![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is added to blood in tubes
Purple tubes Blue top tube - PT and PTT |
Purple - EDTA
Blue - contains citrate add calcium |
|
|
CBC w/ differential contains what cell types?
|
Neutrophil
Leukocytes Mast Eosinophil Basophil |
|
|
What is MCV?
|
Mean cell volume (fL) which measures blood cell volume. Higher voltage pulses for bigger cells
|
|
|
T/F Hemoglobin is seen by spectoscopy
|
True
|
|
|
How do you calculate Hematocrit?
|
Hct = MCV X RBC
|
|
|
RBC counts # of _____
|
voltage pulses
|
|
|
Mean cell hemoglobin is calculated by?
|
Hb/RBC (pg)
|
|
|
Mean Cell Hemoglobin concentration
|
Hb/Hct (gm/dL)
|
|
|
What is RDW?
|
Red cell width distribution. What does it indicate. distribution of the width of Red cell
|
|
|
how does RDW change in?
Iron deficiencies Hemolytic anemia macrocytic anemia other anemias |
typically increases
|
|
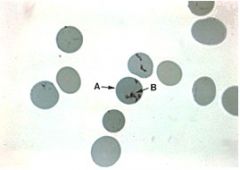
|
reticulocyte. Contain a lot of RNA; Ashlee stain
|
|
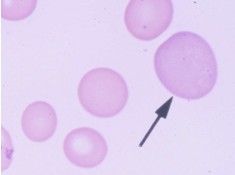
what is cell called and they have a high _____
|
reticulocytes with polychromasia and have a high MCV
|
|
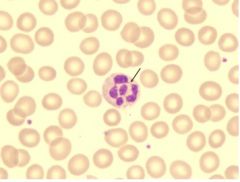
what kind of cell? morphology?
|
neutrophil. cell is multinucleated; constriction point is useful for counting lobes
|
|
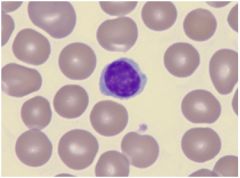
ID
|
Abnormal lymphocyte
|
|
|
Automated testing uses _____ _____ or _____ _____ (what stains)?
|
thiazole orange which is a fluorescent dye that binds RNA
or Methylene blue |
|
|
Manual testing for reticulocytes is done with which stain?
|
methylene blue
|
|
|
T/F Automated Counting is primarily used for normal cells where no disease is suspected
|
True
|
|
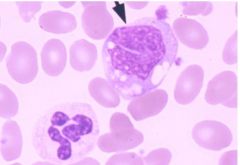
ID cell at arrowtip. what is the other large cell down and left?
|
Monocyte - has irregular nucleus and sometimes has cytoplasmic vacuole
|
|
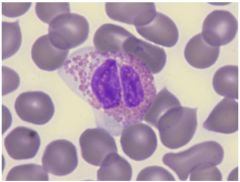
ID cell
|
Eosinophil - big granuales and BILOBED nucleus
|
|
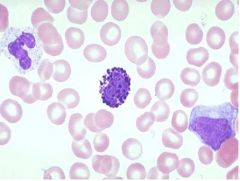
ID cell in the middle
What other cells are present? |
Basophil - Dark blue granuales, uneven borders, nucleus not really visible
right = abnormal lymphocyte |
|
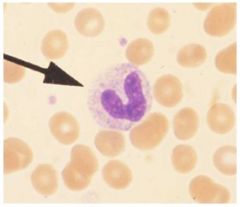
What kind of cell
|
Band cell
|
|
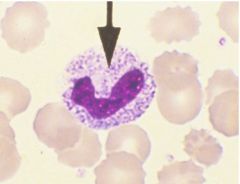
What defect is happening here and what does it indicate?
|
hypergranulation; a toxic change
|
|
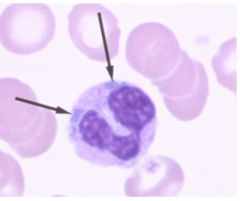
ID and describe
|
Dohle bodies
Hypergranulaton and blue cytoplasmic inclusion at the border |
|

