![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
121 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Middle ear parts |
Tympanic cavity Ossicular chain Bones; malleus incus stapes |
|
|
Middle ear components |
Stapedious muscle Tensor tympani muscle Ligaments |
|
|
Middle ear cavity |
Air filled Water tight Sealed by Tm Irregular shape Size of pea Lined with mucous membrane |
|
|
Mucous membrane |
Thin layer of tissue Fluid secreting cells |
|
|
Incudostepedial junction |
Top of malleus articulates with top of incus Bottom of incus meets stapes |
|
|
Middle ear muscles |
Stapedious and tensor tympani muscles -keeps ochain tight -responds to vibrations of Tm -protects cochlea from dangerously loud sounds |
|
|
Acoustic reflex |
22:1increase 27 db |
|
|
Acoustic reflex |
Involuntary response Contraction of stapes Damper on system |
|
|
Eustachian tube |
Connects middle ear to nasopharynx(back of throat)
Equalizes ambient pressure between mid and inner ear
1,1/2" long in adults
Generally closed |
|
|
Epitympanic cavity/Mastoid cells |
Air filled cavities in mastoid process of temporal bone
EC-attic of mid ear Opening allows air Protected passage for nerves |
|
|
Ossicular discontinuity |
Bones don't move properly Lever action reduced or eliminated |
|
|
Function of middle ear |
Conduct sound energy to inner ear Mechanical energy |
|
|
Inner ear (labyrinth) |
3 major areas Semicircular canals Vestibule Cochlea |
|
|
Semicircular canals |
3 canals channeled through solid bone Endo/peri fluids Sense of balance |
|
|
Vestibule |
2 sacs Saccule-endo lymph Utricle- endo lymph Gravity and acceleration |
|
|
Cochlea |
Coiled like a snail 2,1/2" long 30,000 neural fibers 4 rows hair cells Contains organ of corti |
|
|
Key elements of the cochlea |
Scala vestibule Scala tympani Scala media
Reisners membrane Basilar membrane
Oval window Round window
Base highs Apex lows |
|
|
Promontory |
Seperates oval and round window Bulge in wall of cochlea |
|
|
Scala media |
Cochlea duct Canal of the cochlea Membraneous labyrinth Organ of corti |
|
|
Scala media |
Cochlea duct Canal of the cochlea Membraneous labyrinth Organ of corti |
|
|
Organ of corti |
Essential transducer Sensory end organ Ends organ of hearing Lays across basilar membrane Base-highs Apex-lows |
|
|
Tectorial membrane |
Hangs over neural fibers in organ of corti from base to Apex Place theory Place and volley theory |
|
|
Tectorial membrane |
Hangs over neural fibers in organ of corti from base to Apex Place theory Place and volley theory |
|
|
Place theory |
Neurons fire at a rate identical to stimulus below 1000 |
|
|
Tectorial membrane |
Hangs over neural fibers in organ of corti from base to Apex Place theory Place and volley theory |
|
|
Place theory |
Neurons fire at a rate identical to stimulus below 1000 |
|
|
Place & volley |
Stimulus beyond 1000 are volleyed |
|
|
Auditory nerve |
Auditory nerve VIII cranial nerve Cochlear branch Sense of hearing to brain |
|
|
Vestibular branch |
Sense of balance and motion to brain
Vestibular branch becomes part of the auditory nerve |
|
|
Vestibular branch |
Sense of balance and motion to brain
Vestibular branch becomes part of the auditory nerve |
|
|
Auditory brainstem response |
5-7 identifiable locations up the auditory pathway
Superior olivary complex |
|
|
Auditory nerve |
-30,000 neurons -Afferent transmits from cochlea to brain -efferent transmits from brain to cochlea |
|
|
Spiral ganglion |
Formed and combined by nerve impulses traveling along nerve fibers |
|
|
Spiral ganglion |
Formed and combined by nerve impulses traveling along nerve fibers |
|
|
Synaptic junctions |
Synaptic junctions or synapses -relay stations or transfer points for nerve fibers changing electrical impulses to chemical
Ascending auditory pathways -part of central nervous system pathway composed of primarily afferent fibers -transmits from cochlea |
