![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Palliative care definition |
WHO 2002: An approach that improves the quality of life of individuals and their families facing the problems associated with life-threatening illness, through prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and impeccable assessment and treatment of pain and other problems: physical, psychosocial and spiritual |
|
|
Examples of life-limiting illnesses |
Cancer HIV/AIDS Motor neurone disease Muscular dystrophy Cystic fibrosis Dementia Ageing process Organ failure va |
|
|
Values |
Relief from pain and distress Affirms life Dying a natural process Neither hastens nor postpones death Psychological and spiritual aspects Help patients live actively Support to family during illness and in bereavement Team approach Enhance quality of life |
|
|
Common needs |
Management of physical symptoms Management of psychological symptoms Need for social support Culturally specific needs Spiritual and existential concerns Information and communication - breaking bad news |
|
|
Symptoms assessment |
Contributing factors Characteristics e.g. Intensity, location, freq Meaning - beliefs about the symptom and effect on wellbeing Behavioural responses |
|
|
Symptoms |
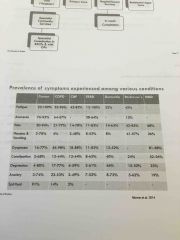
|
|
|
Communicating with pts and fam: PREPARED |
Prepare for the discussion Relate to the person Elicit patient and caregiver preferences Provide info Acknowledge emotions and concerns Realistic hope Encourage questions Document |
|
|
Where do people die? |
54% in hospitals 32% in residential aged care 14% at home (Broad et al., 2013) |
|
|
Barriers to quality end of life care |
Failure of HCW to ack limits of technology Discomfort telling bad news Unwillingness to be honest about poor prognosis Lack of communication Disagreement Failure to implement a timely advanced care plan Lack of training about effective control of pain and symptoms Lack of reaching out to palliative care team |
|
|
Forward planning |
Advanced care planning/directive: -living will - health care directive
End of life plan (terminal phase) |
|
|
Morphine |
Opioid analgesic A/R: constipation (laxatives prescribed at same time) Lightheaded beds, dizziness, mild sedation - only first 24-48h Nausea & vom - 20%, antiemetics Sweating - rare Euphoria - dose too high Bradycardia, hypotension - mild
|
|
|
Morphine |
Opioid analgesic A/R: constipation (laxatives prescribed at same time) Lightheaded beds, dizziness, mild sedation - only first 24-48h Nausea & vom - 20%, antiemetics Sweating - rare Euphoria - dose too high Bradycardia, hypotension - mild
|
|
|
Pain assessment |
P provocation/palliation (what improves or makes it worse) Q quality e.g. dull, sharp R region/radiation S severity scale T timing, when did it start, how long, frequency
Document |
|
|
Vicarious trauma |
Negative effects of caring for others, harmful changes in professional's view of themselves, others and the world as a result of repeated exposure to traumatic material of patients |

