![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Eimeria
|
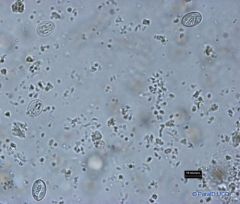
size: 15 to 50 micrometers.
refractile shell mycropyle,--> (small pore) covered by a polar cap A sporulated oocyst (in its infective stage) : outer wall enclosing 4 sporocysts (each containing 2 sporozoites |
|
|
Isospora
|
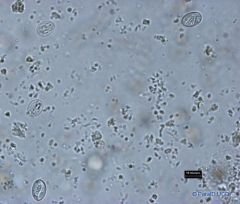
oocyst: sizes range from 15 to 50 micrometers
refractile shell mycropyle,--> (small pore) covered by a polar cap A sporulated oocyst (in its infective stage) : outer wall enclosing 4 sporocysts (each containing 2 sporozoites |
|
|
Crypto
|
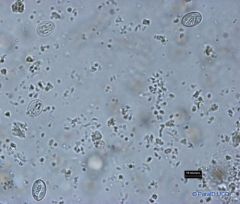
The minute oocysts each have four sporozoites are liberated in the faeces. There are 2 types of oocysts-thin and thick walled.
oocyst: 4-4.5 micrometers |
|
|
Toxoplasma Gondii
|
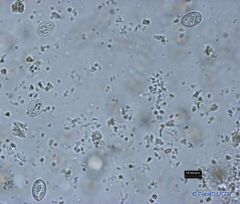
Oocysts are found in the faeces of cats, are spherical and subspherical, and are unsporulated. When sporulated, which takes one to five days, the oocyst contains 2 sporocysts, each with 4 sporozoites (Isospora in type).
oocyst: 12X10 micrometers |
|
|
Toxoplasma tissue cysts
|
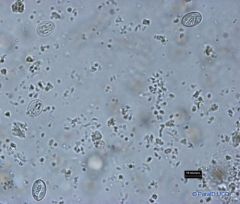
Tissue cysts are found in various organs and contain thousands of bradyzoites.
Cyst walls are thin (in Neospora cyst walls are thicker). Tissue cysts: Can measure up to 100 micrometers in diameter |
|
|
Neospora
|
Neospora oocyst is structurally similar to Toxoplasma gondii.
Oocysts: 12X10 micrometers |
|
|
Neospora
|
Primary Hosts: Dog
Intermediate Hosts: Cattle, dog, and many other mammals |
|
|
Sarcocystis
|
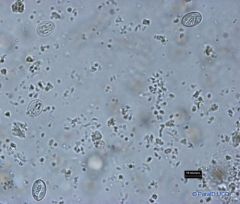
sporulated when passed in the faeces (found free)
two sporocysts each with four sporozoites; size of sporulated sporocysts S. bovicanis 15 X 10 micrometers S. ovicanis, 4 X 9 micrometers respectively. |
|
|
Sarcocystis
|
Primary Hosts: Dogs, cats, wild carnivores, and humans.
Intermediate Hosts: Humans, ruminants, pigs and horses |
|
|
Toxoplasma Gondii
|
Primary Hosts: All felids. The domestic cat is the most important.
Intermediate Hosts: Any mammal, including humans and birds. Note that the cat may also be an intermediate host and harbor extra-intestinal stages. |
|
|
Sarcocystis
|
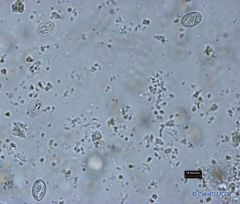
The cyst wall is thin and smooth with a small number of protrusions.
Tisue cysts: range from 0.5-5 mm long (sometimes visible with the naked eye) |
|
|
Giardia trophozoites
|
2 eyes
|
|
|
Giardia cysts
|
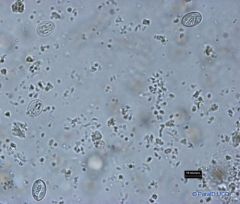
top left and middle
|
|
|
Pseudocysts of Besnoitia
|
?
|
|
|
Tritrichomonas
t. foetus |
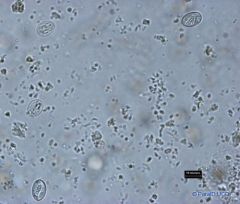
The organism is pear-shaped and the nucleus is anterior, there is a cytostome which is dificult to discern and a sausage-shaped parabasal body. Three anterior flagella are present and the posterior flagellum extends back along the undulating membrane and trails behind the organism. The undulating membane runs the full length of the body, the costa is prominent, the axostyle is well developed and it emerges from the end of the body through a chromatic ring.
Protozoa: 10-25 micrometers long by 3-15 micrometers wide |
|
|
Babesia spp in a blood smear
B. divergens |
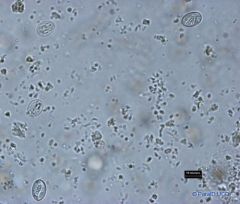
Organisms within red cells, almost always singly or as pairs, often arranged at a characteristic acute angle with their narrow ends opposed. Typically they are pyriform, but may be round, elongated or cigar-shaped.
