![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What flavours of quark is a proton made of |
2 up quarks and one down quark |
|
|
Define a fundamental particle (2)what is the quad |
•cannot be split up •is not made up of any other particles (Quarks and electrons are fundamental) |
|
|
What is the quark structure of a neutron |
One up quark and two down quarks |
|
|
What flavour of quarks is the proton and neutron limited to |
Up and down quark |
|
|
Define Baryon (2) |
•name given for particles made up of 3 quarks •has a baryon number of +1 (Protons and neutrons are both baryons) |
|
|
What is the relative charge of a muon |
-1 |
|
|
What is the charge and mass of neutrinos |
0 |
|
|
What is the lepton number of all leptons |
+1 |
|
|
What is the lepton number for non leptons |
0 |
|
|
What is a muon |
A fundamental particle like an electron 200x bigger than an electron |
|
|
What are the 4 quantum numbers |
•strangeness •charge •baryon number •lepton number |
|
|
What is electrons antiparticle known as |
Positron |
|
|
What’s the range for strong nuclear force |
0-3fm |
|
|
When is the strong nuclear force repulsive |
Below distances of 0.5fm |
|
|
What are the 4 fundamental forces |
Strong nuclear, weak nuclear, gravitational, electromagnetic |
|
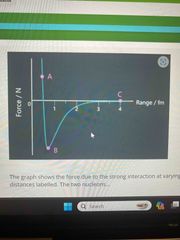
Explain what is happening at A B C
|
A-the two nucleons repel B- the two nucleons attract C-the two nucleons are neutral |
|
|
The name of the particle that carries the weak nuclear force is |
W boson (w plus w minus) |
|
|
The exchange particle of the electromagnetic force is |
Virtual photon (fundamental boson) |
|
|
The exchange particle for the strong nuclear force |
Pion (not a fundamental particle) |
|
|
Define hadrons |
Hadrons are particles made up of 2 or more quarks |
|
|
What is a meson made up of |
A quark antiquark pair |
|
|
What are the flavours of quarks pions can contain |
Up down antiup antidown |
|
|
Draw the table to remember all the pions |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What are the 4 pions |
Negative pion Positive pion 2 neutral pions |
|
|
Define kaon |
Made up of a quark antiquark pair where at least one quark needs to be a strange quark or it’s antiparticle |
|
|
Draw a table for the 4 types of kaon |
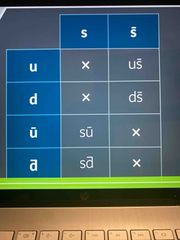
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Name the 4 different kaons |
Positive kaon, negative kaon and 2 neutral kaons |
|
|
What will all mesons everntually do |
Decay into other particles |
|
|
Free neutrons will decay into |
Protons |
|
|
Free neutrons will decay into |
Protons |
|
|
Protons don’t decay because |
They’re the most stable baryon that all baryons eventually decay into |
|
|
Name the two fundamental bosons |
Virtual photon W(+-) boson |
|
|
Describe beta plus decay (4) |
•a proton in parent nucleus changes to neutron in daughter nucleus (proton number decreases by 1) •beta plus particle is emitted •an electron neutrino is also emitted •the nucleon number remains the same |
|
|
Describe beta minus decay (4) |
•a neutron in the parent nucleus changes into a proton in the daughter nucleus •a beta minus particle is emitted •an electron antineutrino is emitted •the proton number increases and the nucleon number stays the same |
|
|
Describe electron capture |
•an inner shell electron is captured by the atoms nucleus •a proton changes to a neutron •an electron neutrino is emitted |
|
|
Describe gamma decay |
•the nucleus of an atom emits a high energy gamma ray photon •no change to the number of protons or neutrons |
|
|
What force is responsible for electron capture? |
Weak force |
|
|
What force is responsible for beta minus and plus decay |
Weak force |
|
|
Compare radiation in terms of how ionising they are and how easily they’re stopped |
Alpha- very strongly ionising but easy to stop Beta- somewhat strongly ionising and somewhat easy to stop Gamma- weakly ionising but very hard to stop |
|
|
Which exchange particle does the neutron interact with to form a proton in beta minus decay |
W minus boson Beta plus- W plus boson |
|
|
What forces do muons and their antiparticles decay due to? And decay products? |
Weak forces •electron , muon neutrino and electron antineutrino (muon) Opposite for antimuon |
|
|
Strange particle production is always a result of |
Strong forces |
|
|
Strange particle decay due to which force |
Weak force |
|
|
What is conserved in every particle interaction |
Charge , baryon number ,lepton number |
|
|
What exchange particles are responsible for EM force , S nuclear force and W nuclear force |
EM: virtual photons S nuclear : pions W nuclear: W- and W+ |
|
|
Describe annihilation |
Process where a particle meets its antiparticle and produces EM radiation in the form of two high energy photons |
|
|
What equation gives us the rest energy of a particle ? |
E=mc^2 |
|
|
How much is 1 electron volt in joules |
1.6x10^-19J |
|
|
Why is the rest energy of the particle equal to the minimum energy of each photon |
The kinetic energy of each particle is assumed to be 0 |
|
|
Pair production is where a high energy photon |
Creates a particle antiparticle pair |

