![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pancreas is retroperitoneal except ? |
Tail is intra peritoneal |
|
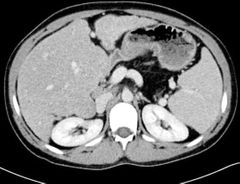
Mention 2 findings? Diagnosis? How it will appear in MRI ? |
Fatty replacement of the pancreas Cirrhotic liver Cystic fibrosis Low t1 and t2 if fibrosis High t1 if fatty replacement |
|
|
Why the pancreas get fibrosis and fatty replacement in cystic fibrosis patients? |
Thick secretions >> obstruction >> recurrent pancreatitis |
|
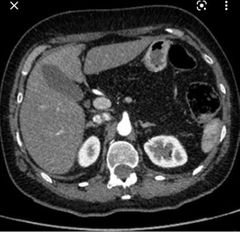
Finding? Buzzword? Diagnosis? |
Fatty enlargement of the pancreas Pseudo hypertrophy of the pancreas Pancreatic lipomatosis |
|
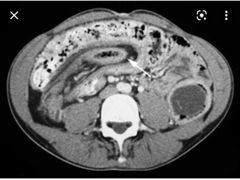
Known case of CF, finding? Diagnosis? Pathophysiology? |
Short segment with wall thickening and stricture of the ascending colon Fibrosing colonopathy Enzyme replacement therapy |
|
|
The second most common cause of pancreatic insufficiency in kids? The most common is? |
Shwachman-diamond syndrome CF |
|
|
Shwachman diamond syndrome, Signs and symptoms? 4 |
Diarrhoea Eczema Short stature ( metaphyseal chondroplasia) Lipomatous pseudohypertrophy of the pancreas |
|
|
Causes of pancreatic Lipomatosis? 5 |
CF Shwachman-diamond syndrome Cushing syndrome Steroid use Hyperlipidemia |
|
|
Pancreatic agenesis vs pancreatic Lipomatosis? |
Agenesis no duct Lipomatosis with duct |
|
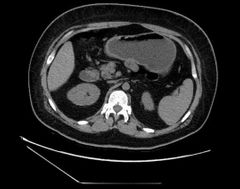
Finding Diagnosis Associated features ?2 |
Absence of the tail of pancreas Pancreatic tail agenesis Diabetes as all beta cells are in tail of Pancreas Polysplenia |
|
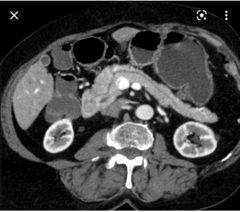
Findings? Diagnosis? Complications in childhood and adulthood? |
demonstrates the second part of the duodenum encircling by pancreatic tissue Annular pancreas Children >> obstruct Adult>> recurrent pancreatitis |
|
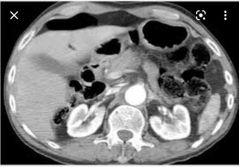
Findings? 3 Next step? |
Laceration of the body of the pancreas with ductal injury Pneumoperitonium MRCP if patient is stable |
|
|
List causes of acute pancreatitis? 10 |
Gallstones Alcohol Scorpion bite ERCP Valproic acid Viral infections Hyperlipidemia, hypercalcemia Trauma Pancreatic divisum Pancreatic CA |
|
|
What radiological score used for grading pancreatitis? |
Balthazar score Necrosis >>>bad No necrosis OK Infected necrosis mortality 50-70% |
|
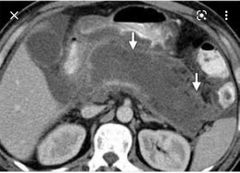
Finding? Mortality rate ? |
Pancreatic collection ( necrosis with air foci) indicating infected necrosis of the pancreas. 50-70% |
|
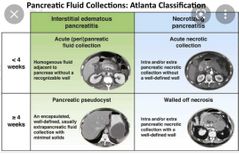
|
Fo studying 📖 |
|
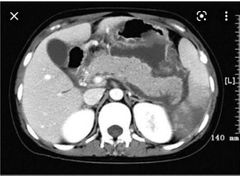
Findings 3? Cause? Other complication? |
Large splenic vein filling defects indicate thrombosis with infarcted spleen. Peripancreatic fluid suggestive of pancreatitis Splenic vein thrombosis due to pancreatitis Portal vein thrombosis |
|
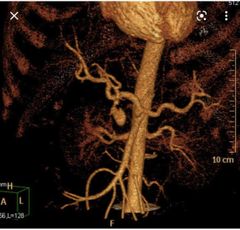
Patient had 4 weeks ago severe abdominal pain radiating to the back Finding? Cause?
|
Pseudoaneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery It can be seen in splenic artery too.
