appearance shown. Past medical history showed no major medical problems. What etiological factor most likely contributed to the development on these lesions?
|
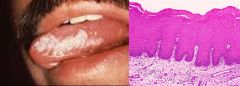
Smoking Tobacco. This whitish, well-defined mucosal patch on the tongue has the characteristic appearance of leukoplakia, a premalignant lesion that gives rise to squamous cell carcinoma. Pipe smoking and tobacco chewing are implicated in the development of leukoplakia
|
|
|
After a bout of the "flu," a 25 year old man notices several .3cm, clear vesicles on his upper lip. The vesicles rupture, leaving shallow, painful ulcers that heal over the course of 4 weeks. Several months later, after a skiing trip, similar vesicles develop, with the same pattern of healing. What is most likely associated with these findings?
|
Positive serologic test for herpes simplex virus type 1. The lesions of HSV-1, also known as cold sores or fever blisters, are common. Many people have HSV-1, and the oral and perianal lesions appear during periods of stress. Recurrence is the norm
|
|
|
What oral pathology is marked by hyperkeratosis
|
Leukoplakia
|
|
|
Atypical lymphocytes are seen with what viral disease
|
Infectious mononucleosis. They may be accompanied by a rash, but do not produce vesicular lesions of the skin
|
|
|
What oral pathology is suggested by budding cells with pseudohyphae
|
Oral thrush caused by Candidal infection
|
|
|
What type of infiltrate may be seen with oral aphthous ulcers
|
A mononuclear infiltrate
|
|
|
50 year old man with mass filling the right nasal cavity. CT shows 4cm mass in the nasopharynx on the right side that erodes adjacent bone. Large epithelial cells with indistinct borders and prominent nuclei. Mature lymphocytes are scattered throughout the undifferentiated neoplasm. What etiologic factor played a role in development of this lesion?
|
Epstein-Barr virus infection. This patient has nasopharyngeal carcinoma. There is a strong association with EBV infection, which contributes to the transformation of squamous epithelial cells
|
|
|
Sjogren syndrome is associated with what pathology of the head and neck
|
Malignant lymphomas. These typically arise in the salivary glands
|
|
|
Smoking contributes to what head and neck cancers
|
Oral and esophageal cancers. It is not associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma
|
|
|
Allergic rhinitis is associated with development of what head and neck pathology
|
Nasal polyps. These do not become malignant
|
|
|
Wegener granulomatosis can involve the respiratory tract, causing what
|
Granulomatous inflammation and vasculitis. The nasopharyngeal region is not commonly affected, and there is no risk of malignant growth
|
|
|
Over the past 10 years, a 60 year old man has had progressive difficulty hearing, particularly with the left ear. Findings suggest bone conduction deafness. CT scan normal. Family members similarly affected. Diagnosis?
|
Otosclerosis. It can be familial, particularly when it is severe. It results in fibrous ankylosis followed by bony overgrowth of the little ossicles of the middle ear
|
|
|
A schwannoma typically involves what cranial nerve
|
The vestibulocochlear nerve, resulting in a nerve conduction form of deafness. They are usually unilateral, although familial neurofibromatosis could result in multiple schwannomas
|
|
|
What is a cholesteatoma
|
Cystic lesions 1-4cm in diameter, lined by keratinizing squamous epithelium or metaplastic mucus-secreting epithelium and filled with amorphous debris. It is typically a unilateral process that complicates chronic otitis media in a child or young adult
|
|
|
What is a rare, solitary, bulky mass in the region of the jaw that may affect the skull in older adults
|
Chondrosarcoma, a malignant neoplasm derived from cartilage cells
|
|
|
A 35 year old man with HIV complains of bad taste in his mouth and discoloration of his tongue for the past 6 weeks. Areas of adherent, yellow-tan, circumscribed plaque on the lateral aspects of the tongue. This plaque can be scraped off as a pseudomembrane to show an underlying granular, erythematous base. Diagnosis?
