![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
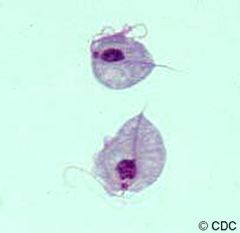
Identify flagella
undulating membrane, blepharoplast, nucleus, axostyle, food vacuole |
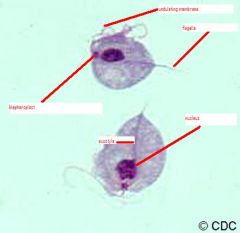
Identify flagella
undulating membrane, blepharoplast, nucleus, axostyle, food vacuole |
|
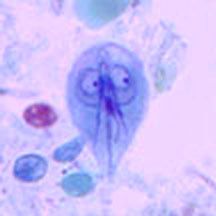
Identify two nuclei, flagella, axonemes, median bodies
|
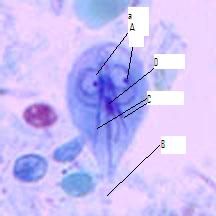
A-two nuclei, B-flagella, C-axonemes, D-median bodies
|
|
|
Where are trophozoites of giardia lamblia found in human?
|
small intestine
|
|
|
What are the diagnostic characteristics of giardia lamblia?
|
tear shaped organism with 2 nuclei
or a cyst with 4 nuclei and retracted flagella |
|
|
What is the transmissiona stage of giardia lamblia?
|
cyst
|
|
|
What confirms an infection with giardia lamblia?
|
finding troph and/or cysts in feces
|
|
|
How are trophozoites/cysts of giardia lamblia released?
|
in feces
|
|
|
Cyst of giardia lamblia
|
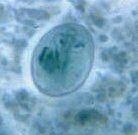
Identify organism
|
|
|
Trophozoite of Trichomonas vaginalis
|
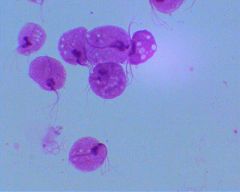
Identify organism
|
|
|
Where are trichomonas vaginalis found in the human?
|
females: vagina, urethra & uterus
Males: urethra & prostate |
|
|
How is trichomonas vaginalis transmitted?
|
through sexual contact
contaminated bath water, wash clothes and towels and 1% through birth |
|
|
How is infection with trichomonas vaginalis confirmed?
|
finding troph in vaginal smear or uterine samples
|
|
|
What is the transmissionable stage of trichomonas vaginalis?
|
the trophozoite
|
|
|
What is diagnostic characteristic of Trichomonas vaginalis?
|
pear-shaped with visible flagella
|
|
|
Where is Entamoeba histolytica found in the human?
|
in large intestine with preference for anterior end in crypts of lining
cysts formation in posterior end |
|
|
How are Entamoeba histolytica released from the human?
|
both trophs and cysts are released in feces
|
|
|
What is diagnostic characteristics of Entamoeba histolytica?
|
immunological tests
(cannont use cysts/trophs - commensals look similar) |
|
|
What are the features for identification for Entamoeba histolytica?
|
peripheral chromatin granules with homogenous cytoplasm
|
|
|
What are diagnostic characteristics of the mature cysts of the Entamoeba histolytica.
