![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
26 YOWF presents with 3wk Hx single, rapidly growing mass in right volar forearm
|
nodular fasciitis
Age, Race, Sex Not Important Reactive fibroblastic proliferation morphologically similar to sarcoma but self limited volar forearm [ > chest > back] rapid ± painful growth over weeks poorly defined nodular drowth of deep dermis, subcutis, muscle Hist: swirls of spindle cells, mitoses, nucleoli |
|
|
|
23 YOWF presents 2 mo postpartum c rapidly growing mass in abdominal wall
|
Grey-white poorly demarcated rubbery iniltrated mass of uniform, plump fibroblasts; occur at many locations in the body, agressive local growth but do not met; tend to recur after excision
M=F 20 ± 10; F ≈ Abdominal Risk Factors: Pregnancy, APC inactivating mutations, Beta catenin activating mutations (APC = Tumor Suppressor, Beta Catenin = Oncogene) Tx: surgery; recur: tamoxifen, ChemoRx, Rad Abdominal desmoids arise in aponeurosis during or after pregnancy intra-abdominal desmoids involve mesentery or pelvic walls ± Gardner Sro Extra-Abdominal in shoulder, chest wall, back thigh |
|
|
|
Desmoid Tumors, Osteoma of the Calvarium, & Colon CA
|
Gardner Sro: APC KO
100% dvlp Colon CA |
|
|
|
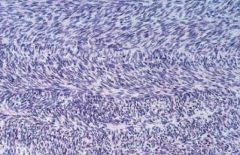
mass lesion
histology: herringbone pattern |
fibrosarcoma
retroperitoneum, thigh or around knee and distal extremities spindle shaped cells in herringbone pattern aggressive, high recurrence ± met; Childhood Good Px |
|
|
|
fibrosarcoma
retroperitoneum, thigh or around knee and distal extremities spindle shaped cells in herringbone pattern aggressive, high recurrence ± met; Childhood Good Px |
|
|
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta aka Brittle Bone Disease
An osteoporotic dz (not enough bone) [Mutated genes for a1 and a2 collagen subchains] Extreme skeletal fragility: joints, eyes, ears, skin & teeth Type 1: normal collagen, ↓ amt → normal lifespan increased childhood fx's [blue sclerae from visualized choroid, hearing loss from condxn problems, dental problems: small blue teeth] Type 2 Osteogenesis Imperfecta: no collagen → many intrauterine fx's → uniformly fatal |
|
|
|
blue sclerae, hearing loss, small misshapen blue teeth
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta aka Brittle Bone Disease
An osteoporotic dz (not enough bone) [Mutated genes for a1 and a2 collagen subchains] Extreme skeletal fragility: joints, eyes, ears, skin & teeth Type 1: normal collagen, ↓ amt → normal lifespan increased childhood fx's [blue sclerae from visualized choroid, hearing loss from condxn problems, dental problems: small blue teeth] Type 2 Osteogenesis Imperfecta: no collagen → many intrauterine fx's → uniformly fatal |
|
|
|
Collagen Produxn Enzyme KO
|
Type 2 Osteogenesis Imperfecta aka Brittle Bone Disease
no collagen → many intrauterine fx's → uniformly fatal Type 1: normal collagen, ↓ amt → normal lifespan increased childhood fx's [blue sclerae from visualized choroid, hearing loss from condxn problems, dental problems: small blue teeth] |
|
|
|
metastatic tumor found in lungs
histology: mix of epithelioid and spindle cells |
synovial sarcoma
t(X:18 translocation) SYT-SSX peaks 35 ± 15 Highly malignant soft ts tumor Arise ADJACENT to large joints: knee & thigh most common Few (<10%) intraarticular Behavior: 5 Year Px: Poor (40%) 10 Yr Px: Very Poor (30%) Mets to lung & Skeleton before regional LN's biphasic growth pattern of epithelial cell "gland" like formation and fibroblast-like spindle cells |
|
|
|
Erlenmyer Flask Bone Deformity
|
Defects in any of several metabolic pathways → Diffuse skeletal sclerosis: stonelike quality of bones: brittle, break like chalk