|
Oral thrush, a lesion resulting from oral candidiasis in persons who are immunocompromised. The lesion is typically superficial. There are typical budding cells and pseudohyphae of Candida
|
|
|
What is a recurrent, superficial oral ulceration that is very common in young persons, but can appear at any age
|
Aphthous ulcers, or "canker sores"
|
|
|
What is fissuring or cracking of the mucosa, typically at the corners of the mouth, which may be seen with vitamin B2 (riboflavin) deficiency
|
Cheilosis
|
|
|
What oral pathology occurs from marked hyperkeratosis, forming a rough "hairy" surface, and is related to Epstein-Barr virus infection
|
Hairly leukoplakia, which can be seen with HIV infections, but is far less common than oral thrush
|
|
|
An oral lesion which has vesicles that typically ulcerate and multinucleated cells suggests what
|
Herpervirus infection
|
|
|
What type of cell usually arises from areas of oral leukoplakia
|
Atypical squamous epithelial cells
|
|
|
What pathology may have an appearance ranging from a shiny red surface of the tongue to ulceration
|
Glossitis.
|
|
|
What oral pathology may be seen with vitamin deficiencies, including vitamin B2, B3, B6, or B12?
|
Glossitis
|
|
|
Over the past 3 years, a 65 year old woman has noticed a slowly enlarging nodule on her face. 3cm, nontender, mobile, discrete mass palpable on the left side of the face, anterior to the ear and just superior to the mandible. Ductal epithelial cells in a myxoid stroma containing islands of chondroid and bone. What is this neoplasm called
|
Pleomorphic adenoma, the most common tumor of the parotid gland. These tumors are rarely malignant, although they can be locally invasive
|
|
|
What type of tumor is composed of cells resembling the serous cells of the salivary gland; they are generally small, but about one sixth metastasize to regional lymph nodes
|
An acinic cell tumor.
|
|
|
What type of salivary gland tumor is high grade and aggressive, but less common than a pleomorphic adenoma
|
Mucoepidermoid tumors
|
|
|
What type of tumor is the primitive neuroectodermal tumor (olfactory neuroblastoma)
|
One of the small, round, blue-cell tumors that occur in childhood. It is likely to arise in the nasopharyngeal region
|
|
|
Where in the head and neck do squamous cell carcinomas arise
|
The buccal mucosa. They are invasive
|
|
|
A 23 year old man has glistening, translucent, polypoid masses filling the nasal cavities. Respiratory mucosa overlying an edematous stroma with scattered plasma cells and eosinophils. What is a notable lab finding that will be found in this patient?
|
Increased serum IgE levels. The patient has nasal polyps, which can be associated with allergic rhinitis, a form of type I hypersensitivity often called hay fever. In some patients, this inflammation results in the formation of polyps in the nasal cavity. Type I hypersensitivity is associated with high IgE levels in the serum
|
|
|
What infection can be found in nasopharyngeal carcinomas
|
Epstein-Barr virus infection
|
|
|
Is diabetes a risk factor for polyp formation?
|
No, but ketoacidosis can lead to nasopharyngeal mucormycosis
|
|
|
65 year old woman notices a lump on the right side of the face that is becoming larger. 3-4cm firm, mobile, painless mass that is palpable in the region of the right parotid gland. The oral mucosa appears normal. No complaints of difficulty in chewing or talking. Diagnosis?
|
Pleomorphic adenoma, the most common benign salivary gland tumor and the most common tumor of the parotid gland. These tumors tend to be slow growing, and most are benign, although local invasion and recurrence are potential problems.
|
|
|
Sialolithiasis is usually accompanied by what?
|
Sialadenitis and pain. It may produce some gland enlargement but usually is not a mass effect
|
|
|
What can happen to the salivary glands in Sjogren syndrome
|
They can enlarge. The process is typically bilateral
|
|
|
Over the past 3 months, a 6 year old boy had had increased difficulty breathing, and the character of his voice has changed. Three soft, pink excrescences are present on the true vocal cords and in the subglottic region. 0.6-1cm in diameter. Fingerlike projections of orderly squamous epithelium overlying fibrovascular cores. Human papillomavirus 6 positive. Diagnosis?
