![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
.
|
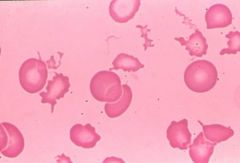
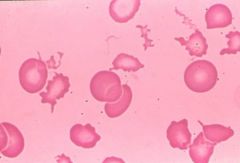
Acanthocytes
Liver Disease. |
|
.
|
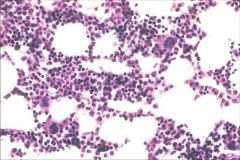
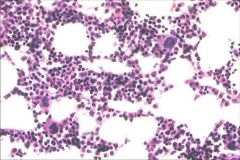
BM core
|
|
.
|
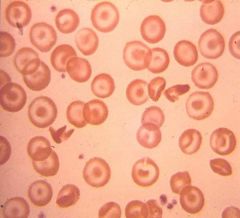
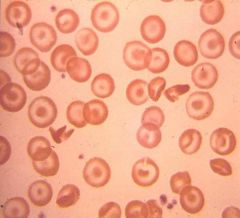
Target Cell / Codocyte
Extra membrane (obese belly pudges out) Manifests with microcytic anemias caused by: Iron deficieny Thalassemias Decreased heme production (sideroblastic) Severe anemia of chronic disease |
|
.
|
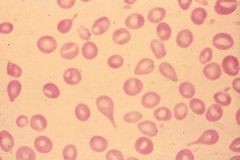
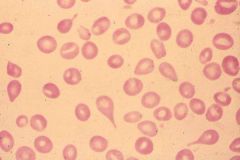
Teardrop cell / Dacrocytes
Myelophthisic anemia Myelofibrosis |
|
.
|
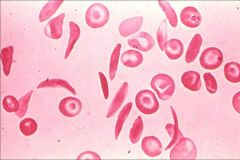
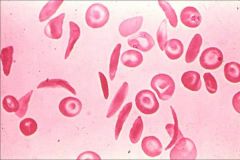
Sickle Cell / Drepanocytes
|
|
.
|
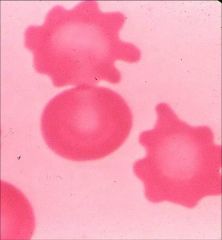
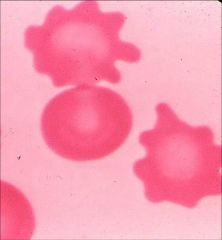
Burr cell / Echinocyte
Anemia of renal failure. Rare. |
|
.
|
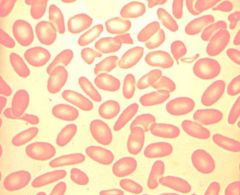
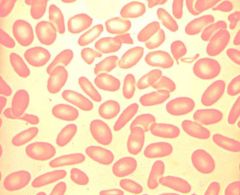
Ovalocyte / Elliptocytes
Hereditary elliptocytosis |
|
.
|
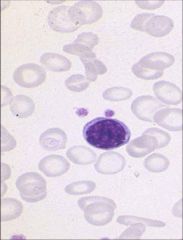
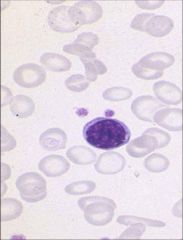
Microcytic
Impaired hemoglobin synthesis will result in microcytic anemia. Hemoglobin gives RBC its color -> hypochromic Remember acronym FLATS Fe+ Lead poisoning Anemia of chronic disease Thalassemia Sidero |
|
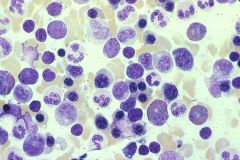
.
|
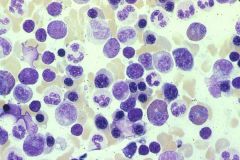
BM aspirate
|
|
.
|
Polychromasia: RBCs that are able to be stained with more than one stain (acids or bases)
|
|
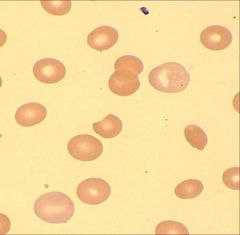
.
|
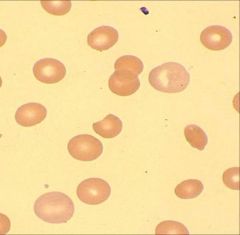
Polychromasia: RBCs that are able to be stained with more than one stain (acids or bases)
|
|
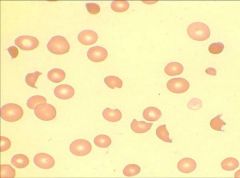
.