ID and describe
|
Pelger-Huet cells
neutrophil with 2 pieces in barbell shape can be malignant |
|
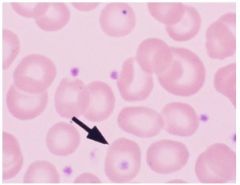
What are these dots on these RBC
|
platelets
|
|

what are stuck to these neutrophils and what are the consequences of this in cell counting?
|
platelets; falsely low platelet count
|
|
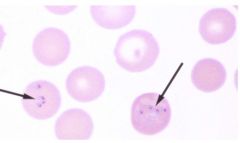
What is found at the tip of the arrow
|
parasite
|
|

What is contained within these cells?
|
bacterium
|
|
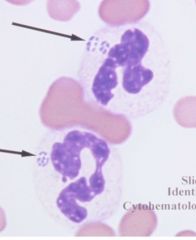
What are these called and where are they found?
|
Ehrlichia - found in neutrophils and monocytes
Not to be confused with Babesia and and Plasmodium which infect RBC |
|
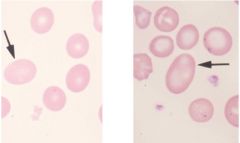
What do you call the condition of these cells?
|
macrocytosis
|
|
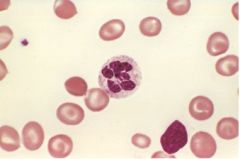
What is unusual about this cell?
|
It is a hyperlobulated neutrophil associated with megaloblastic anemia
|
|
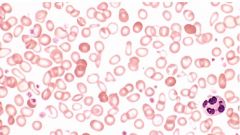
ID condition
|
microcytic anemia
|
|
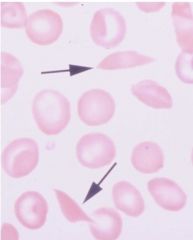
ID cell type
|
Drepanocytes (sickle cell)
|
|
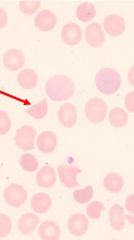
ID cell type; what condition?
|
shistocytes common in microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
|
|

ID cells and what are they associated with?
|
acanthocytes (spur cells); advanced liver disease, abetalipoproteinemia, severe malnutrition
|
|
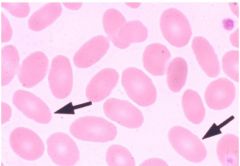
Type of cell; association
|
Ovalocytes; hereditary ovalocytosis, iron deficiency and thalassemia
|
|

what does this finding indicate? People with this are more susceptible to _____
|
Halle Jolley bodies - little blue spot; NO spleen = susceptibility to encapsulated bacteria
|
|

What are these crystals made of?
|
Hb C
|
|

what kind of cell and what kind of hemoglobin?
|
target cells; HbSC
|
|
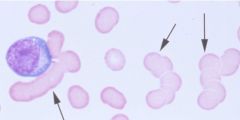
What condition? what artifact
|
Plasma cell dyscrasia with characteristic rouleaux
|
|
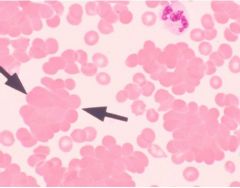
Are these roleaux? If not what are they?
|
no, red cell agglutment as a result of cold agglutinin syndrome
|
|
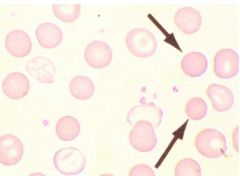
ID cell and condition involved
|
spherocyte; heriditary spherocytosis and autoimmune hemanemia
|
|
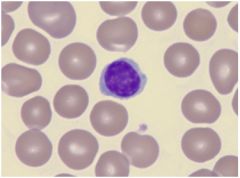
ID cell
|
lymphocyte
|
|
|
Increased band counts can indicate _____
|
infection
|
|
|
T/F automated instruments can't count bands but know when there are too many
|
True;
|
|
|
What does absolute neutrophil count do?
|
Machine counts total white cells x neutrophils
|
|
|
What kind of patients are at risk of low ANC Count?
|
cancer patients < 500 ul
pediatric patients <1000-1500 ul |

