![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sympathetic response
|
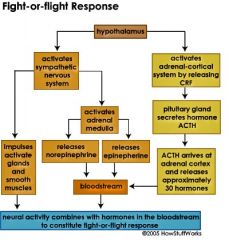
To produce the fight-or-flight response, the hypothalamus activates two systems: the sympathetic nervous system and the adrenal-cortical system. The sympathetic nervous system uses nerve pathways to initiate reactions in the body, and the adrenal-cortical system uses the bloodstream. The combined effects of these two systems are the fight-or-flight response
|
|
|
adrenal medulla
|
release epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) into the bloodstream. These "stress hormones" cause several changes in the body, including an increase in heart rate and blood pressure
|
|
|
the hypothalamus releases
|
corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) into the pituitary gland, activating the adrenal-cortical system. The pituitary gland (a major endocrine gland) secretes the hormone ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone). ACTH moves through the bloodstream and ultimately arrives at the adrenal cortex, where it activates the release of approximately 30 different hormones that get the body prepared to deal with a threat.
|
|
|
fear
|
fear
|
|
|
implications of stress and the ability to heal
|
Medical research suggests that up to 90 percent of all illness and disease is stress-related
Evidence shows chronic stress can lower immunity and make people more susceptible to infections. Stress has been shown to contribute to the development of heart disease and high blood pressure. Skin doctors have found that many skin conditions, such as hives and eczema, are related to stress. cause of everyday aches, pains, and health problems, such as headaches, backaches, stomachaches, diarrhea, sleep loss, and loss of sex drive. Stress also appears to stimulate appetite and contribute to weight gain. |
|
|
Cortisol
|
The adrenal cortex is activated during stress by ACTHThe adrenal cortex is activated during stress by ACTH
One of the primary effects of cortisol is the stimulation of gluconeogenesis, or the formation of glucose from noncarbohydrate sources, such as amino or free fatty acids in the liver. |
|
|
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
|
protein hormone that is produced in the hypothalamus, stored in and released from the posterior pituitary, and acts to increase water reabsorption in the kidney.
( |
|
|
Immune response to stress
|
Stress hormones, especially glucocorticoids (cortisol), have been used therapeutically as powerful antiinflammatory/immunosuppressive agents. This has lead to the conclusion that stress, in general, decreases immunity and inflammation. Data suggests, however, that glucocorticoids and catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) at concentration levels reached during stress may paradoxically result in decreased cellular immunity and increased autoimmune (humoral) responses.
|
|
|
Coping mechanisms
|
AN INDIVIDUAL STRESS MANAGEMENT PROGRAM
Positive thinking. Refocus the negative to be positive. Make an effort to stop negative thoughts. Plan some fun. Take a break. Physical activity: Nutrition: Social support: Relaxation: |
|
|
Endorphins
|
Opiates that are released into the blood as part of the response to stressful stimuli
|

