![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
RBCs |
round, slightly refractile, and lack internal structure and resemble fat droplets |
|
|
WBCs |
round, granular, large than rbcs but smaller than epithelial cells |
|
|
hyaline cast |

|
|
|
cellular |

|
|
|
waxy cast |

|
|
|
granular cast |

|
|
|
Mucus |
narrow, twisted, ribbon-like, homogenous threads and indicates urethral irritation or genital secretion |
|
|
Fat |
highly refractile, variable-sized spheres that are out of focus with other sediments because they rise to the surface and may be stained with Sudan III. |
|
|
fat |
Signifies no pathologic relevance in the urine |
|
|
sudan III |
fat is stained by |
|
|
cocci in chains |

|
|
|
cocci wit wbc |

|
|
|
rods with wbc |
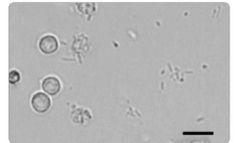
|
|
|
rods with wbc and rbc |
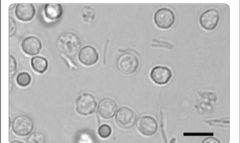
|
|
|
spermatozoa |
indicate contamination of the urine and are normal in dogs |
|
|
• Magnesium Ammonium Phosphate • Calcium carbonates and Calcium oxalate dihydrate |
Normal Crystals |
|
|
• Pigmented crystals • Amino Acid Crystals • Oxalate Crystals |
Abnormal Crystals |
|
|
struvite crystals |

|
|
|
small struvite crystals |
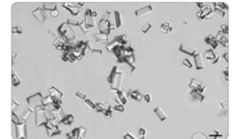
|
|
|
calcium oxalate monohydrate (picket fence) |
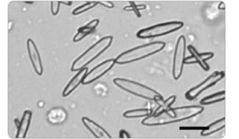
|
|
|
calcium oxalate monohydrate left- dumbbells right- hemp seed |
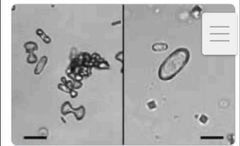
|
|
|
calcium oxalate dihydrate |

|
|
|
calcium oxalate dihydrate |

|
|
|
ammonium biureate crystal |

|
|
|
bilirubin crystal with wbc |

|
|
|
cholesterol crystal |

|
|
|
cystine crystal with rbc |

|
|
|
vaginal cytology |
Examination of exfoliated cells from the vagina of dogs and cats |
|
|
vaginal cytology |
Vaginal epithelium undergoes a predictable hyperplastic response to increasing plasma estrogen concentrations during proestrus |
|
|
cotton-tipped swabs microscope slide methanol |
vaginal smear materials |
|
|
hormone analysis |
Often in tandem with ______ , may provide valuable information about the stage of the ovarian cycle |
|
|
inflammatory neoplastic |
Proven useful to detect ______ and _____ conditions in the female reproductive tract |
|
|
caudal |
Cells are obtained by passing a cotton- tipped swab into the _____ vagina |
|
|
sterile saline |
If no vaginal discharge is present, the swab may be moistened with ______ to avoid discomfort |
|
|
urethral orifice |
Once cranial to the _______, the vaginal wall is gently swabbed |
|
|
true |
The smear is allowed to air-dry thoroughly before staining |
|
|
Romanowsky-type stains |
type of stain for vaginal cytology |
|
|
• Wright • Modified Wright-Giemsa stains |
specific stains |
|
|
Color |
intensity is primarily a reflection of the degree of urine concentration |
|
|
Transparency/Turbidity |
a reflection of the amount of particulate material |
|
|
Ammonia |
prominent in retained urine and formed by bacterial urease action |
|
|
Acetone |
suggests ketosis |
|
|
Foam |
produced by shaking |
|
|
Hemoglobinuria Proteinuria |
type of foams |
|
|
osmolality |
determined by the number of particles in the solution or by the osmotic pressure of the extracellular and intratubular fluids |
|
|
Specific gravity |
Indicates the ability of the kidneys to dilute or concentrate urine solute specifically in the collecting tubules. |
|
|
Indirectly proportional |
proportionality of specific gravity to urine volume |
|
|
Chemical Examination |
done on a semi-quantitative basis using reagent strips especially designed for use in humans and not all tests are either relevant or accurate in animals |
|
|
Protein |
size, shape, and charge influence its ability to pass the glomerular filt |
|
|
• Emotional state (fright) • General anesthesia |
Physiological reasons |
|
|
• Hemorrhage into the urinary tract • Inflammation within the urinary tract |
Pathological causes
|
|
|
Glucose |
Freely filtered by the glomerulus and resorption is complete in the proximal tubules when serum concentrations are <180 mg/dl (dog) 280 (cat) < 100 (cow) |
|
|
• Hyperglycemia• Normoglycemia |
factors affecting glucose |
|
|
Ketones |
Freely filtered by the glomerulus and are completely resorbed by the proximal tubules |
|
|
Bilirubin |
Conjugated and not conjugated forms of this (bound to serum albumin) may pass into the glomerular filtrate and not be absorbed by the tubules. |
|
|
• Hematuria • Hemoglobinuria • Myoglobinuria |
Occult Blood Causes |

