![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is dyspnea
|
difficult or labored breathing; SOB; air hunger
|
|
|
S/sx dyspnea
|
wheeze, anxious or distressed expression; flaring nostrils; gasping
|
|
|
What is orthopnea
|
dyspnea on lying down
|
|
|
What is Kraussmaul resp pattern
|
Consistent, very deep breathing; metabolic acidosis
|
|
|
what is tuberculosis
|
infectious lung disease - previously called consumption; airborne droplets
|
|
|
causes of tb
|
mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
|
|
S/sx tb
|
cough that produces purulent sputum develops slowly; night sweats, fatigue, fever, chills, pleurisy, caseous necrosis
|
|
|
What are Ghon complexes?
|
granulomas of Tb
|
|
|
Tx for TB?
|
Combinations of 4 drugs at once to reduce the chance of antibiotic resistance; 6-9 months
|
|
|
What is pneumonia
|
inflammatory process that can involve all or part of the lungs
|
|
|
cause of pneumonia
|
infection of respiratory tract
|
|
|
S/sx Pneumonia
|
High fever, cough, malaise, breathlessness, symptoms vary upon individual, severity of infection, and causative agent
|
|
|
Tx for pneumonia
|
antibiotics for bacteria, no effective tx for viral pneumonia; supplemental O2
|
|
|
What are two major differences between pneumonia and tuberculosis?
|
Tb can affect other tissues and organs; Tb requires significantly longer treatment than pneumonia does.
|
|
|
what is acute bronchitis
|
inflammation of the bronchial tree caused by infection or irritating factors (smoke)
|
|
|
s/sx of acute bronchitis
|
Productive cough*, chest pain, congestion, wheezing, fever, chills, Difficulty breathing
|
|
|
Tx for acute bronchitis
|
antibiotics, rest
|
|
|
what are the three main types of COPD?
|
Chronic bronchitis; emphysema; asthma
|
|
|
What is chronic bronchitis?
|
inflammation of bronchioles with excess mucus production; bronchitis > 3 months for two or more consecutive years; airway obstruction and hyperplasia of mucus-producing glands
|
|
|
Causes of chronic bronchitis
|
long term pulmonary disorders; smoking; scarring and damage of tissue
|
|
|
S/sx chronic bronchitis
|
BLUE BLOATERS; hypoxemia and polycythemia; productive cough, sob, dib, wheezing
|
|
|
What is emphysema?
|
alveolar destruction - alveoli don't collapse
|
|
|
causes of emphysema?
|
smoking/secondhand smoke, genetic
|
|
|
S/sx emphysema?
|
PINK PUFFERS; increased RR; cough, dyspnea, fatigue, weight loss, clubbing, barrel chest
|
|
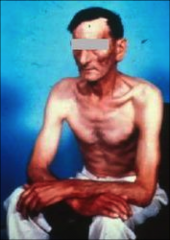
what kind of patient is this?
|
pink puffer - emphysema; ↑ ventilation & ↓ cardiac output
|
|
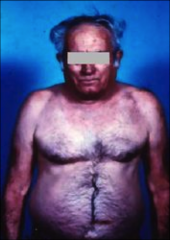
what kind of patient is this?
|
Blue bloater - chronic bronchitis; ↓ventilation & ↑ cardiac output
|
|
|
what is asthma?
|
inflammatory airway disorder with bronchoconstriction
|
|
|
causes of asthma
|
allergies, URI, exercise, cold air, pollution
|
|
|
s/sx asthma
|
cough, wheezing due to difficulty breathing out, mucus production, use of accessory muscles, SOB
|
|
|
what is pulmonary embolism
|
occlusion of a portion of the pulmonary vascular bed by an embolus; can cause infarction; if no infarction, clot will be dissolved by fibrinolytic system
|
|
|
S/sx of pulmonary embolism
|
sudden onset - chest pain and SOB; wheezing, cyanosis, syncope;
|
|
|
S/sx cystic fibrosis
|
persistent cough, wheezing, frequent infections, clubbing and barrel chest develop over time; frequent loose, oily stools
|
|
|
what is bronchiectasis
|
obstruction or infection with inflammation and destruction of the bronchi so that there is permanent dilation
|
|
|
causes of bronchiectasis
|
infection - acute or chronic; CF, TB
|
|
|
S/sx bronchiectasis
|
productive cough - foul-smelling, bloody; DIB, fatigue, clubbing, cyanosis
|
|
|
what is atelectasis?
|
collapsed lung
|
|
|
causes of atelectasis?
|
immobility - bed rest or anesthesia; lung diseases, foreign objects, tumors; obstruction
|
|
|
s/sx atelectasis
|
DIB, chest pain, cough
|
|
|
what is coccidioidomycosis (valley fever)?
|
fungal infection acquired by inhaling the arthrospores in the southwest dust
|
|
|
what are erythema nodosum?
|
painful nodules in the lower legs - valley fever
|