eg path: carbonic anhydrase deficiency: no acidity produced by osteoclasts Most commonly AR malignant type: death in infancy: fx, anemia, hydrocephaly & AD benign type: osteoporosis in adolescence, mild CN deficits, mild anemia Marble Bone Dz, Albers-Schonbert Dz Morph: Erlenmyer Flask Deformity: bones lack medullary canal, misshapen longbones with bulbous ends, no mature trabeculae, no room for marrow Complx: stenotic foramena, compressed nerves; primary spongiosa persists, no mature trabeculae, no hematopoietic marrow Possible Tx: bone marrow transplants |
|
|
|
osteoporosis in adolescence, mild CN deficits, persistent fatigue
|
Defects in any of several metabolic pathways → Diffuse skeletal sclerosis: stonelike quality of bones: brittle, break like chalk
eg path: carbonic anhydrase deficiency: no acidity produced by osteoclasts Most commonly AR malignant type: death in infancy: fx, anemia, hydrocephaly & AD benign type: osteoporosis in adolescence, mild CN deficits, mild anemia Marble Bone Dz, Albers-Schonbert Dz Morph: Erlenmyer Flask Deformity: bones lack medullary canal, misshapen longbones with bulbous ends, no mature trabeculae, no room for marrow Complx: stenotic foramena, compressed nerves; primary spongiosa persists, no mature trabeculae, no hematopoietic marrow Possible Tx: bone marrow transplants |
|
|
|
Defective Osteoclastic Fnx
|
Defects in any of several metabolic pathways → Diffuse skeletal sclerosis: stonelike quality of bones: brittle, break like chalk
eg path: carbonic anhydrase deficiency: no acidity produced by osteoclasts Most commonly AR malignant type: death in infancy: fx, anemia, hydrocephaly & AD benign type: osteoporosis in adolescence, mild CN deficits, mild anemia Marble Bone Dz, Albers-Schonbert Dz Morph: Erlenmyer Flask Deformity: bones lack medullary canal, misshapen longbones with bulbous ends, no mature trabeculae, no room for marrow Complx: stenotic foramena, compressed nerves; primary spongiosa persists, no mature trabeculae, no hematopoietic marrow Possible Tx: bone marrow transplants |
|
|
|
Marble Bone Dz
|
Defects in any of several metabolic pathways → Diffuse skeletal sclerosis: stonelike quality of bones: brittle, break like chalk
eg path: carbonic anhydrase deficiency: no acidity produced by osteoclasts Most commonly AR malignant type: death in infancy: fx, anemia, hydrocephaly & AD benign type: osteoporosis in adolescence, mild CN deficits, mild anemia Marble Bone Dz, Albers-Schonbert Dz Morph: Erlenmyer Flask Deformity: bones lack medullary canal, misshapen longbones with bulbous ends, no mature trabeculae, no room for marrow Complx: stenotic foramena, compressed nerves; primary spongiosa persists, no mature trabeculae, no hematopoietic marrow Possible Tx: bone marrow transplants |
|
|
|
Albers-Schonbert Dz
|
Defects in any of several metabolic pathways → Diffuse skeletal sclerosis: stonelike quality of bones: brittle, break like chalk
eg path: carbonic anhydrase deficiency: no acidity produced by osteoclasts Most commonly AR malignant type: death in infancy: fx, anemia, hydrocephaly & AD benign type: osteoporosis in adolescence, mild CN deficits, mild anemia Marble Bone Dz, Albers-Schonbert Dz Morph: Erlenmyer Flask Deformity: bones lack medullary canal, misshapen longbones with bulbous ends, no mature trabeculae, no room for marrow Complx: stenotic foramena, compressed nerves; primary spongiosa persists, no mature trabeculae, no hematopoietic marrow Possible Tx: bone marrow transplants |
|
|
|
Mosaic Pattern of Lamellar Bone
|
Paget disease aka Osteitis Deformans
Pathogenesis: integrated gene from measles → Osteoclast Dysfnx: furious osteolytic stage followed by hectic bone formation → burnt out osteosclerotic quiescence; stages variation by different sites; net gain in architecturally disordered bone mass; thick trebeculae w/ soft poros cortex. Pt: Western European Whites (England, France, Germany, US, Australia & NZ) Mid-adult onset Pathognomonic Histology: Mosaic Pattern of Lamellar Bone Dx: Radiography: enlarged bone w/ thick coarsened corticies and cancellous bone; Labs: increased blood AP & increased urinary hydroxyproline Presentation: Pain, difficult to hold head erect, compression of posterior fossa structures, severe osteoarthritis of femoral heads, bowing of tibiae, warm skin, high output heart failure Side 3/Different Card for Complications (p1216) |