|
|
Spiral ganglion |
Formed and combined by nerve impulses traveling along nerve fibers |
|
|
Synaptic junctions |
Synaptic junctions or synapses -relay stations or transfer points for nerve fibers changing electrical impulses to chemical
Ascending auditory pathways -part of central nervous system pathway composed of primarily afferent fibers -transmits from cochlea |
|
|
Binaural fusion |
Sounds presented to both ears come together as single sound |
|
|
Spiral ganglion |
Formed and combined by nerve impulses traveling along nerve fibers |
|
|
Synaptic junctions |
Synaptic junctions or synapses -relay stations or transfer points for nerve fibers changing electrical impulses to chemical
Ascending auditory pathways -part of central nervous system pathway composed of primarily afferent fibers -transmits from cochlea |
|
|
Binaural fusion |
Sounds presented to both ears come together as single sound |
|
|
Binaural summation |
6-10db increase |
|
|
Binaural localization |
Two ears help locate sounds |
|
|
Binaural localization |
Two ears help locate sounds |
|
|
A Normal ear.. |
Detects changes 3-4 hz up to 4,000
A25 hz change is required above 4000 to detect change in pitch |
|
|
Binaural localization |
Two ears help locate sounds |
|
|
A Normal ear.. |
Detects changes 3-4 hz up to 4,000
A25 hz change is required above 4000 to detect change in pitch |
|
|
Diffraction |
Bending of sound waves around obstacles
Lows bend more and travel further |
|
|
Binaural localization |
Two ears help locate sounds |
|
|
A Normal ear.. |
Detects changes 3-4 hz up to 4,000
A25 hz change is required above 4000 to detect change in pitch |
|
|
Diffraction |
Bending of sound waves around obstacles
Lows bend more and travel further |
|
|
Phase |
In phase begins 0 ends 360 Out of phase-determines direction |
|
|
Periodic waves |
Smooth waves i.e.:music speech |
|
|
Aperiodic waves |
Noise random tones without pattern |
|
|
Aperiodic waves |
Noise random tones without pattern |
|
|
Mels |
Measure pitch |
|
|
Speed of sound |
Air-1100 ft/sec Liquid-4xfaster Solid-14xfaster Vaccum-never travel |
|
|
134 db |
Loudest sound tolerated by normal human ear |
|
|
134 db |
Loudest sound tolerated by normal human ear |
|
|
Normal ear responds to |
20-20,000 hz sounds |
|
|
Most sensitive |
3000-4000hz |
|
|
Conductive hearing disorders |
Obstruction or breakdown in the outer and or middle ear |
|
|
Sensorineural |
Inner ear disorder or auditory nerve Sensory-cochlea Neural-auditory |
|
|
Central deafness |
Retrocochlear -brain tumor -acoustic neuroma |
|
|
Central deafness |
Retrocochlear -brain tumor -acoustic neuroma |
|
|
Paget's disease |
Disease of bones
Thickening of temporal bone and ossicular chain
Conductive loss
Over40 |
|
|
Monomeric spots |
Healed hole in Tm Mirror membranes No loss |
|
|
Monomeric spots |
Healed hole in Tm Mirror membranes No loss |
|
|
Ruptured perforated eardrum |
5-10db loss Tympanoplasty Myringoplasty |
|
|
Monomeric spots |
Healed hole in Tm Mirror membranes No loss |
|
|
Ruptured perforated eardrum |
5-10db loss Tympanoplasty Myringoplasty |
|
|
Full impaction |
Can cause up to 25db loss |
|
|
Otitis media |
Type b tympanogram |
|
|
Acute suppurative otitis media |
More severe Shorter duration Type b tympanogram |
|
|
Myringotomy |
Ventilation tube Falls out by itself Drains fluid from mid ear cavity |
|
|
Radical mastoidectomy |
Remove of Tm incus and malleus |
|
|
Radical mastoidectomy |
Remove of Tm incus and malleus |
|
|
Otosclerosis |
Spongy growth around stapes
Complete fixation 50-70db
Caucasian mid age after childbirth
Type as tympanogram |
|
|
Radical mastoidectomy |
Remove of Tm incus and malleus |
|
|
Otosclerosis |
Spongy growth around stapes
Complete fixation 50-70db
Caucasian mid age after childbirth
Type as tympanogram |
