![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hymenolepis nana Taenia solium Taenia saginata Echinococcus granulosus Diphyllobothrium latum Dipylidium caninum |
H. nana/H.dimunata(Dwarf tapeworm) T. solium(Pork tapeworm) T. saginata (beef) E. granulosus(hydatid tapeworm) D. latum(fish/broad tapeworm) D. canium(dog tapeworm) |
|
|
Cestode body Cestode head |
Strobila: body cestode Scolex: anterior end(head) to attach to intestine may have sucker/hook |
|
|
What is the proglottids part of cestode? |
Mature part of worm towards the end. Each segment contain both sets reproductive organs. |
|
|
Where is the rostellum part of the cestode |
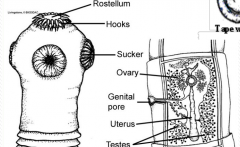
|
|
|
Taenia saginata location association 60 million |
T. saginata Worldwide. More common in developing countries. Associated with beef, sheep, llama, giraffe |
|
|
Taenia solium location association 4 million |
T.solium Countries near equator, hot. Mexico, Central America, South America Associated with pig |
|
|
T. solium+ T. saginata infective stage diagnostic stage |
T. solium+ T. saginata Infective: ingest undercook meat w/ cysticerci w/ invaginated(turned inside out) protoscoles T. solium (cysticercosis) Ingestion of only egg |
|
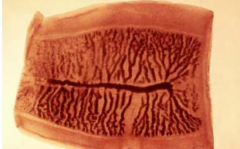
T. solium or T. saginata? |
T.saginata |
|
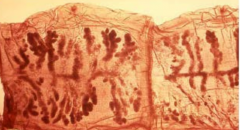
T. solium or T.saginata?
|
T. solium |
|
|
Diagnosis of T. solium + T. saginata |
Cannot differenciate be T. solium and T. saginata ova. Oncosphere has 6 hook To differentiate use proglottid segment or scolex Cysticercosis: serology, MRI, histology |
|
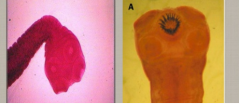
Which is T. saginata and T. solium |
T. saginata No hook, proglottide uterine branch 23, passing of proglottid single spontaneous T. solium Hook, proglotid uterine branch 8, passing of proglottid in group. Labelled A: T. solium |
|
|
Medicine T. solium + T saginata |
Adult tapeworm Praziquantel Niclosamide Cysticercosis: Albendazole, Praziquantel, Must treat seizure, may require surgery |
|
|
D. latum location association |
D. latum Cold area: Baltic sea, Russia, Switzerland, North America Fish(pike, perch, trout) Copepods(crustacean) also found dog, cat, pig Broad tapeworm: proglottids wider than long |
|
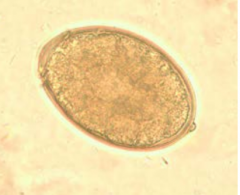
D. latum infective diagnostic **Has operculum+ small knob ***Largest tapeworm found in man |
D. latum infective:plerocercoid larvae from freshwater fish diagnostic:unembryonated egg in feces |
|

D. latum Proglottid in stool. "rosette shaped ovaries" Treatment Symptom Sparganosis?...what is it |
Treatment: Praziquantel Niclosamide Symptom:Vit B12 deficiency. tapeworm may use 100% of Vit B12. Sparganosis: accidental ingestion copepod. Eat only egg no tapeworm development. |
|
|
H. nana + H dimuta association Which is the most common tapeworm worldwide? |
H. dimuta Rate tapeworm Association: rodent H. nana Dwarf tapeworm Association: human, cosmopolitan(city) **Most common tapeworm worldwide |
|
|
H. nana infective **Autoinfection occur if egg remain in intestine. Egg release hexcanth embryo. ((immunecompromised)) How long can eggs survive in enviroment? |
Infective:embryonated egg in feces or accidental ingestion cysticercoid arthropod Eggs can only survive less than 10 days external enviroment. |
|
|
H. nana diagnostic treatment **Rare to find proglottid H. nana intermediate host not required H. diminuta: intermediate host required |
Diagnostic: embryonated egg in feces
Formylether concentrate Rare to find proglottid or worms Treatment: Niclosamide |
|
|
E. granulosus location association |
E.granulosus Location: Utah, Alaska, Canada, Africa, Middle East association: sheep dog also fox, coyotes, rodent |
|
|
E. granulosus diagnostic infective Human accidental host Sheep: intermediate host Dog: Definitive host |
E. granulosus Infective:embryonated egg in feces Diagnostic: serology, MRI/histology Protoscolexes in cyst fluid |
|
|
E. granulosus clinical manifestation |
Anaphylactic shock can occur w/ rupture. Rupture can occur during removal or biopsy. |
|

Dipylidium caninumlocation
location association |
D. caninum Worldwide Flea tapeworm Accidental ingestion of dog or cat flea |
|

D. caninum infective diagnostic |
D. caninum Infective: cysticercoid Diagnostic: finding egg or proglottids in stool |
|
|
D. caninum intermediate host definitive host |
D. caninum Intermediate host: dog/cat flea definitive host: cat, dog, fox, and children |
|
|
D. caninum symptoms treatment |
Mostly asymptomatic Can be associated with anal pruritis(itching) treatment: praziquantel orally injection pet |

