![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mild Pain(1-3) |
APAP ASA NSAIDS COX 2 |
|
|
Moderate Pain (4-7) |
NSAIDS Opioid + APAP Tramadol |
|
|
Severe pain (8-10) |
Opioids |
|
|
Aspirin |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
NSAID Selectivity |
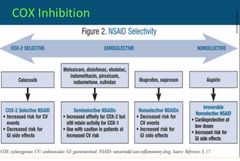
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Cox 2 inhibitor - Celebrex Advantages |
Advantage over nonselective Decreased pain and inflammation with minimal GI side effects No effect on platelet aggregation- improves bleeding profile |
|
|
Cox 2 inhibitor - Celecoxib - Disadvantages |
Disadvantages Rénal Dysfunction Avoid patients with a "sulfa allergy" CV events |
|
|
Phenanthrenes |
Morphine Hydromorphone Levorphenol Oxymorphone Codéine Hydrocodone Oxycodone |
|
|
Phenylpiperidines |
Meperidine Fentanyl Sulfentanil alfentanyl Remifentanyl *all have serotenergic properties |
|
|
Phenylheptanes |
Methadone |
|
|
Morphine |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
NSAIDS adverse events |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
NSAIDS BBW |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
NSAIDS: TORADOL |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
NSAIDS: KETORALAC | TORADOL |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
COX 2 - CELECOXIB | CELEBREX |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
HYDROMORPHONE |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
METHADONE |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
CODEINE |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
HYDROCODONE |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
FENTANYL |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Explain how acetaminophen blocks pain impulse generation |
Inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins in the CNS |
|
|
Your patient has medical conditions of active hepatitis B, osteoarthritis, and psoriasis. What would be a safe dose of Acetaminophen for this patient’s treatment of OA related to joint aches? |
Maximum 2g per day for hepatic impairment Metabolized by liver If patient does not have liver impairment or alcoholism: max dose: 4g/day |
|
|
Name 3 adverse events related to NSAID use |
GI bleed Acute Kidney Injury Fluid Overload / Retention Avoid use with other nephrotoxic drugs ie. lasix,ace inhibitors |
|
|
COX inhibition |
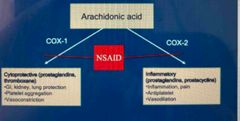
Back (Definition) |
|
|
True or False: Celecoxib is a COX 2 inhibitor that may be used in the prevention of CV events in patients with a hx of GI ulcers and no allergies to sulfa |
FALSE ; COX 2 inhibitors have a high risk for CV events and have no effect on platelet aggregation. COX 2 has anti platelet and vasodilation properties when blocked it causes clotting but decreases inflammation |
|
|
Name 3 different types of medications from different classes that treat neuropathic pain |
SNRIs (Duloxetine) Gabapentin (calcium ion ligand channel blockers) Nortryptylline (TCA) |
|
|
Your 70yo patient receives 10mg IVP morphine over 5 minutes for a complaint of crushing chest pain. You notice his O2 saturation is 85% and his RR has dropped to 6 breaths per minute. What is the best medication to treat in this emergent situation? |
Naloxone for acute reversal |
|
|
Your patient presents to the ED complaining of 10/10 low back pain. When evaluating the appropriate pain intervention you note that he/she has an allergy to morphine. What would be a safe and appropriate medication to receive for severe pain? |
Meperidine (subclass: Phenylpiperidines) Morphine is in the opioid agonist class of phenanthrene. Use a drug in a different sub class. |
|
|
Name three side effects that are not expected from morphine |
Liver failure, tachycardia, diarrhea Expected side effects: hallucinations, pruritis , respiratory depression |
|
|
Your patient with cancer related pain reports inadequate relief from current interventions. You consider starting him on methadone due to his high tolerance of opiates. Which test would be the MOST important to complete before you prescribe methadone? |
EKG Methadone has risk for prolonged QT interval. QT must be <500. |
|
|
If your patient receives 1.5mg of hydromorphone IVP, and the prescriber decided to change the prescription to morphine. Which is the appropriate correlating dose? |
10mg IVP (Ratio is 1.5 to 10) |
|
|
ANTAGONIST |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
ANTAGONIST |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
OPIOID CONVERSIONS |
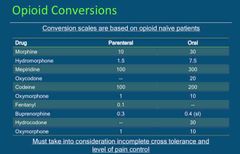
Back (Definition) |
|
|
TRAMADOL |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
CLASS WIDE OPIOID ADVERSE EFFECTS |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Dependence VS Tolerance |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
TOLERANCE DEVELOPMENT |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
CONSIDERATIONS: CHRONIC PAIN REGIMENS |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR NEUROPATHIC PAIN |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Aspirin | Salicylates |
Irreversibly binds to COX 1 and COX 2 enzymes Antiinflammatory Antipyretic Anti platelet (irreversible) Analgesia |
|
|
ASPIRIN TIME |
Onset = 15-20 Peak = 1-3 Half-life = 3 Élimination = Urine & Liver |

