![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease has two types, which one is more common? Which have longer life expectancy? What decade of life does it show itself? |
ADPKD (1) more common. ADPKD(1)- short arm of chromosome 16, 85-90% of pt’s. ADPKD(2) - chromosome 4, 10-15%; slower, chronic. -ADPKD(2) has longer life expectancy than APKD(1). -4th decade of life |
|
|
ADPK affects the liver by cysts but has no association with? What part of the liver does it affect when APKD involved? Most common cause of death for APKD? |
Portal HTN or liver fibrosis. Right lobe liver. Renal failure; both fail at same time. |
|
|
Which is dominant and recessive: APKD and IPKD. What is the most common cause of liver cell necrosis? |
-ADPKD- dominant, large cyst. -IPKD- recessive. -Viral Hepatitis. |
|
|
What is the incubation time of Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E? |
Hep A & D: 2-6 weeks Hep B & C: 2-6 months Hep E: 2- 9 weeks |
|
|
Which hepatitis is more prevalent in Africa, South America, Asia? |
Hepatitis E |
|
|
Will Hep A transition to chronic? |
No. |
|
|
-What hepatitis virus are of the U.S? -Through needles? |
Hep A,B,C Needles: Hep B, C, D |
|
|
This hepatitis is associated with poor socioeconomic conditions, which can lead to epidemics. Can occur in majority of children before 5 years. |
Hep A |
|
|
This hepatitis is associated with poor socioeconomic conditions, which can lead to epidemics. Can occur in majority of children before 5 years. |
Hep A |
|
|
Homosexuals, clotting disorders and individuals working with primates increase chance to get which Hepatitis? |
Hepatitis A |
|
|
Hepatitis A affects children and adults the same? |
Adults- more signs and symptom problems. Kids can bounce back |
|
|
This virus most common mode is through sex in U.S and in Asia most common mode is mother to child. Which virus is this? |
Hepatitis B |
|
|
Acute hepatitis B versus chronic hepatitis B? |
Acute hepatitis B- serum sickness like syndrome with rash, arthralgia, fatigue, anorexia. Chronic- lasts more than 6 mo. ongoing anorexia. Elevation of AST,ALT, bilirubin. Can be asymptomatic, considered “healthy carriers.” |
|
|
What is the most common chronic infection in the U.S? |
Hepatitis C |
|
|
This hepatitis is an RNA that has most common transmission fecal-oral route and similiar to Hep A. Which one? |
Hepatitis E |
|
|
What is the most common type of liver abscess is caused by? |
Bacteria. It is called Pyogenic Abscess |
|
|
What causes Pyogenic abscess? |
Cholangitis, appendicitis, endocarditis, diverticulitis cholecystitis. |
|
|
What causes Pyogenic abscess? |
Cholangitis, appendicitis, endocarditis, diverticulitis cholecystitis. |
|
|
This finding is usually in hospitalized patients, elderly. Located in right lobe livers associated with bright echogenic focus and distal, dirty shadowing. In newborns or infants relatable to umbilical cord infections. |
Pyogenic abscess |
|
|
This finding is in the liver. It’s a cyst with a cyst appearance. Pt has been around a lot of livestock recently. Finding? |
Ecchinococcus |
|
|
This finding is in the liver. It’s a cyst with a cyst appearance. Pt has been around a lot of livestock recently. Finding? |
Ecchinococcus |
|
|
What strains of echinococcus? |
E. Granulosa, E. Vogeli, E, multilocularis. |
|
|
This finding is in the liver. It’s a cyst with a cyst appearance. Pt has been around a lot of livestock recently. Finding? |
Ecchinococcus |
|
|
What strains of echinococcus? |
E. Granulosus, E. Vogeli, E, multilocularis. |
|
|
Tapeworm that is locally invasive are found in Canada, U.S, Asia. Known of mice and other rodents for this type. |
E. Multilocularis |
|
|
This finding is found in places of Central America, South America. This host is dogs. |
E. Vogeli |
|
|
This finding is found in places of Central America, South America. This host is dogs. |
E. Vogeli |
|
|
This cyst develops from host of sheep, cattle, and horses. Association with dogs. Finding? |
E. Granulosus |
|
|
This is a watery cyst that has echoes inside- Sandlike appearance. |
Hydatid cyst |
|
|
Echinococcus is involved in what most common sites? |
Liver and lung |
|
|
Echinococcus have sx? |
Asymptomatic, several years later the cyst enlarges. This is when Sx can occur. Abdominal pain, palpable mass in RUQ. |
|
|
Hepatic echinococcus can mimic? |
Bile duct compressed, cyst fluid in the biliary tree, may mimic recurrent cholelithiasis, biliary obstruction can result in jaundice. |
|
|
Echinococcus increases chances of? (What organ) |
Cancer (echinoccocus in the liver) |
|
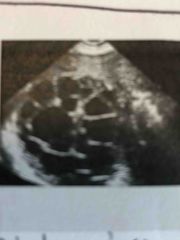