|
|
|
von Recklinghausen Dz
|
Generalized osteitis fibrosa cystica = von Recklinghausen (Bone) Dz = ↑ brown cell activity, peritrabecular fibrosis and cystic brown tumors; hallmark of severe hyperparathyroidism;
X-ray pattern of radial aspect of middle phalanges of index & middle fingers Dissecting osteitis: tunnelling osteoclasts dissecting through trabeculae Brown Tumor: reactive fibrous ts 2° to microfx c hemorrhage; brown is vascularity + hemosiderin; Px: cystic degeneration |
|
|
|
Generalized osteitis fibrosa cystica
|
Generalized osteitis fibrosa cystica = von Recklinghausen (Bone) Dz = ↑ brown cell activity, peritrabecular fibrosis and cystic brown tumors; hallmark of severe hyperparathyroidism;
X-ray pattern of radial aspect of middle phalanges of index & middle fingers Dissecting osteitis: tunnelling osteoclasts dissecting through trabeculae Brown Tumor: reactive fibrous ts 2° to microfx c hemorrhage; brown is vascularity + hemosiderin; Px: cystic degeneration |
|
|
|
↑ brown cell activity, peritrabecular fibrosis and cystic brown tumors
|
Generalized osteitis fibrosa cystica = von Recklinghausen (Bone) Dz = ; hallmark of severe hyperparathyroidism;
X-ray pattern of radial aspect of middle phalanges of index & middle fingers Dissecting osteitis: tunnelling osteoclasts dissecting through trabeculae Brown Tumor: reactive fibrous ts 2° to microfx c hemorrhage; brown is vascularity + hemosiderin; Px: cystic degeneration |
|
|
|
Brodie Abscess
|
small intraosseus abscess that freq involves cortex and is walled off by reactive bone
|
|
|
|
Involucrum
|
sleave of newly formed bone around infected, necrotic bone
|
|
|
|
Sequestrum
|
dead peice of bone; 2* to suppruation & ischemia
|
|
|
|
Tuberculous Osteomyelitis in the spine
|
Pott disease
breaks through IV discs to involve multiple vertebrae and exctends into soft ts to form abscesses; Presentation: pain c motion; local tenderness over spine, low grade fever, chills, weight loss Px: severe destrx of veretrae, compression fx's, kyphoscoliosis, neurologic deficits |
|
|
|
Brown Tumor
|
reactive fibrous ts 2° to microfx c hemorrhage; brown is vascularity + hemosiderin;
Px: cystic degeneration a manifestation of hyperparathyroidism |
|
|
|
Dissecting osteitis
|
tunnelling osteoclasts dissecting through trabeculae
a manifestation of hyperparathyroidism |
|
|
|
severe nocturnal pain localized in lower leg relieved by aspirin
|
classic triad of osteoid osteoma
Common Bones: lower leg Typical Location on Bone: cortex Radiographic Description: centrally lytic lesion w/ rim of sclerotic ts in cortex Histology: interconnecting trabeculae of woven bone surrounded by osteoblastsidentical to osteoblastomas, but always <2cm; sharply demarcated, surrounded by reactive scleortic bone proliferation; Pt male 20 yo ± ~15 Behavior: always <2 cm Px: benign; tx radioablation well circumscribed, round mass of gritty hemorrhagic ts |
|
|
|
2* osteosarcomas
|
more common in elderly
arise in pre-existing bone pathologies: Paget's, Radiation, Bone infarcts, Fibrous Dysplasia, Osteochondromas |
|
|
|
sunburst pattern of calcification around bone
|
Conventional Osteosarcoma
Presentation: painful progressively enlarging mass presents from pathologic fx Bones: long bones of extremities esp around knee Location: intramedullary most common, cortical & surface variants exist Gross: gritty, gray white, bulky tumor w/ areas of hemorrhage, degeneration Radiography: mixed lytic and blastic lesions w/ permeative margins; extension through cortex common; reactive periosteal bone formation; Codman's triangle of raised periosteium. sunburst pattern of calcified osteoid. Histology: variant: defined by formation of bone surrounded by poorly differentiated pleomorphic cells Pt: M ≥ F 1° tumors <20yo, 2° tumors in elderly Biochemistry: RB gene in most, else p53 Behavior: solitary: arises in intramedullary canal w/in metaphysis of long bones, spreads through canal; destroys overlying cortex "blows through" into surrounding soft ts; hematogenous dissemination esp to lungs; death from distant mets Tx: surg + chemoRx; Px: Fair (66%) |
