![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Hemochromatosis |
Rare disease of iron metabolism; excess in deposits throughout the body |

|
|
|
Glycogen Storage Disease |
Inherited disease; abnormal storage and accumulation of glycogen in the tissues, especially the liver and kidneys |

|
|
|
Budd-Chiari Syndrome |
Caused by thrombosis of hepatic veins or IVC; primary-congenital webbing, secondary-thrombosis |

|
|
|
Fatty liver |
Acquired, reversible disorder of metabolism resulting in an accumulation of triglycerides within the hepatocytes; mild, moderate, or severe |
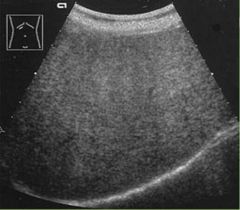
|
|
|
Cirrhosis |
Chronic degenerative disease of the liver |

|
|
|
Simple hepatic cyst |
Usually found incidentally (mostly in women) because most patients are asymptomatic |

|
|
|
Diffuse hepatocellular disease |
Affects hepatocytes and interferes with liver function throughout liver and measured through liver function tests |

|
|
|
Portal hypertension |
May develop when hepatopetal flow is impeded by thrombus or tumor invasion; dilation of PV >13mm |

|
|
|
Cavernous hemangioma |
Benign, congenital tumor consisting of large, blood-filled cystic spaces; more frequent in women and the most common benign tumor of the liver (aka tumbleweed) |

|
|
|
Focal nodular hyperplasia |
Asymptomatic mass thought to arise from developmental hyperplastic lesions related to an area of congenital vascular formation; 2nd most common benign liver mass |

|
|
|
Liver cell adenoma |
Tumor of the glandular epithelium in which the cells of the tumor are arranged in a recognizable glandular structure |

|
|
|
Hepatitis |
Inflammatory and infectious disease of the liver; 6 types: Hep A-G; acute- clinical recovery within months, chronic-inflammation past 6 months with small necrotic patches of cells |

|
|
|
Liver disease classifications |
Hepatocellular disease-hepatocytes are primary problem Obstructive disorders-something is blocking liver and making it sick |
|
|
|
Shunts |
Closing the portal system and redirecting blood flow to venous system; portacaval-connects MPV at portal confluence to anterior IVC, mesocaval-connects mid-distal SMV to IVC, splenorenal-connects splenic vein to left renal vein, TIPS (transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt)-uses metallic expandable stents |
|
|
|
Polycystic liver disease |
Inherited autosomal neonatal dominant disorder |

|
|
|
Pyogenic abscess |
Pus forming mass from a bacterial infection coming from vessels, contagious infection,or trauma |

|
|
|
Hepatic candidiasis |
Cyst caused by candida parasite in immunosuppressed hosts |

|
|
|
Amebic abscess |
Collection of pus formed by disintegrated tissue in a cavity caused by Entamoeba histolytica parasite that travelled from intestines through portal system when ingesting contaminated water/food |

|
|
|
Echinococcal Cyst |
(aka hydatid disease-honeycomb/lily pad structure) infectious cystic disease caused by a tapeworm larvae burrowing through intestines and into the portal system common in sheep-herding areas; 2 layers-inner and outer |

|
|
|
Pneumocystis carinii |
Most common organism causing infection with patients with HIV, aired filled cyst |
|
|
|
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) |
Most common primary malignant neoplasm, more frequent in menformed from cirrhosis, chronic Hep B, and hepatocarinogens in food |

|
|
|
Metastatic disease |
Most common of neoplastic involvement, primary sites-lungs, colon, breast |

|
|
|
Lymphoma |
Malignant neoplasm involving lymphocyte proliferation in lymph nodes; Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin |

|