|
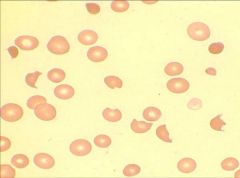
Schistocytes:
Seen in hemolytic anemia |
|
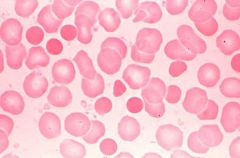
.
|
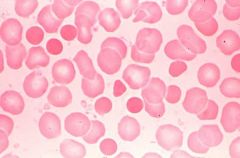
Spherocytes
Too little membrane (anorexic) Little red cells with no central pallor. Sometimes seen in immune hemolytic anemias or Hereditary Spherocytosis caused by decreased spectrin. RBC has normal volume but each time cell passes through spleen some membrane is taken away. "Hyperchromic" with increased MCHC is seldom seen in other forms of anemia. |
|
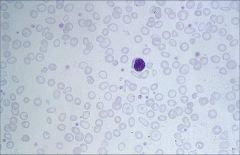
.
|
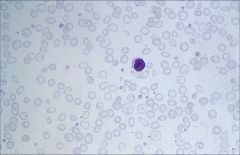
Microcytic, hypochromic
Decreased hemoglobin (hypochromic) Greater area of pallor Microcytic: Impaired hemoglobin synthesis will result in microcytic anemia. Remember acronym FLAT: Fe+ Lead poisoning Anemia of chronic disease Thalassemia |
|
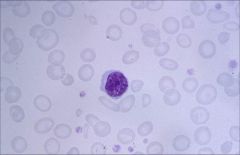
.
|
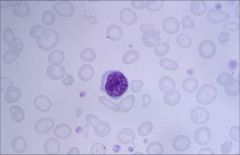
Microcytic
Decreased hemoglobin Greater area of pallor |
|
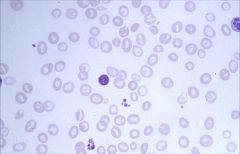
.
|
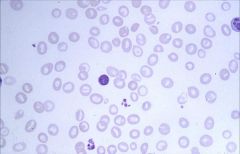
Macrocytic:
Impaired DNA synthesis results in enlarged cells because cells can't divide. Common causes are folate and B12 deficiency. Also caused by MDS, drugs, hypothyroidism. Macroovalocytes are large, oval-shaped RBCs that are well filled with Hgb and pathognomonic features of Megaloblastic Anemia! |
|
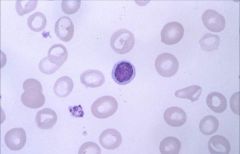
.
|
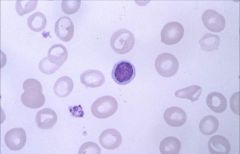
Macrocytic:
Impaired DNA synthesis results in enlarged cells because cells can't divide. Common causes are folate and B12 deficiency. Also caused by MDS, drugs, hypothyroidism. |
|
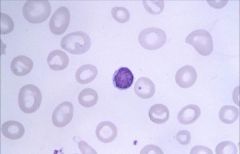
.
|
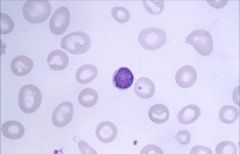
Macrocytic:
Impaired DNA synthesis results in enlarged cells because cells can't divide. Common causes are folate and B12 deficiency. Also caused by MDS, drugs, hypothyroidism. |
|
.
|
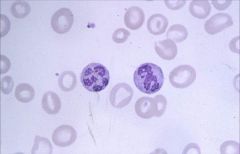
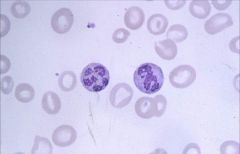
Polysegmented Neutrophil (greater than 5): seen in Macrocytic (Megaloblastic) Anemia.
Impaired DNA synthesis results in enlarged cells because cells can't divide. Common causes are folate and B12 deficiency. |
|
.
|
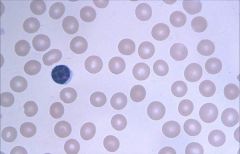
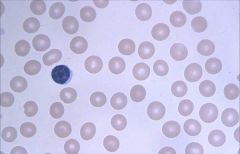
Normocytic, Normochromic
Common causes of this morphology of anemia: decreased RBC production, hemolysis, acute blood loss. There are no platelets in this smear. It happens to be aplastic anemia which shows pancytopenia. GET RETIC COUNT! Decreased count = aplastic or myelophthistic. Common cause = idiopathic, drugs, or cancer. Treat with immunosuppressive agents! |
|

.
|

BM biopsy showing aplastic anemia:
All 3 cell lineages fail to develop leading to pancytopenia. Different from Pure Red Cell Aplasia, which will only cause decreased numbers of RBCs. Produces a normocytic, normochromic anemia. |