|
|
|
triangle of raised periosteum
|
Conventional Osteosarcoma
Presentation: painful progressively enlarging mass presents from pathologic fx Bones: long bones of extremities esp around knee Location: intramedullary most common, cortical & surface variants exist Gross: gritty, gray white, bulky tumor w/ areas of hemorrhage, degeneration Radiography: mixed lytic and blastic lesions w/ permeative margins; extension through cortex common; reactive periosteal bone formation; Codman's triangle of raised periosteium. sunburst pattern of calcified osteoid. Histology: variant: defined by formation of bone surrounded by poorly differentiated pleomorphic cells Pt: M ≥ F 1° tumors <20yo, 2° tumors in elderly Biochemistry: RB gene in most, else p53 Behavior: solitary: arises in intramedullary canal w/in metaphysis of long bones, spreads through canal; destroys overlying cortex "blows through" into surrounding soft ts; hematogenous dissemination esp to lungs; death from distant mets Tx: surg + chemoRx; Px: Fair (66%) |
|
|
|
Ollier disease
|
unilateral
sporadic developmental multiple enchondromas w/ risk for condhrosarcoma |
|
|
|
Ollier disease
|
unilateral
sporadic developmental multiple enchondromas w/ risk for condhrosarcoma |
|
|
|
Maffuci Sro
|
Genetid defect
multiple enchondromas Soft Ts hemangiomas 50% dvlp chondrosarcoma; also brain and ovarian malignancies |
|
|
|
Maffuci Sro
|
Genetid defect
multiple enchondromas Soft Ts hemangiomas 50% dvlp chondrosarcoma; also brain and ovarian malignancies |
|
|
|
t(11:22)
|
Ewing Sarcoma/Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET)
Small Rount Blue Cell Tumors Genetics: t(11:22) translocation in vast majority forms EWS-FLI-1 fusion transcription factor oncogene Ewing Sarcoma Significant Minority of 1* Malignant Bone Tumors (10%) Pt Caucasian M≥F, 12yo ± 3 Arise in Medullary Cavity in Diaphysis of Long Tubular Bones esp femur or Flat bones of pelvis; Invade Cortex Radiograph: Permeative pattern with onion skin periosteal rxn Hist: small round blue cells Presentation: Painful, enlarging mass ± infx-mimicing sx: fever, increased ESR, anemia, leukocytosis Tx: Surgery & ChemoRx ± Rad Px: Very Poor w/o Tx (15%) W/ Agressive 50% cure, majority can survive 5 years |
|
|
|
lytic soap-bubbly eccentric mass that erodes the subchondral plate
|
giant cell tumor of bone
Benign but Aggressive Osteoclast like giant cells of monocyte lineage F>M 35 ± 15 50% around knee, else any bone esp epiphysis if adolescent in metaphysis Radiography: lytic soap-bubbly eccentric mass that erodes the subchondral plate [Gross: yellow, red brown w/ cystic degeneration] Hist: osteoclast-like giant cell w/ 100+ nucli in sea of mononuclear cells w/ identical nuclei; Presentation: arthritis: joint swelling & pain ± pathologic fx Behavior: unpredictable, few metastasize Tx: surgical curettage w/ bone graph, 50% recurrence Px: sarcomatous transformation is infrequent but possible |
|
|
|
Chronic Progressive Low Back Pain Characterized by Spinal Immobility & SI Joint Pain
|
Ankylosing Spondylitis
M 3x>F Adolecent Onset Genetic predisposition of : HLAB27, IL23R (receptor), ARTS1 (involved in antigen processing) Chronic progressive arthritis with cartilage destrx & ankylosis: SI joint, Apophyseal joints btw tuberosities and processes Enthesitis w/ ossification of annuli fibroses → "bamboo spine" immobility Presents as Progressive low back pain, Often pierphal joints involved: hip, shoulder Extra-articular invlvmt: Uvietis, aortitis, SAA type amyloidosis p1241 |
|
|
|
HLA-CW6
|