Acute pancreatitis |
|
|
Ultrasound features of acute pancreatitis? |
Hypertrophy Hypoechoic compared to the liver |
|
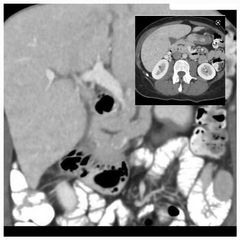
Finding? Diagnosis? It is a risk for ? |
The MPD drains into the minor duodenal papilla, while the common bile duct and the ventral pancreatic duct both drain into the major papilla
Pancreatic divisum Pancreatitis |
|
|
Other names for major and minor ducts of the pancreas? Their opening? |
Major Wirsung >> inferior, big Minor Santorini>> superior, small |
|
|
The cause #1 and #2 for chronic pancreatitis? |
1 alcohol 2 gallstones |
|
|
Features of early chronic pancreatitis 3 and late chronic pancreatitis 3? |
Early: Loss of T1 bright signal Delayed enhancement Dilated side branches Late: Small atrophy Pseudocyst formation ***Dilatation and beaded appearance of the pancreatic duct with calcification |
|
|
How to differentiate BTW pancreatic duct dilatation in chronic pancreatitis and malignant dilatation? 2 |
CP >> irregular, <50% of AP diameter of the pancreas
Malignant >> uniform dilatation, > 50% of the AP diameter ( obstructive atrophy) |
|
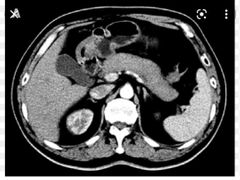
Finding? Diagnosis? Association? Treatment? |
Diffuse enlargement of the pancreas with loss of lobulations ( sausage shaped pancreas) *** delayed rim enhancement ( scar) No ductal dilatation, no calcification Autoimmune pancreatitis IgG4 disease Steroids |
|
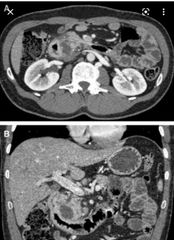
Finding? Diagnosis? Complication? 2 |
Soft tissue lesion is seen in the pancreatic duodenal groove with dilated CBD and not shown pancreatic duct. It may or may not enhance. Groove pancreatitis Duodenal stenosis, strictures of CBD |
|
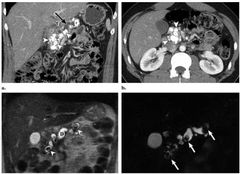
Findings? Diagnosis? Age group affected? Risk of ? |
Dilated pancreatic duct with large calcifications Tropic pancreatitis
Young age group with malnutrition
Adenocarcinoma |
|
|
Another ddx for tropic pancreatitis ? Asscociated gene? Risk of ? |
Hereditary pancreatitis Young age at onset SPINK-1 gene Adenocarcinoma |
|
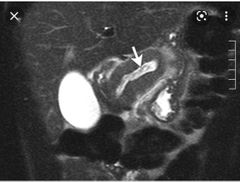
Finding Diagnosis |
Dilated pancreatic duct with worm like structure within it Ascaris induced pancreatitis |
|
|
Associated IgG4 disease ? 6 |
Retroperitoneal fibrosis Autoimmune pancreatitis Fibrosing mediastinitis Inflammatory pseudotumors Riedel's thyroiditis Sclerosing cholangitis |
|
|
What are the associated syndromes that have simple pancreatic cysts? 3 |
VHL Polycystic kidney disease CF |
|
Findings? 4 Diagnosis? Age group ? Another subtype ? |
Multilcystic lesion at the head of pancreas with central scar. It shows no communication with the pancreatic duct and no calcifications. Like a sponge 🧽. Serous cystadenoma Grandma 👵 elderly females Macrocystic serous cystadenoma |
|
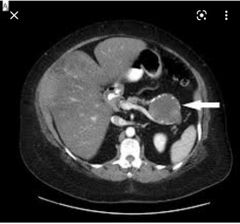
Findings? Diagnosis? Age group? Risk ? |
Unilocular cyst at the tail of pancreas With peripheral calcifications. Not communicating with main pancreatic duct. Mucinous cystadenoma 50s mother Premalignat When multilocular each cyst will be more than 2 cm each. |
|
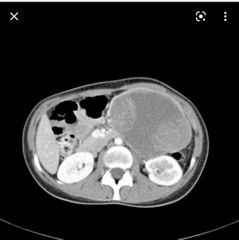
Finding? Diagnosis? Age group and ethnicity? |
well-encapsulated lesion with varying solid and cystic components owing to haemorrhagic degeneration. Following IV contrast administration, enhancing solid areas are typically noted peripherally, whereas cystic spaces are usually more centrally located. Calcifications and enhancing solid areas may be present at the periphery of the mass. Solid pseudopapillary tumor Young age daughter 30s Asian and African Like hemangioma with progressive fill in of the solid portion |