|
4 nuclei with peripheral layer of chromatin granules
|
|
|
Trophozoite of Entamoeba histolytica
|
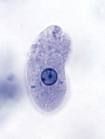
Identify stage and organism
|
|
|
Mature cyst of Entamoeba histolytica
|
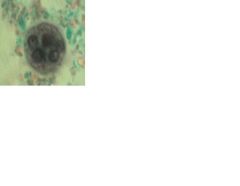
Identify stage and organism
|
|
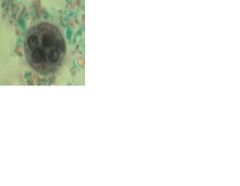
Identify cyst wall, cytoplasm, nuclei and chromatoid body
|

cyst of Entamoeba histolytica
a-cyst wall b-cytoplasm c- nuclei d-chromatoid body |
|
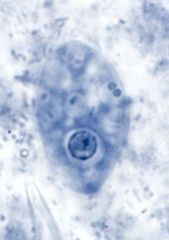
Identify organism, then
cell membrane, cytoplasm, food vacuole, nuclear membrane, karyosome, chromatin granule |
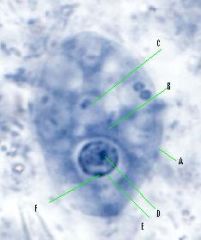
Trophozoite of Entamoeba histolytica
A - cell membrane B-cytoplasm C- food vacuole D-karyosome E -Nuclear membrane F-chromatin granules |
|
|
Immature cyst of Entamoeba histolytica
|
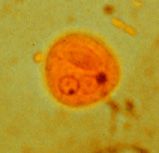
Identify stage and organism
|
|
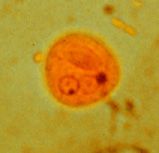
Identify cyst wall, cytoplasm, nuclei, glycogen vacule, chromatoid bodies
|
A-cyst wall, B-cytoplasm, C-nuclei, D-glycogen vacule, E-chromatoid bodies
|
|
|
A-cyst wall, B-cytoplasm, C-nuclei, D-glycogen vacule, E-chromatoid bodies
|
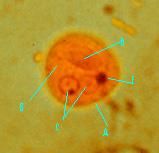
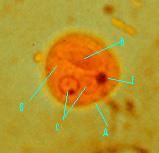
Identify
|
|
|
What is phylum and class of the plasmodium species?
|
Phylum: Apicomplexa
Class: Hemosporea |
|
|
What are the four species of plasmodium that infect humans?
|
P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. malaria, P. ovale
|
|
|
What are schiiffner's dots?
|
invaginations of cell membrane of RBC - characteristic of P.vivax or P.ovale
|
|
|
What is diagnostic characteristic of ring stage blood infected with a Plasmodium species?
|
RBC with internal organism with outer ring of blue cytoplasm, large central vacuole and a red nucleus.
|
|
|
What is diagnostic characteristic of microgametocytes/macrogamerotcytes in RBC?
|
organism inside of RBC with pigment granules, pink-red nucleus
|
|
|
Plasmodium species - ring stage
|
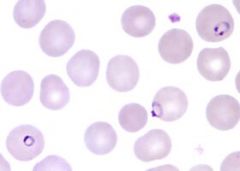
Identify organism and stage
|
|
|
Plasmodium falciparum - gametocyte
|
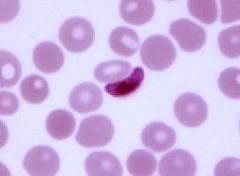
Identify species and stage
|
|
|
trophozoite of toxoplasma gondii
|
Identify organism and stage
|
|
|
Where are Toxoplasma gondii found in the human?
|
in any cell, prefers skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle and certain brain cells & phagocytes
|
|
|
How are toxoplasma gondii release from human body?
|
They are not released
|
|
|
How is a person infected with Toxoplasma gondii?
|
by ingesting infected meat (pork, beef, mutton) ingesting oocysts or through congenital transmission
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic characteristics of toxoplasma gondii?
|
size and shape & nucleus that stains blue
|
|
|
How is toxoplasma gondii diagnosed?
|
Through immulogical tests
|
|
|
What is unique about Balantidium coli?
|
Only ciliated protozoan that infects humans
|
|
|
What disease does B. coli cause?
|
balantidiasis
|
|
|
What is transmissable stage of Balantidium coli?
|
cysts released in feces
|
|
|
What are the vehicles of transmission for Balantidium coli?
|
contaminated food, hands and water
|
|
|
What is the main source of infection of Balantidium coli for humans?
|
other humans
|
|
|
What is the major damage caused by Balantidium coli?
|
ulceration of lining of large intestine
|
|
|
Where are amastigotes of hemoflagellates found in the human body?
|
primarily intracellular
|
|
|
How are hemoflagellates transmitted to humans?
|
exclusively by insecto vectors
|
|
|
How is the species determined when finding an amastigote in the human?
|
by finding one in human cells, geographic distribution and disease manifestation
|
|
|
Amstigote of tryanosoma cruzi
|
Identify organism and stage
|
|
|
What are the diagnostic characteristics of an amastigote of trypanosoma cruzi?
|
Very small, oval to round nucleus w/kintoplast.