Predisposition to Psoriatic Arthritis:
~10% of psorasis pts 40 ± 10 M=F HLAB27, HLA CW6 Gradual onset of joint involvement, destrx similar to RA interphalangeal joints most common → sausage digits Asymmetric invlmt of hands, feet Extra-articular conjunctivitis, iritis Often SI & Spinal p1241 |
[30% SI & Spinal]
|
|
|
ARTS1
|
Genetic Predisposition to Ankylosing Spondylitis:
M 3x>F Adolecent Onset Genetic predisposition of : HLAB27, IL23R (receptor), ARTS1 (involved in antigen processing) Chronic progressive arthritis with cartilage destrx & ankylosis: SI joint, Apophyseal joints btw tuberosities and processes Enthesitis w/ ossification of annuli fibroses → "bamboo spine" immobility Presents as Progressive low back pain, Often pierphal joints involved: hip, shoulder Extra-articular invlvmt: Uvietis, aortitis, SAA type amyloidosis p1241 |
|
|
|
IL23R
|
Genetic Predisposition to Ankylosing Spondylitis:
M 3x>F Adolecent Onset Genetic predisposition of : HLAB27, IL23R (receptor), ARTS1 (involved in antigen processing) Chronic progressive arthritis with cartilage destrx & ankylosis: SI joint, Apophyseal joints btw tuberosities and processes Enthesitis w/ ossification of annuli fibroses → "bamboo spine" immobility Presents as Progressive low back pain, Often pierphal joints involved: hip, shoulder Extra-articular invlvmt: Uvietis, aortitis, SAA type amyloidosis p1241 |
|
|
|
CASR
|
Ca2+ Sensing Receptor
AD mutation → hypocalciuric hypercalcemia Never present in sporadic |
|
|
|
Large joint arthritis: remitting and migratory
|
Borrelia burgdorferi, Ixodes Tick
Erythema chronicum migrans "bull's eye" majority of unTx → arthritis sometime w/in 2 years; indicative of late, stage 3 dz Arthritis is remitting and migratory, involves large joints esp knees 1-2 joints/attack for weeks at a time synovitis, papillary (pannus like RA), onionskin thickening of blood vessels (c spirochetes in the walls!) Occasional (10%) → chronic refractory arthritis w/ deformity |
|
|
|
Lesch-Nyhan Sro
|
X linked deficiency of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase HGPRT, part of salvage pathway → → ↑ purine synth/↑ urate prodxn → Hyperuricemia,
Severe MR, Self Mutilation ± Gouty Arthritis |
|
|
|
HGPRT Deficiency
|
Lesch-Nyhan Sro
X linked deficiency of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase HGPRT, part of salvage pathway → → ↑ purine synth/↑ urate prodxn → Hyperuricemia, Severe MR, Self Mutilation ± Gouty Arthritis |
|
|
|
Most common benign soft tumor of adulthood
|
lipoma: Benign tumor of mature fat calls
esp overweight Soft, mobile, usually painless & slow growing, do not regress with weight loss Histologic variants have no clinical significance Characteristic Chrom Abnormalities |
|
|
|
Second most common sarcoma
|
Liposarcoma: Malignant Tumor of Fat Cells
55 ± 15 Loc: Deep soft ts of proximal extremities, retroperitoneum Lipoblasts & lipocytes Indolent to Agressive, behavior correlates to grade Tx: Surgery + ChemoRx |
|
|
|
most common soft ts sarcoma
|
Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma/undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma
undifferentiated, heterogenous histology most common sooft ts sarcoma >40 yo arise in prox extremities & retroperitoneum aggressively malignant often met (40%) hist: spindle cells, storiform/cartwheel pattern, xanthoma cells and bizarre giant cells p1253 |
|
|
|
most common mesenchymal neoplasm of the hand
|
Giant Cell Tumor of the Tendon Sheath
localized form of pigmented villonodular, involves tendon sheath of wrist fingers and toe presents as slow growing painless mass may erod underlying bone local recurrence following inadequate excision solid, golden nodule attached to synovium neoplastic cells resemble synoviocytes and form giant cells; infiltrates of hemosiderin and foamy M∅ present |
|
|
|
most common cause of aSx ↑ Ca2+
|
Hyperparathyroidism
assoc c ↓ Phosphate |
|
|
|
most common cause of Sx ↑ Ca2+
|
CA
|
|

