![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
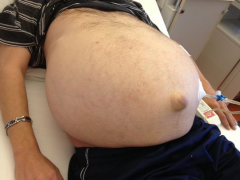
|
Ascites (edema of peritoneal cavity) |
|
|
Dependent pitting edema |
High hydrostatic pressures are at the greatestdistance from the heart (legs and feet) -pitting means that when you press down on it, it leaves a depression and doesn't goes back to normal slower than it should. |
|
|
Periorbital edema |
Happens with nephrotic syndrome, in which edema affects all parts of the body equally. However, initally edema happens in places with loose connective tissue matrix, and the periorbital area is one of them. |
|
|
Anascara |
Generalized edema, usually happens in infants. |
|
|
Lung biopsy in CHF patient shows edema in alveoli. This is caused by: |
Increased hydrostatic pressure in the arteriolar arteries, so they push fluid into alveolar septa, causing edema (pinkish alveolar septa instead of white) |
|
|
CHF causes reduced cardiac output and renin-angiotensin aldosterone activation due edema caused by what? |
-INCREASED hydrostatic pressure |
|
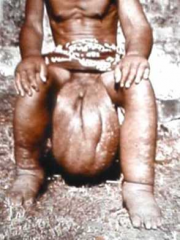
Name the diseaes and what causes it. |
-Lymphatic Filariasis (causes elephantiasis of lower limbs) -Caused by lymphatic obstruction, which stops excess interstitial fluid from being drained, and causes edema. |
|
|
Brain edema |
Serious and can be rapidly fatal. Brain substance can herniate (Ex: be pushed through foramen magnum) or brain stem vascular supply can become compressed. This causes death. |
|
|
What happens to alveoli in pulmonary edema? |
Fluid gets in alveolar spaces and around capillaries. This impedes oxygen diffusion. *Also creates favorable environment for bacterial infection. |
|
|
Nephrotic syndrome or renal dysfunction edema: |
-edema equally throughout body, but initially manifests in tissues with loose connective tissue. |
|
|
Chronic pulmonary congestion shows what in microscope view of alveoli? |
-fibrosis and cell death -edema -hemosiderin-laden macrophages (yellow-brown color) |
|
|
Hyperemia |
-active -arterolar dilatation and increased blood flow -red, engored with oxygenated blood -Caused by inflammation or exercising skeletal muscle |
|
|
Congestion |
-passive -impaired outflow of venous blood -cyanosis -long standing congestion leads to hypoxia, death and fibrosis, edema. |
|
|
Petechiae are due to what? |
-platelet deficiency |
|
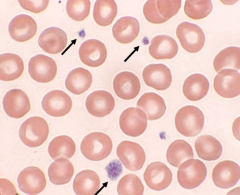
Arrows pointing to? |
Platelets y'all. |
|
|
At the final stage of coagulation: |
Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin. |
|
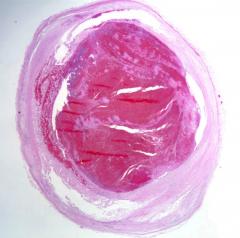
What is one way to know this is a clot developed before death? |
Lines of Zahn |
|
|
Thrombi inevitably form around vascular catheters because of: |
-endothelial injury -impeded blood flow (stasis) -thrombogenicity of foreign material -turbulent blood flow (if blood turbulently goes around it) |
|
|
Most common genetic hypercoagulability disorder |
Factor V Leiden mutation |
|
|
-Prothrombin mutation -Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase homozygous mutation -anti-thrombin 3 deficiency -protein C deficiency -protein s deficiency What types of disorders are these? |
primary hypercoagulability (genetic) |
|
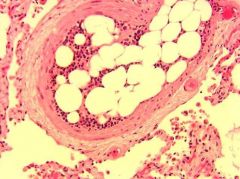
What type of embolism? |
Fat embolism -can happen after fractures of long bones. Fat comes from bone marrow. -or can happen from soft tissue tramua or burns. |
|
|
Most infarcts are what shape? |
Wedge-shaped -occluded arteryat the apex and the periphery ofthe organ forming the base. |
|
|
Why are pulmonary infarcts hemorrhagic? |
Because the lungs have a dualblood supply,85% from the pulmonary arteries and 15% from the bronchial arteries. -Bronchial arteries alone aren't enought to sustain tissue, but blood from them pours into necrosed tissue caused by embolus in pulmonary arteries. |
|
|
Amniotic fluid embolism |
amniotic fluid in mom's blood -see fetus sqaumous cells (baby sqaumes!) |
|
|
DIC |
disseminated intravascular coagulation - widespread fibrin thrombi in the microcirculation. -not visible on gorss inspection, but readily apparent microscopically. |
|

? |
Lines of Zahn -pink: red blood cells -pale: fibrin and platelets -seen in clots that formed before death. |
|
|
Causes of secondary (acquired) hypercoagulability: |
-surgery -cancer -trauma -bed-ridden state -disseminated intravascular coagulation -heparin-induced thrombocytopenia -antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. |