This patient has been around a lot of livestock. Scanning the liver and this is the finding. Patient has been experiencing jaundice and epigastric pain. |
Multiple daughter cyst |
|
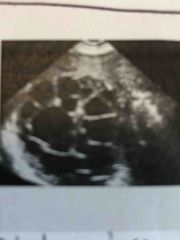
This patient has been around a lot of livestock. Scanning the liver and this is the finding. Patient has been experiencing jaundice and epigastric pain. |
Multiple daughter cyst |
|
|
Cyst within a cyst is what sono appearance of what finding? |
(Echinococcus) |
|
|
Moving membrane in the liver within a large cyst surrounded by fluid. Septations separate. Sono sign? |
Water lily sign |
|
|
The cantlies line is the landmark for? |
Main lobar fissure |
|
|
The cantlies line is the landmark for? |
Main lobar fissure |
|
|
List liver function tests? |
ALP, bilirubin, AST, ALT, Albumin, Prothrombin time, AFP, Lactic dehydrogenase, Glutamyl transpeptidase |
|
|
The cantlies line is the landmark for? |
Main lobar fissure |
|
|
List liver function tests? |
ALP, bilirubin, AST, ALT, Albumin, Prothrombin time, AFP, Lactic dehydrogenase, Glutamyl transpeptidase |
|
|
Large amounts of ALT in the liver, monitor for? |
Cirrhosis and Hepatitis |
|
|
The cantlies line is the landmark for? |
Main lobar fissure |
|
|
List liver function tests? |
ALP, bilirubin, AST, ALT, Albumin, Prothrombin time, AFP, Lactic dehydrogenase, Glutamyl transpeptidase |
|
|
Large amounts of ALT in the liver, monitor for? |
Cirrhosis and Hepatitis |
|
|
What is the specific indicator for hepatocellular damage?? |
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) |
|
|
The cantlies line is the landmark for? |
Main lobar fissure |
|
|
List liver function tests? |
ALP, bilirubin, AST, ALT, Albumin, Prothrombin time, AFP, Lactic dehydrogenase, Glutamyl transpeptidase |
|
|
Large amounts of ALT in the liver, monitor for? |
Cirrhosis and Hepatitis |
|
|
What is the specific indicator for hepatocellular damage?? |
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) |
|
|
This lab is to identify biliary obstruction. It generally excretes with bile. What lab should be evaluated? |
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) |
|
|
Bilirubin can be associated with direct or indirect. How to differentiate? |
direct- liver just needs to be excrete by the kidneys. Indirect- elevated bilirubin because liver can’t process it or it can’t get into the liver / excessive form. |
|
|
What’s the most sensitive indicator for LFT for alcohol abuse? |
Glutamyl transpeptidase (GTT or GGTP) |
|
|
What’s the most sensitive indicator for LFT for alcohol abuse? |
Glutamyl transpeptidase (GTT or GGTP) |
|
|
What is albumin? |
Protein- controls oncotic pressure in the tissue. |
|
|
This is a branch of the celiac axis that supplies the liver and divides into the GDA and Proper hepatic artery= |
Common hepatic artery |
|
|
This is a branch of the celiac axis that supplies the liver and divides into the GDA and Proper hepatic artery= |
Common hepatic artery |
|
|
Branch of the main portal vein that marks the anterior border of the caudate lobe and carries blood from the GI tract to the left lobe. |
Left portal vein |
|
|
This is a small sac posterior to the stomach and anterior to the pancreas and part of the transverse colon. |
Lesser sac |
|
|
This is a small sac posterior to the stomach and anterior to the pancreas and part of the transverse colon. |
Lesser sac |
|
|
This vessel in the liver drains blood from Gi tract to the liver to be processed. |
Main portal vein |
|
|
Splenic, superior and inferior mesenteric vein unite near head of pancreas. |
Portal confluence |
|
|
“Fourth” lobe of the liver- medial portion of the left lobe. |
Quadrate lobe |
|
|
Branch of the main portal vein that carries blood from the GI tract to the right lobe of liver= |
Right portal vein |
|
|
What’s the terminal end of the falciform ligament? |
Ligamentum Teres (Round ligament) |
|
|
What spaces form part of the morison pouch? |
Subhepatic space and subphrenic space. |
|
|
Another name for Morrison pouch? |
Hepatorenal recess, right subhepatic space. |
|
|
Another name for Morrison pouch? |
Hepatorenal recess, right subhepatic space. |
|
|
Liver size measurement? |
12-15 cm length |
|
|
What structure encloses most of the abdominal organs; enclose organs of intraperitoneal. |
Greater sac |
|
|
This ligament connects the posterior superior surface of the liver to diaphragm. This ligament connects the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and to the diaphragm. |
Coronary ligament. Falciform ligament. |
|
|
The transverse fissure for the ligamentum venosum contains which ligament? |
Gastrohepatic ligament |
|
|
Portal veins drain which structures? |
Digestive tract, pancreas, spleen. |

