![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
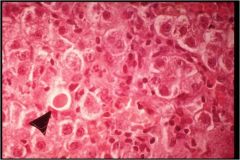
Photo shows apoptotic hepatocytes common pattern of liver cell injury:
Pt with liver damage often present with peripheral edema, cerebral dysfunction and hyper erythema & spider angioma of skin, all are the MOA, EXCEPT: a. hyperammonemia b. hyperalbuminemia c. hypoalbuminemia d. hyperestrogen |
hyperammonemia --> cerebral dysfunciton
hypOalbuminemia --> peripheral edema hyperEstrogen --> hyper erythema and spider angioma |
|
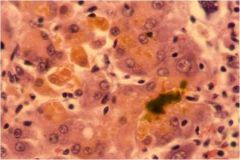
Photo shows choleostatsi in the liver can't store bile due to apoptosis of hepatocyes
The liver has many functions, results of hyperestrogen can be due to damage of what liver funciton a. synthesis b. metabolism c. clearance of hormones d. phagocytosis e. storage |
c. clearance of hormones (can't clear Estrogen it accumulates)
• Synthesis: plasma proteins, endogenous lipids & lipoproteins, coagulation factors, glycogen & glucose • Metabolism: Drugs, toxins, bilirubin • Phagocytosis: bacteria, Ag/Ab complexes • Storage: glycogen, iron, vitamins A,D,B12 • Hormone synthesis: angiotensinogen, insulin-like growth factor I, T3 • Clearance of hormones: insulin, PTH, estrogen, cortisol |
|

Acute hepatic failure is often due to all EXCEPT:
a. etoh b. toxic chemical exposure c. mushroom exposure d. SHOCK |
• Acute hepatic failure
Toxic chemical exposure (carbontetraCl-) Drug reaction (Tylenol 50%) Mushroom poisoning Shock liver (hypotension, septic, ARDS) etoh usually leads to cirrohsis |
|
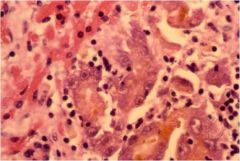
Pt presents with jaundice, peripheral edema, spider angiomas on skin and hyper erythema, you also notice a 'musty' odor. You r/o any chemical, viral, or mushroom causing this massive hepatic necrosis. Pt admits to high use of this medication?
a. propranalol b. NSAID c. ASA d. acetominophen |
long standing acetominophen Tylenol use can result in massive hepatic necrosis
|
|
|
Neonatal jaundice and hemolyisis often results in an increase in UNCONJUGATED bilirubin for varying reasons, in neonates it is because they are not able to conjugate bilirubin due to decreased liver function, while with hemolysis:
a. liver hepatocytes get damaged b. biliary obstruction c. bilirubin can't be transported d. increase in RBC production can't keep up with degradation |
a. liver hepatocytes get damaged --> trauma/iinjury
b. biliary obstruction --> leads to increase in CONJUGATED bilirubin c. bilirubin can't be transported --> Dubin Johnson defect in receptor leads to increase in CONJUGATED bilirubin d. increase in RBC production can't keep up with degradation YES |
|
|
While Crigler-Najjar disease leads to an increase in unconjugated bilirubin due to failure of conjugation mechanism, why does Dubin Johnson lead to an increase in CONJUGATED bilirubin
a. liver hepatocytes get damaged b. biliary obstruction c. bilirubin can't be transported d. increase in RBC production can't keep up with degradation |
failure of transport
a. liver hepatocytes get damaged --> trauma/iinjury b. biliary obstruction --> leads to increase in CONJUGATED bilirubin c. bilirubin can't be transported --> Dubin Johnson defect in receptor leads to increase in CONJUGATED bilirubin YES d. increase in RBC production can't keep up with degradation leads to increase in UNCONJUGATED |
|
|
The liver and the intestines are important sites for metabolism of bilirubin. In the liver bilirubin is glucorinated, while in the gut
a. bilirubin is bound to albumin b. bilirubin results from degradation of RBC's c. bacteria conjugate bilirubin d. bacteria deconjugae bilirubin |
in the gut bacteria deconjugate bilirubin resulting in in UNCONJUGATED bilirubin
|
|
|
Pt presents with elevated AST and ALT, what part of liver function is damaged
a. hepatocyte integrity b. hepatocyte function c. damage to bile canaliculi d. hepatocyte metabolism |
hepatocyte integrity
|
|
|
Pt presents with hyperestrogenemia, you can assume
a. damage to hepatocyte integrity b. damaged biliary c. damaged bile canaliculi d. chronic liver damage |
chronic liver damage, since the liver can no longer degrade estrogen so it is building up
|
|
|
Liver fibrosis results in apotptotic hepatocyes, the initial cells activated are Kupffer cells as they secrete several cytokines, which activate stellate cells
a. TGF beta b. MCP-1 and TNF c. PDGF and TNF d. MCP-1 and TGF beta |
PDGF and TNF --> activate stellate cells
ET-1 --> contraction of stellate cells TGF-beta --> fibrionogenesis |