Small Babesia: 1.5-4.0 micrometers |
|
|
Theileria parva in a blood smear
Schizont |
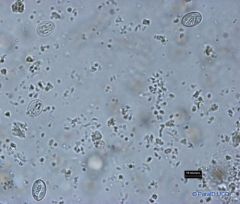
Macroschizonts contain chromatin granules 0.4-2.0 micrometers in diameter and Microschizonts contain chromatin granule 0.3-0.8 in diameter.
Primary Hosts: Buffalo Intermediate Hosts: They are transmitted by ixodid ticks Where found: Piroplasus- RBC Schizont-lymph nodes Distribution:East, Central and South Africa |
|
|
Trypnosoma spp in a blood smear
T. theileri T. brucei key features |
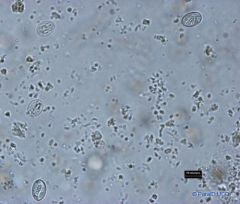
Primary Hosts: Cattle and domestic animals and livestock.
Intermediate Hosts: Tabinid Spp. Where found:Bloodstreams of vertebrates Distribution: Worldwide ID: relatively large species with the posterior end long and pointed and the kinetplast lying some distance from the posterior end. The undulating membrane is well developed and the free flagellum is well defined. |
|
|
Theileria parva
Blood smear with protozoa key id features |
Primary Hosts: Buffalo
Intermediate Hosts: They are transmitted by ixodid ticks Where found: Piroplasus- RBC Schizont-lymph nodes Distribution:East, Central and South Africa 1.5-2 X .5-1 micrometers ID features: The forms of T. parva (piroplasms) in red blood cells are usually rod-shaped but can also be round, oval, comma-, and ring shaped as well. With giemsa stains, the cytoplasm of each is blue with a red chromatin dot at one end. Commonly there is more than one parasite in each erythrocyte. |
|
|
Theileria equi in a blood smear
|
Primary Hosts: Equids
Intermediate Hosts: They are mainly transmitted by ixodid ticks Where found: Blood Distribution: Worldwide except Australia, the UK, Ireland, Japan and parts of the USA 2-3 micrometers rounded ID: The merozoites in the erythrocytes are small, amoeboid or most often pyriform, are are readily recognized in blood smears. The piroplasms characteristically form a "Maltese cross" of four organisms. |
|
|
B. divergens
primary Host secondary host intermediate host where found? distribution? |
Primary Hosts: Cattle
Secondary Hosts: Roe and red deer act as reservoirs Intermediate Hosts: Hard ticks of the family Ixodidae Where found: The organisms lie singly or in pairs inside the red blood cells. Distribution: Europe including Ireland |
|
|
B. major
primary host? intermediate host? where found? distribution? size? |
Primary Hosts: Cattle
Intermediate Hosts: The three-host tick Haemaphysalis puctata Where found: The organisms lie singly or in pairs inside the red blood cells. Distribution: Northern Europe large 3.2 X 1.5 micrometers |
|
|
Babesia bovis
small |
Primary Hosts: Cattle
Intermediate Hosts: The one host tick Boophilus Where found: The organisms lie singly or in pairs inside the red blood cells. Distribution: Tropics and subtropics Small: 2.0-1.5 micrometers |
|
|
Babesia Bigemenia
large |
Primary Hosts: Cattle
Intermediate Hosts: The one host tick Boophilus Where found: The organisms lie singly or in pairs inside the red blood cells. Distribution: Tropics and subtropics large: 3.2 X 1.5 micrometers |
|
|
Babesia Caballi
large |
Primary Hosts: Horses and donkeys
Intermediate Hosts: It is transmitted by a variety of tick species including Dermacentor, Hyalomma, and Rhipicephalus. Where found: The organisms lie singly or in pairs inside the red blood cells. Distribution: The Americas, Africa, Asia, and mainland Europe. Large: the pyroform shaped ones are 2.5-4 micrometers in length. Round or oval forms, 1.5-3 micrometers, may also occur. |
|
|
Babesia canis
large pyriform |
Primary Hosts: Domestic dog
Secondary Hosts: Wild canids Intermediate Hosts: Hard ticks of the family Ixodidae Where found: The organisms lie singly or in pairs inside the red blood cells. Distribution: Asia, Africa, southern Europe, USA, Puerto Rico, Central and South America. (Naturally infected wolves, striped jackals and black-backed jackals have been found in Turkestan, East Africa, and South Africa, respectively. The red fox and silver fox have been artificially infected in Germany.) Large: pyriform in shape, 4-5 micrometers long |
|
|
Babesia gibsoni
key id features: |
Primary Hosts: Domestic dog
Intermediate Hosts: The transmitting ticks include Haemaphysalis bispinosa and Rhipicephalus sanguineus. Where found:The organisms lie singly or in pairs inside the red blood cells. Distribution: India, Sri Lanka, parts of China, Turkestan, possibly parts of North Africa. (Additionally the jackal in India, the wolf in Turkestan, and the fox in the Sudan are naturally infected.) ID features: B. gibsoni is a small form, is pleomorphic and lacks the usual pyriform-shaped trophozoites. Characteristically the trophozoites are annular or oval; signet ring forms may occur and, rarely large ovoid to circular blue forms, about half the diameter of the host cell, or elongate forms stretching across the cell, may be seen. |