(nested in cardiac muscle) |
|
|
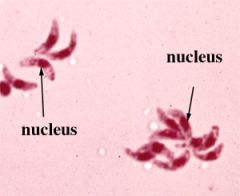
trypomastigote of trypanosoma sp
|
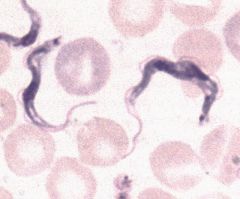
Identify organism and stage
|
|
|
Where are trypomastigote of trypanosoma sp found in humans?
|
blood, CSF, lymph.
|
|
|
How is trypomastigote of trypanosoma sp released?
|
It is not released
|
|
|
How are humans infected with trypanosoma?
|
by insect vectors
|
|
|
What is diagnostic importance of finding a trypomastigote in the blood?
|
presence, along with geographic location will give sp ID
|
|
|
What are the diagnostic characteristics of the trypomastigote?
|
spindle-shaped organism w/undulating membrane or flagellum
|
|
|
What is the phylum and class of the hemoflagellates?
|
Phylum: sarcomastigophora
class: mastigophora |
|
|
What stages are present in the human for Leishmania
|
only promastigote and amastigote
|
|
|
What stages are present in the human for Trypanosoma cruzi?
|
trypomastigote and amastigote
|
|
|
Trophozoite of Balantidium coli
|
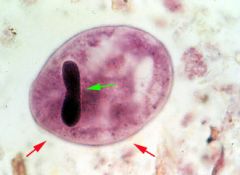
Identify organism and stage
|
|
|
Trophozoite Balantidium coli
|
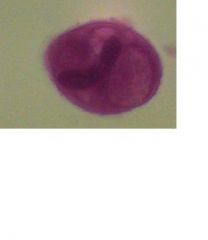
Identify organism and stage
|
|
|
Cyst of Balantidium coli
|
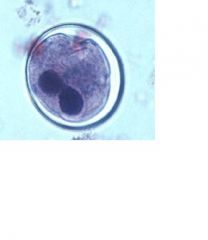
Identify organism and stage
|
|
|
How is an infection of Balantidium coli diagnosed?
|
finding trophs/cysts in feces
|
|
|
How does Balantidum coli reproduce?
|
by transverse binary fission
or sexual conjugation |
|
|
What is macronucleus' function in Balantidium coli?
|
metabolic nucleus, day-to-day functions
|
|
|
What is micronucleus' function in Balantidium coli?
|
Hereditary/permenant nucleus
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic characteristics of the Balantidium coli?
|
large protist w/large nucleus and presence of cilia
|
|
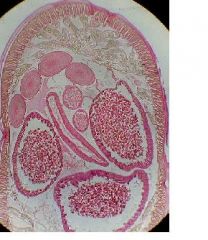
Identify A- cuticle, B-hypodermis, C- muscular layer
|
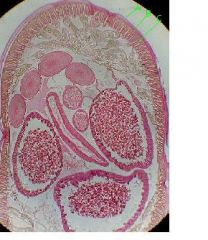
Identify A- cuticle, B-hypodermis, C- muscular layer
|
|
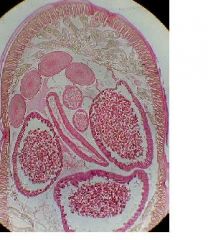
Identify A-lateral lines, B-dorsal line, C-dorsal nerve cord
|
Identify A-lateral lines, B-dorsal line, C-dorsal nerve cord
|
|
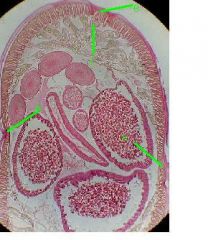
Identify: contractile portion of muscle cell, non contractile portion portion, cytoplasmic extension
|
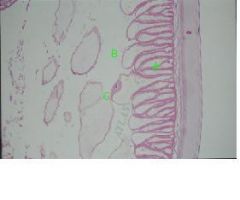
dentify: A-contractile portion of muscle cell, B-non contractile portion portion, C-cytoplasmic extension
|
|
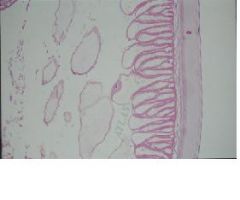
Identify the A-intestine, B-Columnar epithelial cells, C-
Brush border, D-Amorphous layer |
Identify the A-intestine, composed of Columnar epithelial cells with a Brush border, The Amorphous layer is the outermost layer.