|
Juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis, which is caused by HPV 6 and 11. These lesions frequently recur after excision. They may regress after puberty. In adulthood they are usually solitary and do not recur. There is no effective antiviral therapy for HPV. Although the lesions can be found in the airway, they are benign and do not become malignant. Their occurence is not related to use of the voice. This is not a congenital condition nor part of a syndrome
|
|
|
A 68 year old man has some discrete white patches with a leathery surface in the right buccal mucosa. The lesions are spread over an area of .7x2.5cm. Squamous epithelial acanthosis with marked hyperkeratosis. What is a risk factor that likely caused this?
|
Chewing tobacco. The clinical and histologic features suggest leukoplakia. Oral leukoplakia may appear in various intraoral sites and on the lower lip border. Pipe smoking and tobacco chewing are implicated in the development of these white patches. Irritation from misaligned teeth or dentures may also produce leukoplakia. Transformation to dysplasia and carcinoma is possible.
|
|
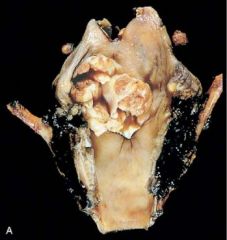
A 70 year old man who experienced increasing hoarseness for almost 6 months has recently had an episode of hemoptysis. No lesions are noted in the nasal or oral cavity. Firm, nontender anterior cervical lymph node. Lesion shown in figure. Patient undergoes biopsy, followed by laryngectomy and neck dissection. What is the most common risk factor associated with this pathology
|
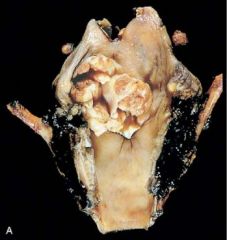
Smoking tobacco. The figure shows a large, fungating neoplasm that has the typical appearance of a laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. The most common risk factor is smoking, athough chronic alcohol abuse also plays a role. 5% of patients harbor human papillomavirus. Etiological significance is not clear.
|
|
|
Allergies with type I edema may cause what to happen to the larynx
|
Transient laryngeal edema. Neoplasia is not a typical complication
|
|
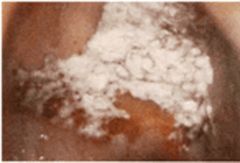
49 year old man who has used tobacco and snuff for many years. Lesion on hard palate is shown. Cannot be removed by scraping. Thickened squamous mucosa. Several years later, biopsy shows carcinoma in situ. Diagnosis?
|
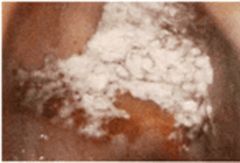
The raised white patches suggest leukoplakia. This is a premalignant condition. Risk factors include tobacco use and chronic irritation. HPV has been implicated in some lesions
|
|
|
What forms reticulate, lacelike, white keratotic lesions in the oral cavity that may ulcerate and have intense submucosal chronic inflammation, and usually appears in conjunction with skin lesions
|
Lichen planus, which is seen in more than 50% of patients with cutaneous lichen planus.
|
|
|
What head and neck pathology forms a painful gingival nodule of granulation tissue
|
A pyogenic granuloma
|
|
|
Xerostomia, or "dry mouth," is seen with what syndrome
|
Sjogren syndrome
|
|
|
A 60 year old woman noticed an enlarging bump beneath her tongue for the past year. Does not smoke or drink alcohol. 2.5cm movable, submucosal mass arising in the minor salivary glands on the buccal mucosa beneath the tongue on the right. Malignant and locally invasive. Recurs within 1 year. Diagnosis?