|
|
Ossicular discontinuity |
Dislodged ossicular chain
Altered lever capability
Type ad tympanogram |
|
|
Radical mastoidectomy |
Remove of Tm incus and malleus |
|
|
Otosclerosis |
Spongy growth around stapes
Complete fixation 50-70db
Caucasian mid age after childbirth
Type as tympanogram |
|
|
Ossicular discontinuity |
Dislodged ossicular chain
Altered lever capability
Type ad tympanogram |
|
|
Ossicular fixation |
Stiffening
Tissue turns to bone
Involves ligaments
Tympanosclerosis
Type As tympanogram |
|
|
Diseases that can cause HL |
Diabetes Auto immune ear disease Hiv Ms Syphillis Polyaryeritis nodosa Cogans syndrome Lupus Lyme |
|
|
Autoimmune ear disease |
Fluctuation unilateral bilateral loss
Unilateral facial stiffness or paralysis
Rapid and progressive |
|
|
Sensorineural hearing loss |
Perceptive Nerve loss Sensory=cochlea Neural=auditory nerve and ascending pathways |
|
|
Sensorineural hearing loss |
Most often affects highs Difficulty w consequences Mumbling Difficulty in noise |
|
|
Sensorineural |
Speaks louder |
|
|
Sensorineural |
Speaks louder |
|
|
Conductive |
Speaks softer |
|
|
Sensorineural hearing |
Recruitment Tinnitus |
|
|
Tinnitus |
70% have hearing loss 50 million suffer |
|
|
Objective tinnitus |
Only heard and measures externally |
|
|
Subjective tinnitus |
Only evident to patient Can't hear them externally |
|
|
Acoustic neuroma |
Tumor on 5th cranial nerve Unilateral loss Facial stiffness Atypical poor SRTS Poor discrim Vertigo/tinnitus |
|
|
Acoustic neuroma |
Tumor on 5th cranial nerve Unilateral loss Facial stiffness Atypical poor SRTS Poor discrim Vertigo/tinnitus |
|
|
Tone decay |
Perstimulatory fatigue Menieres patients Acoustic neuroma Can't hold threshold more than 60 seconds |
|
|
Acoustic neuroma |
Tumor on 5th cranial nerve Unilateral loss Facial stiffness Atypical poor SRTS Poor discrim Vertigo/tinnitus |
|
|
Tone decay |
Perstimulatory fatigue Menieres patients Acoustic neuroma Can't hold threshold more than 60 seconds |
|
|
PB rollover |
Common in Cochlear and Retrocochlear loss
Loss of ability to discriminate as words are presented louder (90db) |
|
|
Articulation curve |
Correct percentage of words a listener can identify as the words are presented gradually at louder levels |
|
|
Oval window fistula |
Loss of perilymph Rupture of stapes footplate or annular rings |
|
|
Oval window fistula |
Loss of perilymph Rupture of stapes footplate or annular rings |
|
|
Round window fistula |
Increase in perilymph Direct trauma Barotrauma Pressure related |
|
|
Tuning fork tests |
Weber-determines most conductive ear
Most sensitive cochlea Asymmetrical circumstances Masking indicator
Rinne- Assumes conductive loss Rinne negative-conductive Rinne positive- sensorineural/normal hearing |
|
|
Type a tympanogram |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Type b tympanogram |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Type b tympanogram |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Type C tympanogram |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Type as tympanogram |
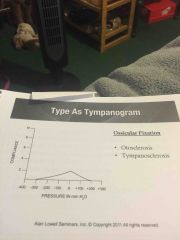
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Type ad tympanogram |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Type ad tympanogram |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Otoacoustic emissions |
Method for Hard to test population |
|
|
Infection control |
Wash hands or use alcohol gel
Bacteriacide fungicide viruside
Wear protective equipment
Prevent cross contamination |
|
|
Asymmetrical loss |
Both ears have loss Greater than 15 between ears |
|
|
Asymmetrical loss |
Both ears have loss Greater than 15 between ears |
|
|
Symmetrical |
Loss in both Within 15 of each other |
|
|
Pure conductive |
Bone scores normal limits |
|
|
Mixed hearing loss |
Conductive and sensorineural |