|
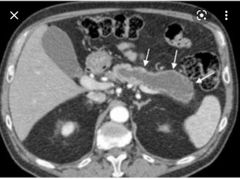
Finding? Diagnosis? Risk |
Diffuse dilatation of the main pancreatic duct with atrophy of the pancreas and sometimes dystrophic calcifications. Main branch IPMN High risk for malignancy |
|
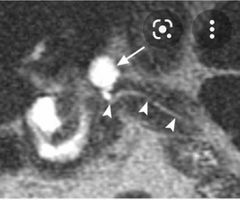
Finding? Diagnosis Worrisome sign? |
Small cystic lesion at the head of pancreas that communicate with the main pancreatic duct. Side branch IPMN If more than 3 cm |
|
|
Features concerning for malignancy in IPMN? 4 |
Dilated duct >1 cm Diffuse multifocal involvement Enhancing nodules Solid hypovascular mass |
|
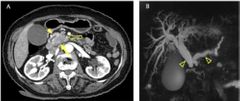
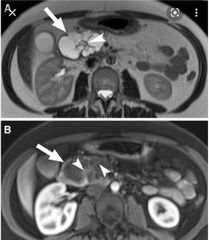
Finding? Diagnosis? Symptoms ? Associated sign? Age group? Risk factor? Optimal timing for pancreatic imaging? |
Axial pancreatic phase CT image shows lower attenuating mass (arrow) compared with the pancreas parenchyma (arrowhead) in the pancreatic head, which encases the first jejunal branch of the superior mesenteric artery (open arrow). (B) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) image shows dilatation of the bile and pancreatic ducts, the so-called double duct sign (open arrowheads). Note the abrupt narrowing of both bile and pancreatic ducts. ( hypoenhancing lesion) Adenocarcinoma of pancreatic head Enlarged gall bladder with painless jaundice ** Trousseou' syndrome migratory thrombophlebitis 70-80s, smoking 40 seconds |
|
|
What makes pancreatic adenocarcinoma inoperable?? |
Encases SMA or celiac trunk Encasing GDA is OK as it will be taken by whipple |
|
|
Adenocarcinoma of pancreas Tumor marker ? Hereditary syndrome with pancreatic Ca? 4 |
CA 19-9 BRCA Ataxic telengiectasia HNPCC Peutz-Jeghers |
|
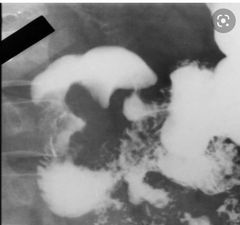
Sign ? Diagnosis? |
Inverted 3 sign Pancreatic adenocarcinoma |
|
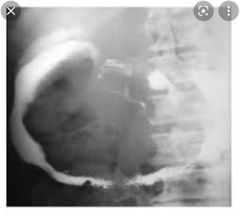
Sign ? Diagnosis? |
Wide duodenal sweep Adenocarcinoma of pancreas |
|
|
Ampullary carcinoma is seen more in --------- syndrome |
Gardner's syndrome |
|
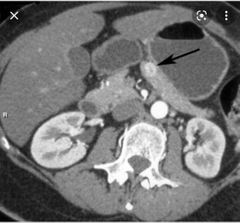
Finding? Diagnosis? Subtypes? 2 Associated syndromes? 2 Most common type ? Second most common type? |
Hypervascular lesion at the body of pancreas Islet cell tumor ( neuroendocrine tumor) Functional and non functional MEN1 and VHL Insulinoma 90% benign Gastrinoma 30-60% malignant |
|
|
Insulinoma features? 3 Insulinoma features? 3 |
Small < 2 cm Solitary Benign 90% |
|
|
Gastrinoma is most common neuroendocrine tumor in --------- syndrome Risk of malignancy ----- They can result in ---------- syndrome |
MEN1 30-60% Zollinger Ellison syndrome |
|
|
The buzzword for Zollinger Ellison syndrome? |
Jejunal ulcers |
|
|
Where gastrinoma can be found ? What are the borders? |
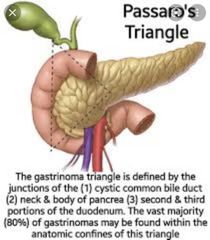
Gastrinoma triangle 🔺️ |
|
|
Non functional islet cell tumors are -------- When I say non functional you say? |
80% malignant Large with calcification |
|
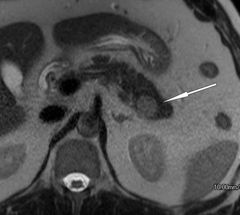
Finding? Diagnosis? Risk factor? Signal in T1, T2, DWI Arterial phase in CT Nuclear radiotracer? 2 |
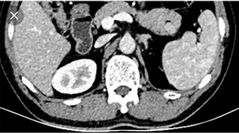
Soft tissue lesion within the pancreatic tail following the signal of the spleen Intrapancreatic spleen Trauma Dark T1, bright T2, and restrict in DWI Tiger 🐅 striped appearance in Arterial phase Heat trated RBC and sulfur colloid |
|
|
Complications of whipple surgery? 2 |
Delayed gastric emptying Pancreatic fistula ( amylase more than 50 ml for longer than 8-10 days) |

