![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
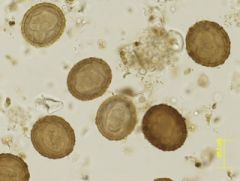
-Parascaris Equorum
-Roundworm -Rarely seen in adults -Nematode |
|
|
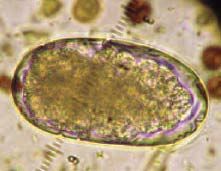
-Strongylus
-Bloodworm -Oval, thin shell, like hookworm -Small and Large strongyles -nematode |
|
|
Small Strongyles
|
-appear to have become resistant to available anthelmintics
-go to cecum and mature -40 species |
|
|
Life cycle of strongyles
|
-larvae develop inside the ova and hatch
-larvae undergo a free living existence -larvae are ingested by host |
|
|
Large Strongyles
|
-migratory
-very complex life cycle Types: Vulgaris, equinus, edentatus |
|
|
Large strongylus life cycle
|
-prepatient period 6-12 months
-larvae spend time in mesenteric arteries and liver -end up in large intestine |
|
|
Effect of Strongyles on horse
|
-damage to liver, intestine
-diarrhea, anemia, unthriftiness -obstruction or damage to mesenteric arteries -cause colic, death |
|
|
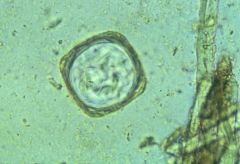
-Anoplocephala
-tapeworm -angular shape-baseball diamond -often can see scolex (head of tapeworm) -grey, deflated appearance -smaller than dog roundworms, but bigger than taenia -square segments can be seen on gross exam |
|
|
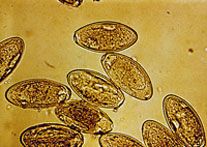
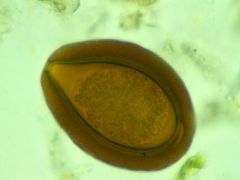
-oxyuris equi
-pinworm -operculum (hatch) at one end -often embryonated -more pointy at base than strongyle |
|
|
-Eimeria
-type of coccidia -pore at more pointed end -solid red/brown -look closely - can see nucleus in middle sometimes -thick outer shell -looks like half an avocado |
|
|
Pinworm life cycle
|
-adult females in large intestines migrate to perianal area to lay eggs
-larvae become infective in eggs -host ingests infective eggs |
|
|
Pinworm effect on host
|
-tail rubbing
-pruritis in anal area |
|
|
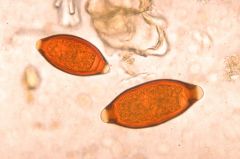
Toxacara
aka roundworm |
|
|
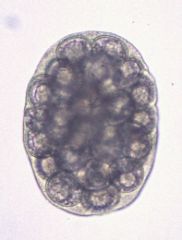
Trichuris Vulpis
aka whipworm |
|
|
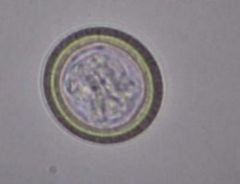
Dipyllidium
aka tapeworm |
|
|
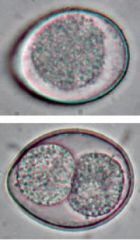
Taenia
aka tapeworm |
|
|
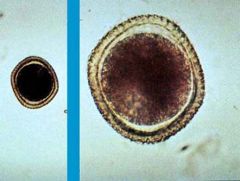
isospora
one type of coccidia |
|
|
Steps for Simple Flotation
|
-place 1-2 tsp feces in cup
-fill 1/4 way with floatation solution -mix well with tongue depressor -strain thru tea strainer into cup 2 -dispose of remains in trash - not sink -pour liquid into test tube which is in rack -place coverslip on tube -wait for 15 minutes before reading - don't take too long -put coverslip on a slide to read -liquid should fill space below coverslip -examine entire coverslip on low power using low light |
|
|
What does floatation test for?
|
-nematode ova
-coccidian oocysts -cestode ova and packets of ova -light-weight trematode ova -it is not a good method for other protozoan parasites, most flukes, any larvae or adult parasites |
|
|
What are 4 floatation solutions?
|
-sodium nitrate
-zinc sulfate -magnesium sulfate -sheather's solution |
|
|
What is Sheather's Solution made of?
|
-Super saturated sugar water
|
|
|
What do we look for in the gross exam?
|
-color
-mucus/blood -consistency -adult worms (rounds and tapes) -presence of foreign bodies |
|
|
steps for fixed rotor centrifuge
|
-prep sample same as for simple floatation
-only fill 90% or 3/4 inch below top -DO NOT COVERSLIP -balance centrifuge if needed (equal volume of liquid on opposite side) -spin 5 minutes @ 1500 rpm (revolutions per minute) -after centrifuge, put in rack -top off with more solution and coverslip -wait 10 minutes before reading |
|
|
Steps for swinging centrifuge
|
-preparation same as simple float
-place cover-slipped test tube in centrifuge -balance the centrifuge -equal volume of liquid, opposite side -spin @ 5 minutes @ 1500 rpm -remove coverslip and read |
|
|
Steps for simple fecal sedimentation
|
-FOR LARVAE OR VERY LARGE OVA
-mix sample w/ water or saline, strain -centrifuge, pour off supernatant -look at drop of sediment under coverslip |
|
|
What are the steps for a Direct exam?
|
-mix tiny bit of feces with a drop of saline on a slide
-coverslip -high power, low light, 10 field minimum (usually more) -not the method of choice for detecting coccidians or non-protozoans -main reason is to look for trophozooites |
|
|
When do we do a direct exam/direct smear?
|
-routine for all birds, reptiles, and amphibians
-other species with unformed or semi-formed stool |
|
|
What do we use a Baermann apparatus for?
|
-fecal sedimentation (recovery of larvae only)
|
|
|
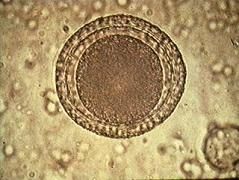
Toxacaris Vitularium
bovine/ruminant roundworm |
|
|
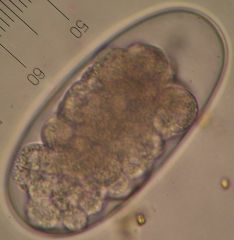
Ruminant Trichostrongylus
|
|

|
Trichuris
|
|
|
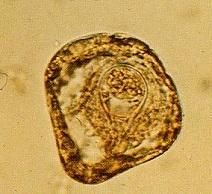
Monezia
aka tapeworm |
|
|
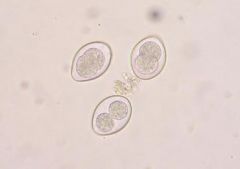
Ruminant eimeria
aka coccidia |