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma, which can arise in major and minor salivary glands. They account for most neoplasms that arise within minor salivary glands, particulary those that are malignant. Low-grade mucoepidermoid carcinomas may be invasive, but the prognosis is usually good, with a 5 year survival rate of 90%. High grade can metastasize and have a 5year survival of 50%.
|
|
|
17 year old girl notices a small, sensitive, gray-white area forming along the lateral border of her tongue 2 days before the end of her final examinations. Afebrile. Shallow, ulcerated, .3cm lesion with an erythematous rim. No therapy is given, and the lesion disappears within 2 weeks. No history of tobacco. Diagnosis?
|
Aphthous ulcer, also known as a canker sore. The lesions are never large but are annoying and tend to occur during periods of stress. Aphthous ulcers are not infectious; they probably have an autoimmune origin.
|
|
|
What is a superficial candidal infection that occurs in diabetic, neutropenic, and immunocompromised patients
|
Oral Thrush
|
|
|
How do herpetic lesions in the mouth appear
|
They are typically vesicles that can rupture
|
|
|
What appears as white patches of thicker mucosa from hyperkeratosis
|
Leukoplakia. It may be a precursor to squamous cell carcinoma in a few cases
|
|
|
What is the name for inflammation of a salivary gland
|
Sialadenitis. It is typically a minor salivary gland in the oral cavity, and may produce a localized, tender nodule
|
|
|
5 year old boy with repeated earaches, accompanied by a red, bulging tympanic membrane, either unilaterally or bilaterally, sometimes with a small amount of yellowish exudate. S. aureus and P. aeruginosa present. Right tympanic membrane has perforated. Responsive to antibiotics. What complication is likely to occur as a consequence of these events?
|
Cholesteatoma. These are not true neoplasms, but they are cystic masses lined by squamous epithelium. The desquamated epithelium and keratin degenerates, resulting in cholesterol formation and giant cell reaction. Although their histologic findings are benign, cholesteatomas can gradually enlarge, eroding and destroying the middle ear and surrounding structures. They occur as a complication of chronic otitis media. Although cholesteatomas have a squamous epithelial lining, malignant transformation does not occur
|
|
|
What is an abnormal bone deposition in the ossicles of the middle ear that results in bone deafness in adults
|
Otosclerosis
|
|
|
What is labyrinthitis typically caused by
|
A viral infection, and is usually self-limited
|
|
|
An eosinophilic granuloma of bone, which occasionally may be seen in the region of the skull in young children, is characterized by what
|
The presence of Langerhans cells
|
|
|
17 year old girl is concerned about a bump on her neck that she has noticed for several months. Does not seem to have increased in size. Discrete, slightly movable nodule in the midline of the neck just above the thyroid gland. Cystic mass lined by squamous and respiratory epithelium. What additional histologic elements would most likely be located adjacent to this cyst?
|
Thyroid tissue. The location of this nodule is classic for a thyroglossal duct (tract) cyst, which is a developmental abnormality that arises from elements of the embryonic thyroglossal duct extending from the foramen cecum of the tongue down to the thyroid gland. One or more remnants of this tract may enlarge to produce a cystic mass. Although lymphoid tissue often surrounds these cysts, malignant transformation does not occur. The cysts may contain squamous epithelium, but squamous cell carcinoma will not arise from such a cyst.
|
|
|
21 year old woman with lump on the left side of her neck that has remained the same size for the past year. Painless, 2cm nodule beneath the skin of the left lateral neck just above the level of the thyroid cartilage. Granular and keratinaceous cellular debris. Diagnosis?