|
|
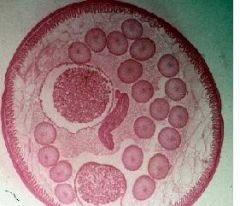
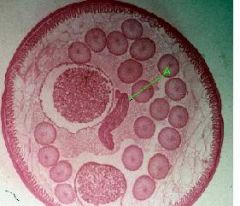
Identify Ovaries, oocytes, rachis, oviducts, wall of oviduct, lining of oviducts, oocytes, Uteri, wall of uteri, nurse cells, eggs
|
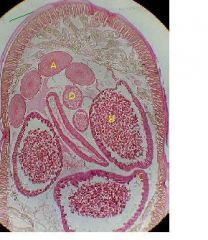
Identify (A)Ovaries, oocytes, rachis,(D) oviducts, wall of oviduct, lining of oviducts, oocytes, (B) Uteri, wall of uteri, (C)nurse cells, eggs
|
|
|
filariform larva of necator americanus
|
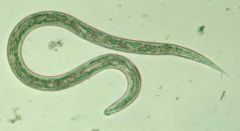
Identify organism and stage
|
|
|
Necator americanus
filariform esophogus |
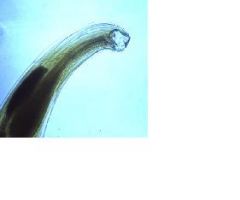
identify organism and stage and type of esophogus
|
|
|
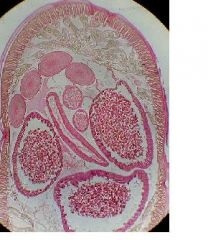
Encapsulated larva of Trichinella spiralis
|
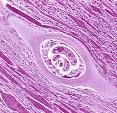
Identify organism and stage
|
|
|
First stage larva of Trichinella spiralis (encapsulated)
|
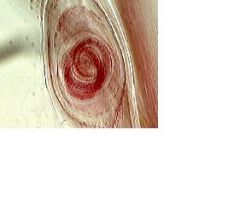
Identify larva (what stage?) and cyst wall
|
|
|
microfilaria of Wuchereria bancrofti
|
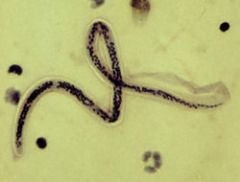
Identify organism and stage
|
|
|
Microfilaria of Wuchereria bancrofti
|
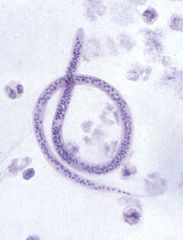
identify organism and sheath, body wall, nuclei
|
|
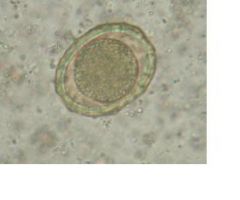
Identify organism and visible parts
|
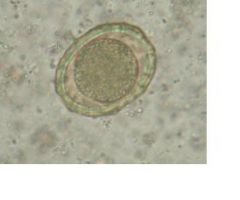
Egg of Ascaris lumbricoides
(zygote, egg shell, rough outer coat) |
|
|
Egg of Necator americanus or Ancylostoma duodenale
(cells of embryo, thin shell) |
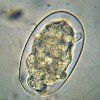
Identify and identify visible parts
|
|
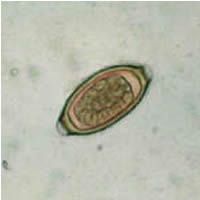
identify and label features
|
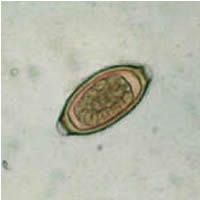
Egg of Trichuris trichiura
(zygote, outer shell, inner shell, polar plugs) |
|

Identify and name visible features
|

Egg of Enterobius vermicularis
(zygote, shell) |

