![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
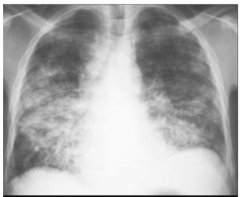
Pt with bronchopneumonia, Bilateral patchy infiltrate
|
|
|
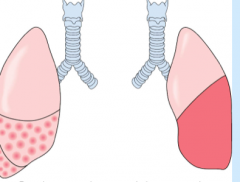
Lobar pneumonia: Strep pneumoniae, intraalveolar infiltrate
Left is bronchopneumonia Right is lobar pneumonia |
|
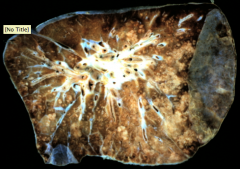
|
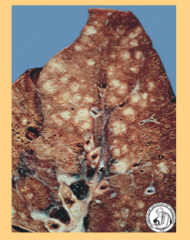
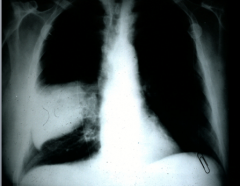
Multifocal areas of consolidation through the lung
Second pic is Multiple areas of induration and consolidation |
|
|

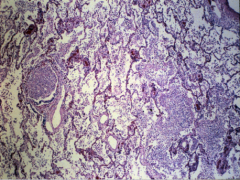
Bronchioles full of pus, the neutrophils have gone out to the alveoli sacs and this is what corresponds to areas of consolidation.
Second pic is Pts can develop subplural abscess. |
|
|

Lobar pneumoia…localized siteinvolving only one lobe (bronchopneumonia, there was bilateral patchy infiltrates)
Second pic is Lobe completely consolidated |
|
|
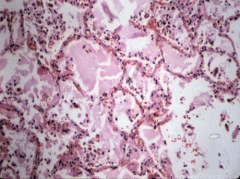
lobar pneumoniae congestion Early disease..looks like edema
|
|

|
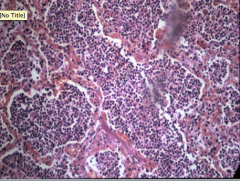
Lobar pneumonia Red hepatization
|
|
|
Lobar pneumoniae gray hepatization
|
|
|
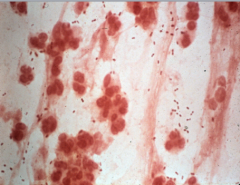
Sputum with person with lobar pneumonia. Two things of significance, the background inflammatory cells are almost exclusively neutrophils. Characteristic bacteria stained strep pneumo.
|
|
|
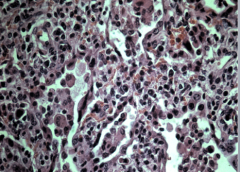
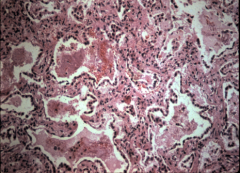
Widening of alveoli septa is due to the infiltration of inflammatory cells. Widening causes irritation and causes the patients to cough but there is no pus
|
|
|
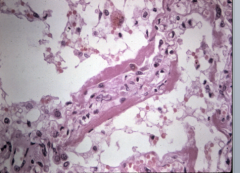
Severe case where there is diffuse alveolar damage, hyaline membrane formation
Atypical pneumoniae |
|

|
Pt who died of pneuomia. Small bronchiole lined by cells with inclusions (adenovirus)
-atypical pneumonia |
|

|
Heres a lung of a patient who pneumonia alba, rare finding.
|
|
|
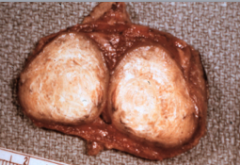
Segment of lung tissue with sclerotic tissue, a ghon complex,
|
|
|
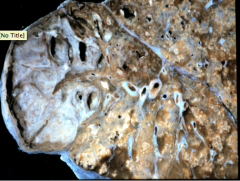
Manifestation of someone with secondary reactivated disease, it is a lung with miliary tb. It is patchy and multifocal and upper lobe cavitary disease, where the initial infection took place, reactivated and disseminated
|
|
|
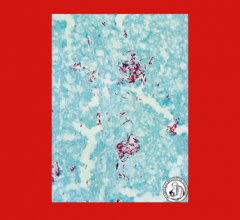
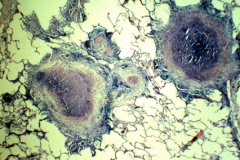
Characteristic feat of the infection, you see caseating granulomas with necrosis in the center of granuloma
second pic is acid fast stain |
|
|
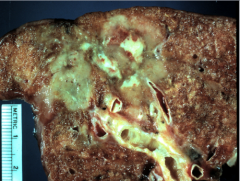
Example of localized aspiration of pneumonia. Nothing tells you here that this is aspiration
|
|
|
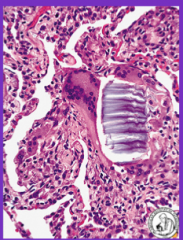
Formed body vegetable material, indicative of aspiration
|
|
|
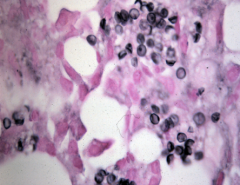
Disc like structures are pneumocystic. Not clinically signiciant unless immune system is compromised.
|

