![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nucleon |
Constituent particle of the atomic nucleus, either protons or neutron. |
|
|
Nuclide |
A species of an atom characterized by the constitution of its nucleus, which is specified by its atomic mass and atomic number, or by its number of protons, number of neutron and energy content. |
|
|
Isotope |
Nuclides which have the same number ofprotons but different number of neutrons. Nuclides that have the same atomic number but different atomic mass numbers are isotopes. |
|
|
Mass-energy Equivalence |
Mass may be transformed to energy and vice versa. E=mc^2 |
|
|
Pair Annihilation |
Occurs when two particles with mass, specifically a positron and an electron (negateon), collide and are transformed into two days of electromagnetic energy. |
|
|
Mass Defect |
Total mass of the atom is less than the sum of the masses of the individual protons and neutrons |
|
|
Binding energy |
The energy equivalent of mass defect. |
|
|
Binding energy per nucleon |
Total Binding energy of nucleus divided by the total number on nucleons in the nucleus. Represents average energy that must be supplied in order to remove a nucleon from nucleus. |
|
|
Nuclear transformation equation |
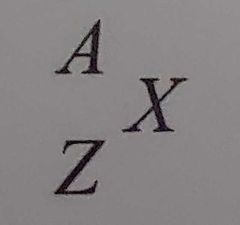
Using this format, equations can be written that depict a transformation that has occurred in a nucleus or nuclear. Both sides must be equal there for total mass-energy on the left must be equal to total mass-energy on the right. |
|
|
Nuclear fission |
The splitting of the nucleus into at least two smaller nuclei with an accompanying release of energy. |
|
|
Criticality |
The condition in which the neutrons produced by fisson are equal to the number of neutrons in the previous generation. |
|
|
Sub-critical |
If too many neutrons escape from the system or are absorbed but do not produce fission. The chain reaction will eventually stop. |
|
|
Supercritical |
If the two or three neutrons produced in one fission each go on to produce another fission, the number of fissions and the production of neutrons will increase exponentially. |
|
|
Effective multiplication constant |
Or Keff, the ratio of the number of neutrons in the reactor in one generation to the number of neutrons in the previous generation. |
|
|
Fusion |
The act combining or "fusing" two or more atomic nuclei. |
|
|
Terrestrial Radiation |
Radioactivity of the earth. U.S. average exposure 28 mrem. |
|
|
Medical exposures |
Largest source of man-made radiation. Annual U.S. dose of 298mrem per year. |
|
|
Types of medical exposures |
Diagnostic X-Rays Radiography Fluoroscopic Photo-fluoroscopic |
|
|
Typea of medical radionuclides |
Nuclear medicine Radiation oncology |
|
|
Consumer products |
Daily used in home items: Tv Shoe-fitting fluoroscopes Radioluminous watches Dental prosthesis Annual U.S. exposure: 12mrem |
|
|
Nuclear Facilities |
Man made backround radiation. <1mrem annual dose |
|
|
Cosmic Radiation |
Radiation coming from space. Two part of radiation, galactic cosmic rays and solar cosmic rays. U.S. average exposure 30 mrem. |
|
|
Internal Emitters |
Radioactive elements naturally occurring in the human: potassium (40K), rubidium (87Rb), radium (226Ra), uranium (238U), polonium (210Po), carbon (14C). Annual exposure 30mrem |
|
|
Inhaled radionuclides |
Inhaled radiation from background radiation of radon and thoron gas. Annual exposure 229mrem |
|
|
Nuclear Fallout |
Debris that settles to the earth as the result of a nuclear blast. <1mrem annual exposure |
|
|
Nuclear Stability |
The particular combination and arrangement of neutrons to protons in a given nucleus. |
|
|
Forces acting in the nucleus |
Gravitational Electrostatic Nuclear force |
|
|
Gravitational Force |
Negligible attractive force between all nucleons. Relatively long range. |
|
|
Electrostatic Force |
Strong repulsive force between like charged particles. Relatively long range. |
|
|
Nuclear Force |
Strong attractive force be tween all nucleons. Extremely short range. |