|
Branchial cyst, also known as lymphoepithelial cysts. These may be remnants of an embryonic branchial arch or a salivary gland inclusion in a cervical lymph node. They are distinguished from thyroglossal duct cysts by their lateral location, the absence of thyroid tissue, and their abundant lymphoid tissue
|
|
|
Where do mucoceles form
|
Minor salivary glands
|
|
|
Where do mucoepidermoid tumors form
|
In salivary glands
|
|
|
What are solid tumors that may arise deep in the region of the carotid body near the common carotid bifurcation
|
Paragangliomas
|
|
|
76 year old man has been bothered by pain on the left side of the face for 2 weeks. Tender area of swelling 4cm diameter beneath the skin, anterior to the left auricle above the angle of the jaw. Patient somnolent and has mild muscular rigidity and expressionless facies. CT cystic and solid areas in the region of an enlarged left parotid gland. Minimal improvement with antibiotics. Acute and chronic inflammation, with fibrosis and abscess formation, and atrophy of acini. S. aureus present. Diagnosis?
|
Sialadenitis, which is more common in older persons and persons receiving phenothiazine therapy for schizophrenia, such as Thioridazine. Most neuroleptic drugs are domaninergic receptor blockers, but they have extrapyramidal and anticholinergic side effects. The dry mouth, coupled with dehydration, favors inspissation of salivary gland secretions and stone formation to block ducts, and increases the risk of inflammation and infection.
|
|
|
What is Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) deficiency associated with
|
Cheilosis
|
|
|
55 year old woman with enlarging lump on the right side of her neck for the past 7 months. 3cm nodule in the right upper neck, medial to the sternocleidomastoid muscle and lateral to the trachea at the angle of the mandible. CT circumscribed, solid mass adjacent to the carotid bifurcation. Nests of round cells with pink, granular cytoplasm. Marks chromogranin and S-100. EM neurosecretory granules in the tumor cell cytoplasm. Recurs 1 year later. Diagnosis
|
Paraganglioma, which is a neuroendocrine tumor that rarely produces sufficient catecholamines to affect blood pressure, unlike their adrenal medullary counterpart, the pheochromocytoma. Metastases should be considered in a patient of this age
|
|
|
Where does a Warthin tumor arise
|
A salivary gland
|
|
|
28 year old singer who has noticed that his voice quality has become progressively hoarser over the past year. Afebrile. No palpable masses in the head and neck area. No cough or significant sputum production, but he has been advised to give up smoking. Diagnosis?
|
Reactive nodule. Vocal cord polyps, or "singer's nodules," occur most often in men who are heavy smokers or who strain their vocal cords. The nodules are generally only a few millimeters in size and have a fibrovascular core covered by hyperplastic and hyperkeratottic squamous epithelium. Not premalignant
|
|
|
What is an acute laryngotracheobronchitis that occurs in children and produces airway narrowing with inspiratory stridor
|
Croup
|
|
|
3 year old child with difficulty breathing for past 24 hours. Febrile, harsh cough with prominent inspiratory stridor. Lungs clear. Subglottic edema. O2 sat normal. Improves over the next three days while taking nebulized glucocorticoids. What caused this
|
Parainfluenza virus. The child has croup, a laryngotracheobronchitis that is most often caused by parainfluenza virus. The inflammation may be severe enough to produce airway obstruction
|
|
|
What virus is associated with laryngeal papillomatosis
|
Human papillomavirus
|
|
|
20 year old man with progressive swelling on the left side of his face for the past year. Painless swelling in the region of the left posterior mandible. CT circumscribed multilocular cyst of the left mandibular ramus. Surgically excised with wide bone margins. Cysts lined with stratified squamous epithelium with a prominent basal layer; no inflammation or granulation tissue is seen. Diagnosis?
|
Odontogenic keratocyst. This is the typical location and histology for an odontogenic keratocyst which arises from rests of odontogenic epithelium within the jaw. They are benign but can recur if inadequately excised
|
|
|
What are two tumors arising from odontogenic epithelium
|
Ameloblastoma and odontoma
|
|
|
What lesion originates around the crown of an unerupted tooth, typically the third molar, and is lined by a thin, nonkeratinizing layer of squamous epithelium. Also contains a dense chronic inflammatory infiltrate in the stroma?
|
Dentigerous cyst
|
|
|
What are inflammatory lesions that develop at the apex of teeth as a complication of long-standing pulpitis?
|
Periapical cysts/granulomas
|

